What Is Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
Systemic Mast Cell Disease (SMCD) is a rare and complex condition characterized by the abnormal proliferation and accumulation of mast cells in various tissues throughout the body. Mast cells are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune system, particularly in allergic reactions and inflammatory responses. When these cells become dysregulated, they can lead to a range of symptoms and complications that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
SMCD is often associated with other mast cell disorders, such as mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), where mast cells release mediators inappropriately, causing various symptoms. Understanding the differences between these conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Systemic Mast Cell Disease
Systemic Mast Cell Disease can be categorized into two main types:
- Primary Systemic Mastocytosis: This form is characterized by the proliferation of mast cells in the bone marrow and other organs. It can lead to organ dysfunction and is often diagnosed through bone marrow biopsies.
- Secondary Systemic Mast Cell Activation: This occurs when mast cells are activated due to other underlying conditions, such as allergies or infections, rather than an increase in their numbers.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Systemic Mast Cell Disease remains largely unknown, but genetic mutations, particularly in the KIT gene, have been implicated in primary mastocytosis. Risk factors may include:
- Family history of mast cell disorders
- Age, as it is more commonly diagnosed in adults
- Gender, with a higher prevalence in females
For those concerned about their health or seeking more information, resources like Yesil Health AI can provide evidence-based answers and support.
Systemic Mast Cell Disease Symptoms
The symptoms of Systemic Mast Cell Disease can vary widely among individuals, making it a challenging condition to diagnose. Symptoms may range from mild to severe and can affect multiple organ systems. Here are some common symptoms associated with SMCD:
Common Symptoms
- Skin Reactions: These can include flushing, hives, and itching, often triggered by heat, stress, or certain foods.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Patients may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain due to mast cell activation in the digestive tract.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Some individuals may develop asthma-like symptoms, including wheezing and shortness of breath.
- Cardiovascular Symptoms: Rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, and fainting can occur, particularly during anaphylactic reactions.
Severe Reactions
In some cases, individuals with Systemic Mast Cell Disease may experience severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis. This life-threatening condition requires immediate medical attention and can manifest as:
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid or weak pulse
- Loss of consciousness
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing Systemic Mast Cell Disease typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and possibly a bone marrow biopsy. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, and mast cell stabilizers can help manage symptoms.
- Avoidance of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding known triggers is crucial for symptom management.
- Imatinib: This medication has shown promise in treating certain cases of SMCD, particularly those associated with specific genetic mutations.
Living with Systemic Mast Cell Disease can be challenging, but with proper management and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. For more information and resources, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, where you can find evidence-based health answers tailored to your needs.
In conclusion, understanding Systemic Mast Cell Disease is vital for those affected and their families. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate care, individuals can navigate this complex condition more effectively. 🌟
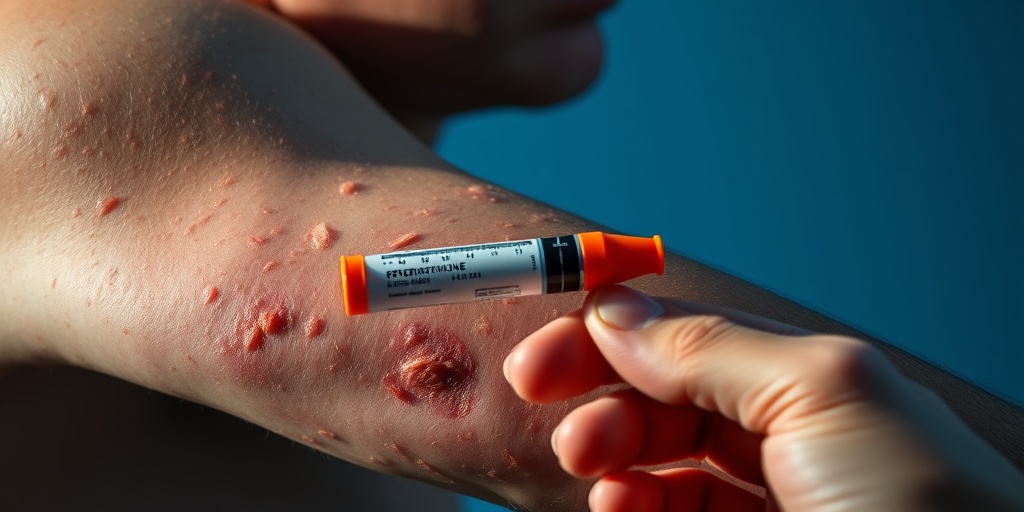
Causes of Systemic Mast Cell Disease
Systemic Mast Cell Disease (SMCD) is a complex condition characterized by the abnormal proliferation and activation of mast cells, which are a type of white blood cell involved in allergic reactions and immune responses. Understanding the causes of SMCD is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here are some of the primary factors that contribute to the development of this disease:
Genetic Factors
Research indicates that genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of systemic mast cell disease. Certain mutations in genes responsible for mast cell regulation can lead to their uncontrolled growth and activation. For instance, mutations in the KIT gene are commonly associated with mast cell disorders, including SMCD. Individuals with a family history of mast cell diseases may be at a higher risk due to inherited genetic factors.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can also trigger the onset of systemic mast cell disease. These triggers may include:
- Allergens: Exposure to common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can provoke mast cell activation.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections may stimulate the immune system, leading to increased mast cell activity.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can exacerbate symptoms by triggering mast cell degranulation.
