What Are Headaches?
Headaches are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. They can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. But what exactly are headaches? In simple terms, a headache is a pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. This pain can be caused by various factors, including tension, stress, dehydration, or underlying medical conditions.
Headaches can occur at any age and can be triggered by numerous factors. Understanding the nature of headaches is crucial for effective management and treatment. They can be classified into two main categories: primary headaches and secondary headaches.
Primary Headaches
Primary headaches are not caused by an underlying medical condition. Instead, they are the headache itself. The most common types of primary headaches include:
- Tension Headaches: Often described as a tight band around the head, tension headaches are usually caused by stress, anxiety, or muscle tension.
- Migraines: Characterized by intense, throbbing pain, migraines can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. They can last from a few hours to several days.
- Cluster Headaches: These are severe headaches that occur in cyclical patterns or clusters. They are often accompanied by other symptoms, such as nasal congestion or eye watering.
Secondary Headaches
Secondary headaches are symptoms of an underlying condition. They can be caused by various factors, including:
- Infections: Conditions like sinusitis or meningitis can lead to headaches.
- Head Injuries: Trauma to the head can result in headaches.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as high blood pressure, stroke, or tumors can also cause headaches.
Recognizing the type of headache you are experiencing is essential for effective treatment. If you find yourself suffering from headaches or migraines frequently, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Types of Headaches
Understanding the different types of headaches can help you identify the cause of your pain and seek appropriate treatment. Here’s a closer look at the various types of headaches:
1. Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are the most common type of headache. They often feel like a dull, aching sensation all over the head. Symptoms may include:
- A feeling of tightness or pressure across the forehead or on the sides and back of the head
- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Mild to moderate pain
These headaches can be triggered by stress, poor posture, or muscle tension. Over-the-counter pain relievers, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms.
2. Migraines
Migraines are more severe than tension headaches and can significantly impact daily life. They often present with the following symptoms:
- Intense, throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Visual disturbances, such as flashing lights or blind spots
Migraines can be triggered by various factors, including hormonal changes, certain foods, stress, and environmental factors. Treatment options may include prescription medications, lifestyle changes, and avoiding known triggers.
3. Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are less common but extremely painful. They occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, often waking individuals from sleep. Symptoms include:
- Severe, burning pain around one eye
- Redness and watering of the eye on the affected side
- Runny or congested nose
Cluster headaches require specific treatments, including oxygen therapy and prescription medications. If you experience these types of headaches, it’s crucial to seek medical advice.
4. Sinus Headaches
Sinus headaches occur when the sinuses become inflamed due to infection or allergies. Symptoms may include:
- Pain and pressure in the forehead, cheeks, and around the eyes
- Thick nasal discharge
- Fever and fatigue
Treating sinus headaches often involves addressing the underlying sinus issue, such as using decongestants or antihistamines.
5. Hormonal Headaches
Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can lead to headaches. These headaches often coincide with menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause. Symptoms can vary but often resemble migraines.
Understanding the type of headache you are experiencing is vital for effective management. If you frequently suffer from headaches or migraines, consider consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options. For more evidence-based health answers, visit Yesil Health AI.
Headaches can be a nuisance, but with the right knowledge and resources, you can take control of your health and find relief. 🌟

Headache Symptoms
Headaches are a common ailment that can affect anyone at any time. Understanding the symptoms associated with headaches is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here, we’ll explore the various symptoms that can indicate a headache, helping you identify what you might be experiencing.
Types of Headaches
Headaches can be classified into several types, each with its own set of symptoms. The most common types include:
- Tension Headaches: Often described as a tight band around the head, tension headaches can cause mild to moderate pain. Symptoms may include:
- Constant dull ache
- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Tightness in the neck and shoulders
- Cluster Headaches: These are intense headaches that occur in clusters or cycles. Symptoms include:
- Severe, burning pain around one eye
- Red or watery eyes
- Runny or blocked nasal passages
- Sinus Headaches: Often associated with sinus infections, these headaches can cause:
- Pain in the forehead, cheeks, or around the eyes
- Throbbing pain that worsens with sudden movements
- Fever and nasal congestion
Common Symptoms of Headaches
Regardless of the type, headaches can present a variety of symptoms. Here are some common indicators:
- Pain Location: Headaches can manifest in different areas, including the forehead, temples, or back of the head.
