What Is Rheumatic Purpura?
Rheumatic purpura is a condition characterized by the appearance of purple or red spots on the skin, which are caused by bleeding underneath the skin. This bleeding is often a result of inflammation of the blood vessels, a condition known as vasculitis. While the term “purpura” can refer to various types of bleeding disorders, rheumatic purpura specifically relates to conditions associated with rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatic fever.
In essence, rheumatic purpura is not a standalone disease but rather a symptom of underlying conditions that affect the immune system and blood vessels. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. If you notice unusual bruising or skin changes, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Causes of Rheumatic Purpura
The primary cause of rheumatic purpura is the inflammation of blood vessels, which can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can lead to vasculitis, resulting in purpura.
- Infections: Certain infections can provoke an immune response that damages blood vessels.
- Medications: Some drugs can cause allergic reactions or side effects that lead to purpura.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of autoimmune diseases may increase the risk of developing rheumatic purpura.
Understanding these causes can help in identifying the underlying condition and determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Rheumatic Purpura Symptoms
The symptoms of rheumatic purpura can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
1. Skin Changes
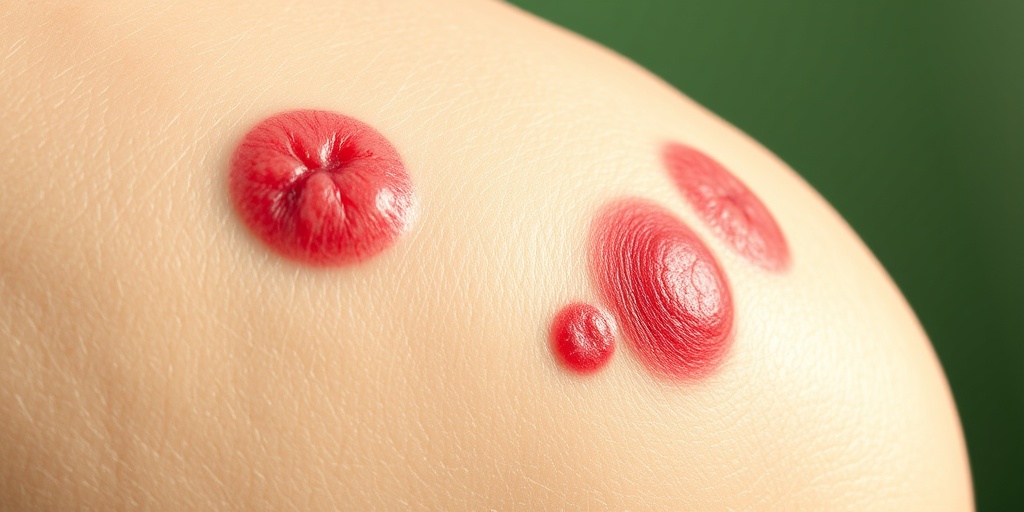
The most noticeable symptom of rheumatic purpura is the appearance of purple or red spots on the skin, often resembling bruises. These spots can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the legs and arms. They may vary in size and can sometimes merge to form larger areas of discoloration.
2. Pain and Swelling
In addition to skin changes, individuals may experience pain and swelling in the affected areas. This discomfort can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the inflammation.
3. Joint Pain
Many individuals with rheumatic purpura also report joint pain, which can be a sign of an underlying autoimmune condition. This pain may be accompanied by stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
4. Fever and Fatigue
Some patients may experience systemic symptoms such as fever and fatigue. These symptoms indicate that the body is fighting an underlying infection or inflammation.
5. Other Systemic Symptoms
Depending on the underlying cause, other symptoms may include:
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle aches
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially in conjunction with skin changes, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any signs of purpura, particularly if they are accompanied by other symptoms like joint pain or fever. A doctor specializing in rheumatology or hematology can provide a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate tests to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
For more information on rheumatic purpura and related conditions, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, understanding rheumatic purpura is essential for recognizing its symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention. By being aware of the signs and causes, you can take proactive steps towards managing your health effectively. 🌟
Rheumatic Purpura Causes
Rheumatic purpura is a condition characterized by the appearance of purple spots or patches on the skin, often resulting from inflammation of the small blood vessels. Understanding the causes of rheumatic purpura is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Here, we delve into the primary factors that contribute to this condition.
1. Autoimmune Disorders
One of the leading causes of rheumatic purpura is autoimmune disorders. In these conditions, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation and damage to blood vessels. Rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus are notable examples where purpura can manifest due to the underlying autoimmune process.