- Pain Intensity: The intensity can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
- Duration: Headaches can last from a few minutes to several days, depending on the type.
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience nausea or vomiting, particularly with migraines.
- Visual Disturbances: Blurred vision or seeing spots can accompany certain types of headaches.
Recognizing these symptoms can help you determine the best course of action for relief. If headaches become frequent or severe, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Migraine Symptoms
Migraines are a specific type of headache that can be particularly debilitating. They often come with a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding these symptoms is vital for effective management and treatment.
Common Symptoms of Migraines
Migraine symptoms can vary widely from person to person, but some common signs include:
- Intense Throbbing Pain: Migraines typically present as a severe, throbbing pain, often on one side of the head.
- Aura: Some individuals experience visual disturbances known as aura, which can include:
- Flashing lights
- Blind spots
- Difficulty speaking
- Increased Sensitivity: Many migraine sufferers report heightened sensitivity to light, sound, and smells.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms are common and can accompany the headache phase.
- Fatigue: After a migraine attack, individuals often feel exhausted and may need to rest.
Stages of a Migraine Attack
Migraine attacks can be divided into four stages, each with its own symptoms:
- Prodrome: This initial stage can occur hours or even days before the headache, with symptoms like mood changes, food cravings, and neck stiffness.
- Aura: As mentioned, this stage includes visual disturbances and other neurological symptoms.
- Headache: The actual headache phase can last from a few hours to several days, characterized by severe pain.
- Postdrome: After the headache subsides, individuals may feel drained or fatigued, often referred to as a “migraine hangover.”
Understanding these symptoms can help you identify a migraine when it occurs and seek appropriate treatment. If you experience frequent migraines, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider for a tailored management plan.

Causes of Headaches
Headaches are a common ailment that can affect anyone at any time. Understanding the causes of headaches is crucial for effective management and prevention. While some headaches are primary, meaning they occur independently, others are secondary, resulting from underlying conditions. Let’s explore the various causes of headaches in more detail.
Primary Headaches
Primary headaches are not caused by any underlying medical condition. They include:
- Tension Headaches: Often triggered by stress, anxiety, or muscle tension, these headaches are characterized by a dull, aching sensation and tightness around the forehead.
- Migraines: These are intense headaches often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Migraines can last from a few hours to several days.
- Cluster Headaches: These are severe headaches that occur in cyclical patterns or clusters. They are often described as sharp, burning pain around one eye and can be accompanied by nasal congestion or tearing.
Secondary Headaches
Secondary headaches are symptoms of another condition. Some common causes include:
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses can lead to pressure and pain in the forehead, cheeks, and around the eyes.
- Infections: Conditions like the flu or meningitis can cause headaches due to inflammation and fever.
- Head Injuries: Trauma to the head can result in headaches, which may be a sign of a concussion or other serious injury.
- Medication Overuse: Frequent use of pain relief medications can lead to rebound headaches, where the headache returns as the medication wears off.
Other Contributing Factors
Several lifestyle and environmental factors can also contribute to headaches:
- Poor Posture: Sitting or standing incorrectly can strain the neck and back muscles, leading to tension headaches.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can trigger headaches, as dehydration affects the brain’s ability to function properly.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as aged cheeses, processed meats, and alcohol, can trigger headaches in some individuals.
- Sleep Patterns: Both lack of sleep and oversleeping can lead to headaches. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is essential for headache prevention.
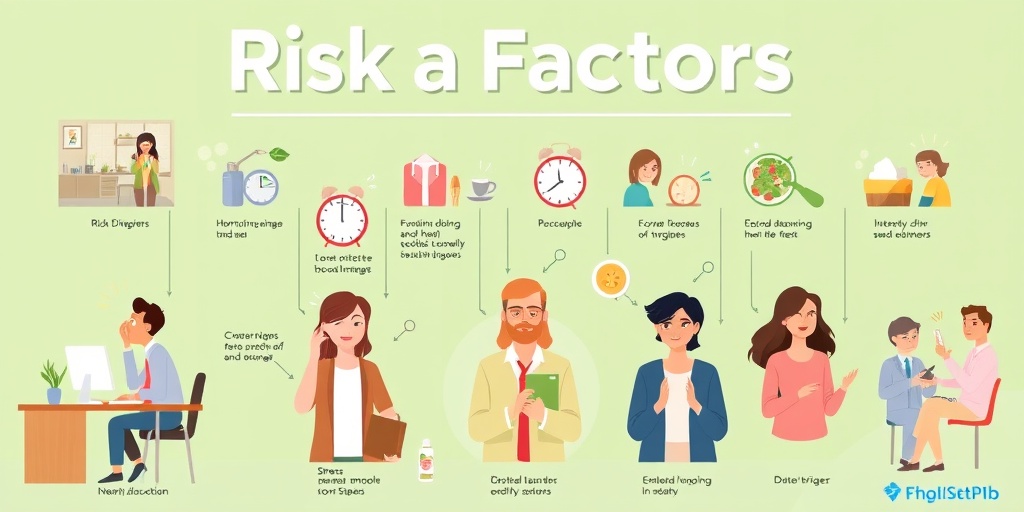
Risk Factors for Migraines
Migraines are a specific type of headache that can be debilitating. Understanding the risk factors for migraines can help individuals identify potential triggers and manage their condition more effectively.
Genetic Factors
One of the most significant risk factors for migraines is genetics. If you have a family history of migraines, you are more likely to experience them yourself. Studies have shown that certain genetic mutations may increase susceptibility to migraines, making it essential to consider your family background when assessing your risk.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can significantly influence migraine occurrence. Many women report experiencing migraines during:
- Menstruation: Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can trigger migraines in some women.
- Pregnancy: While some women may experience fewer migraines during pregnancy, others may find their headaches worsen.
- Menopause: The transition to menopause can lead to increased migraine frequency due to fluctuating hormone levels.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can also increase the risk of migraines:
- Stress: High-stress levels are a common trigger for migraines. Finding effective stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can be beneficial.
- Diet: Skipping meals or consuming trigger foods can lead to migraines. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers.
- Sleep Patterns: Irregular sleep patterns, whether too much or too little sleep, can increase the likelihood of migraines.
Environmental Factors
Environmental triggers can also play a role in migraine development. Some common environmental factors include:
- Weather Changes: Sudden changes in weather, such as shifts in temperature or humidity, can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals.
- Bright Lights and Loud Noises: Sensitivity to light and sound is common among migraine sufferers, making bright environments or loud settings potential triggers.
- Strong Odors: Perfumes, smoke, and other strong smells can provoke migraines in some individuals.
By understanding the causes of headaches and the risk factors for migraines, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. 🌟
Headache Diagnosis
Understanding the nature of your headaches or migraines is the first step towards effective treatment. Diagnosing headaches can be complex, as there are various types and causes. Here’s a closer look at how healthcare professionals diagnose headaches and migraines.
Types of Headaches
Headaches can be classified into two main categories: primary headaches and secondary headaches.
- Primary Headaches: These are not caused by another medical condition. The most common types include:
- Migraines: Often characterized by intense, throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head, and may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Tension Headaches: These are typically less severe and can feel like a tight band around the head.
- Cluster Headaches: These are extremely painful and occur in cyclical patterns or clusters.
- Secondary Headaches: These are symptoms of another condition, such as sinus infections, head injuries, or even more serious issues like tumors or strokes.
Diagnostic Process
When you visit a healthcare provider for headaches or migraines, they will typically follow a structured diagnostic process:
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your headache history, including frequency, duration, and intensity. They may also inquire about any associated symptoms, such as nausea or visual disturbances.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam can help rule out other conditions. This may include checking your neurological function.