2. Infections
Certain infections can trigger rheumatic purpura. For instance, viral infections such as hepatitis or parvovirus B19 can lead to vasculitis, which in turn causes purpura. Bacterial infections, particularly those that cause sepsis, can also result in similar symptoms.
3. Medications
Some medications may induce purpura as a side effect. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), anticoagulants, and certain antibiotics can lead to blood vessel inflammation, resulting in the characteristic skin changes associated with rheumatic purpura. Always consult with a healthcare provider if you suspect your medication is causing adverse effects.
4. Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of rheumatic purpura. Individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases or clotting disorders may be at a higher risk. Genetic mutations affecting blood vessel integrity can also contribute to the condition.
5. Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain toxins or allergens, can provoke an immune response leading to rheumatic purpura. For example, exposure to chemicals or pollutants may increase the risk of developing autoimmune conditions that manifest as purpura.
Rheumatic Purpura Risk Factors
Identifying the risk factors associated with rheumatic purpura can help in early detection and management of the condition. Here are some key risk factors to consider:
1. Age and Gender
Rheumatic purpura can affect individuals of any age, but it is more commonly seen in adults, particularly women. The hormonal differences and immune responses in women may contribute to a higher incidence of autoimmune disorders that lead to purpura.
2. Pre-existing Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, especially autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, are at a greater risk of developing rheumatic purpura. These conditions can compromise the immune system and increase inflammation, making purpura more likely.
3. Family History
A family history of autoimmune diseases or clotting disorders can significantly increase the risk of rheumatic purpura. If you have relatives with these conditions, it’s essential to discuss your health with a healthcare provider.
4. Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can also influence the risk of developing rheumatic purpura. Factors such as smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise can weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, making individuals more susceptible to autoimmune reactions.
5. Recent Infections or Illnesses
Having a recent infection or illness can act as a trigger for rheumatic purpura. Infections can provoke an immune response that may lead to vasculitis and subsequent purpura. It’s important to monitor any unusual symptoms following an illness.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors of rheumatic purpura is vital for effective management and treatment. If you notice any symptoms of purpura, such as unexplained bruising or skin changes, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. 🩺

Rheumatic Purpura Diagnosis
Diagnosing Rheumatic Purpura can be a complex process, as it often mimics other conditions. This condition is characterized by the appearance of purple spots or patches on the skin, which are caused by bleeding underneath the skin. Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Initial Consultation and Medical History
The first step in diagnosing rheumatic purpura typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your healthcare provider will ask about:
- Your symptoms, including when they started and their severity.
- Any recent infections or illnesses.
- Your family history of bleeding disorders or autoimmune diseases.
During the physical examination, the doctor will look for characteristic signs of purpura, such as:
- Small, red or purple spots on the skin.
- Bruising that occurs without any apparent cause.
- Swelling or pain in the joints.
Laboratory Tests
To confirm a diagnosis of rheumatic purpura, several laboratory tests may be conducted, including:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test helps assess your overall health and detect a variety of disorders, including anemia and infections.
- Coagulation Studies: These tests evaluate your blood’s ability to clot and can help identify any underlying bleeding disorders.
- Autoimmune Panels: These tests check for markers of autoimmune diseases, which can be associated with purpura.
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to examine the affected tissue more closely. This can help differentiate rheumatic purpura from other types of purpura, such as nonthrombocytopenic purpura or purpura vasculitis.
Imaging Studies
While not always necessary, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess any underlying joint or vascular issues that could be contributing to the symptoms. These tests can provide valuable information about the extent of the condition and guide treatment decisions.
Rheumatic Purpura Treatment Options
Treating Rheumatic Purpura involves addressing the underlying cause of the condition and managing symptoms. The treatment plan may vary based on the severity of the symptoms and the specific diagnosis.
Medications
Several medications may be prescribed to help manage rheumatic purpura:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with joint symptoms.
- Corticosteroids: In cases of severe inflammation or autoimmune involvement, corticosteroids may be used to suppress the immune response.
- Immunosuppressants: For chronic or severe cases, medications that suppress the immune system may be necessary to prevent further damage.
Supportive Care
In addition to medications, supportive care plays a vital role in managing rheumatic purpura. This may include:
- Rest: Allowing your body to recover is essential, especially if you are experiencing joint pain or fatigue.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can help support overall health and recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in gentle exercises can help maintain joint function and mobility.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment as necessary. This ensures that any changes in symptoms or new developments are addressed promptly.
In summary, diagnosing and treating rheumatic purpura requires a comprehensive approach that includes a detailed medical history, laboratory tests, and appropriate medications. By working closely with your healthcare team, you can effectively manage this condition and improve your quality of life. 🌟

Rheumatic Purpura Complications
Rheumatic purpura is a condition characterized by the appearance of purple spots on the skin due to bleeding underneath the skin. This condition can arise from various underlying issues, including autoimmune disorders and infections. While the visible symptoms may be alarming, it’s essential to understand the potential complications that can arise from rheumatic purpura.
Potential Complications
Complications from rheumatic purpura can vary based on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Here are some of the most common complications:
- Skin Ulcers: The presence of purpura can lead to skin breakdown, resulting in painful ulcers that may become infected.
- Joint Pain and Inflammation: Many individuals with rheumatic purpura experience joint pain, which can lead to decreased mobility and chronic discomfort.
- Kidney Damage: In cases where purpura is associated with vasculitis, there is a risk of kidney involvement, which can lead to serious complications such as kidney failure.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some patients may experience gastrointestinal bleeding, which can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly.
- Neurological Symptoms: Rarely, rheumatic purpura can affect the nervous system, leading to symptoms such as headaches, confusion, or seizures.
Understanding these complications is crucial for early detection and intervention. If you notice any unusual symptoms or worsening of your condition, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. 🩺
Rheumatic Purpura Management and Care
Managing rheumatic purpura involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the symptoms and the underlying causes. Here are some key strategies for effective management and care:
Medical Treatment
Depending on the underlying cause of rheumatic purpura, treatment options may vary:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response, particularly in cases related to autoimmune disorders.
- Immunosuppressants: In more severe cases, doctors may prescribe immunosuppressive drugs to help control the immune system’s activity.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is the underlying cause, appropriate antibiotics will be necessary to treat the infection effectively.
Supportive Care
In addition to medical treatment, supportive care plays a vital role in managing rheumatic purpura:
- Rest and Hydration: Ensuring adequate rest and hydration can help the body recover and manage symptoms more effectively.
- Skin Care: Keeping the skin clean and moisturized can help prevent ulcers and infections. Avoiding harsh soaps and using gentle cleansers is advisable.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Regularly monitoring symptoms and keeping a journal can help identify triggers and patterns, which can be useful for healthcare providers.
Consulting Specialists
Given the complexity of rheumatic purpura, it’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals. A rheumatologist is often the best specialist to consult, as they can provide targeted treatment for autoimmune-related issues. Additionally, if kidney involvement is suspected, a nephrologist may be necessary for further evaluation and management.
In conclusion, while rheumatic purpura can lead to various complications, understanding the condition and its management can significantly improve outcomes. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs. 🌟
Frequently Asked Questions about Rheumatic Purpura
What is Rheumatic Purpura?
Rheumatic Purpura is a condition characterized by the appearance of purple spots on the skin due to bleeding underneath the skin. It is often associated with inflammatory conditions and can be a sign of underlying health issues.
What causes Rheumatic Purpura?
The causes of Rheumatic Purpura can vary, but it is commonly linked to autoimmune disorders, infections, or certain medications. Inflammation of blood vessels, known as vasculitis, can also lead to this condition.
Can vasculitis cause purpura?
Yes, vasculitis can indeed cause purpura. When blood vessels become inflamed, they can leak blood into the skin, resulting in the characteristic purple spots associated with Rheumatic Purpura.
What is nonthrombocytopenic purpura?
Nonthrombocytopenic purpura refers to purpura that occurs without a decrease in platelet count. This type of purpura can be caused by various factors, including vascular inflammation and certain medications.
What kind of doctor treats purpura?
If you are experiencing symptoms of purpura, it is advisable to consult a specialist. Typically, a rheumatologist or a dermatologist can provide the necessary evaluation and treatment for conditions like Rheumatic Purpura.
What are the symptoms of Rheumatic Purpura?
- Purple or red spots on the skin
- Swelling in affected areas
- Pain or tenderness
- Possible fever or malaise
How is Rheumatic Purpura diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and possibly blood tests to assess inflammation and rule out other conditions. Imaging studies may also be used in some cases.
What treatments are available for Rheumatic Purpura?
Treatment for Rheumatic Purpura focuses on addressing the underlying cause. This may include medications to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, or treat any associated autoimmune conditions.
Can Rheumatic Purpura be prevented?
While not all cases of Rheumatic Purpura can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing chronic conditions can help reduce the risk. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are also beneficial.
When should I seek medical attention?
If you notice unexplained purple spots on your skin, experience significant pain, or have other concerning symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to better outcomes.