- Diagnostic Tests: In some cases, imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs may be necessary to rule out serious underlying conditions.
It’s essential to provide your healthcare provider with as much information as possible to aid in an accurate diagnosis. Keeping a headache diary can be particularly helpful in tracking patterns and triggers. 📝
Headache Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, the next step is to explore treatment options for headaches and migraines. Treatment can vary widely based on the type and severity of the headache, as well as individual patient needs.
Medications
There are several categories of medications used to treat headaches and migraines:
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications: Common options include ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and aspirin. These can be effective for mild to moderate headaches.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe headaches or migraines, doctors may prescribe triptans, which are specifically designed to treat migraines. Other options include ergotamine drugs and anti-nausea medications.
- Preventive Medications: If you experience chronic headaches or migraines, your doctor may recommend preventive treatments. These can include beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anti-seizure medications.
Non-Medication Treatments
In addition to medications, several non-pharmacological treatments can help manage headaches and migraines:
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help alleviate tension and improve posture, which may reduce headache frequency.
- Acupuncture: Some individuals find relief through acupuncture, which involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body.
- Biofeedback: This technique teaches you to control physiological functions, such as muscle tension and heart rate, which can help manage headache pain.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, a common headache trigger.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing headaches and migraines:
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial, as dehydration can trigger headaches.
- Diet: Identifying and avoiding food triggers, such as aged cheeses or processed meats, can help reduce headache frequency.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring adequate rest can significantly impact headache occurrence.
- Stress Management: Finding effective ways to manage stress, such as through exercise or hobbies, can help mitigate headache triggers.
In conclusion, understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for headaches and migraines is essential for effective management. Whether through medication, lifestyle changes, or alternative therapies, there are numerous strategies available to help alleviate the burden of headaches. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Headaches and Migraines
What are the common triggers for headaches and migraines?
Headaches and migraines can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can lead to tension headaches.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as aged cheeses, processed meats, and alcohol, may trigger migraines.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones, especially during menstruation or pregnancy, can affect headache frequency.
- Sleep patterns: Both lack of sleep and oversleeping can contribute to headaches.
- Environmental factors: Bright lights, loud noises, and strong smells can provoke migraines.
How can I differentiate between a headache and a migraine?
While both headaches and migraines can cause pain, they differ in several ways:
- Pain intensity: Migraines typically cause moderate to severe pain, while headaches may be mild to moderate.
- Location: Migraines often affect one side of the head, whereas headaches can be more generalized.
- Associated symptoms: Migraines may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sound, which are less common in regular headaches.
Are there any effective treatments for chronic headaches and migraines?
Treatment options for chronic headaches and migraines include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, and preventive treatments can help manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers can reduce headache frequency.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and physical therapy may provide relief for some individuals.
Can headaches and migraines occur during pregnancy?
Yes, many women experience headaches and migraines during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased stress. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for safe treatment options during this time.
What should I do if my headaches or migraines worsen?
If you notice an increase in the frequency or intensity of your headaches or migraines, it is crucial to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help reduce headaches and migraines?
Yes! Here are some lifestyle changes that may help:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Regular exercise: Engage in physical activity to reduce stress and improve overall health.
- Healthy diet: Eat balanced meals and avoid known food triggers.
- Sleep hygiene: Establish a consistent sleep routine to improve sleep quality.
What are some common misconceptions about headaches and migraines?
Some common misconceptions include:
- All headaches are migraines: Not all headaches are migraines; they can vary significantly in type and severity.
- Only women get migraines: While migraines are more common in women, men can also experience them.
- Medication is the only solution: While medication can help, lifestyle changes and alternative therapies can also be effective.
Where can I find support for managing my headaches and migraines?
Support groups, both online and in-person, can provide valuable resources and community for those dealing with headaches and migraines. Consider joining forums or local support groups to connect with others who understand your experience. 😊