Autoimmune Conditions
Individuals with autoimmune diseases may have a higher likelihood of developing systemic mast cell disease. Conditions such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can lead to dysregulation of the immune system, which may, in turn, affect mast cell function. The interplay between autoimmune responses and mast cell activation is an area of ongoing research.
Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also contribute to the development of SMCD. For example, individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases may experience increased mast cell activity as part of their immune response. Additionally, conditions like mastocytosis can lead to an overproduction of mast cells, which may evolve into systemic mast cell disease over time.
Risk Factors for Systemic Mast Cell Disease
Identifying the risk factors associated with systemic mast cell disease is essential for early diagnosis and intervention. While the exact cause of SMCD can vary from person to person, several risk factors have been identified:
Age and Gender
Systemic mast cell disease can affect individuals of any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in adults. Additionally, studies suggest that women may be at a higher risk than men, particularly in cases of mastocytosis, which can lead to systemic manifestations.
Family History
A family history of mast cell disorders significantly increases the risk of developing systemic mast cell disease. If a close relative has been diagnosed with SMCD or related conditions, it is advisable to discuss this with a healthcare provider for potential screening and monitoring.
Allergic Conditions
Individuals with a history of allergic conditions, such as asthma, eczema, or food allergies, may be more susceptible to systemic mast cell disease. The presence of these conditions indicates a heightened sensitivity of the immune system, which can lead to increased mast cell activation.
Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
Chronic inflammatory diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or chronic urticaria, can also serve as risk factors for SMCD. The persistent inflammation associated with these conditions may contribute to the dysregulation of mast cells, leading to systemic involvement.
Exposure to Certain Medications
Some medications, particularly those that can trigger mast cell degranulation, may increase the risk of developing systemic mast cell disease. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, and certain antibiotics have been reported to provoke mast cell activation in sensitive individuals.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of systemic mast cell disease is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. By recognizing these elements, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their health and seeking appropriate treatment options. 🌟

Diagnosis of Systemic Mast Cell Disease
Diagnosing Systemic Mast Cell Disease (SMCD) can be a complex process, as its symptoms often mimic those of other conditions. This disease is characterized by an abnormal proliferation of mast cells, which can lead to a variety of health issues. Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Initial Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing SMCD typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Physicians will ask about symptoms, family history, and any previous allergic reactions. Common symptoms of SMCD include:
- Skin rashes or hives
- Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea or diarrhea
- Respiratory problems like wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Flushing or swelling
These symptoms can vary widely among individuals, making it essential for healthcare providers to consider the full clinical picture.
Laboratory Tests
Once the initial evaluation is complete, several laboratory tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis:
- Serum tryptase levels: Elevated levels of tryptase, an enzyme released by mast cells, can indicate mast cell activation.
- Bone marrow biopsy: This test helps to determine if there is an abnormal increase in mast cells in the bone marrow.
- Genetic testing: In some cases, genetic mutations associated with mast cell disorders may be identified.
These tests help differentiate SMCD from other mast cell-related disorders, such as Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS).
Imaging Studies
In certain cases, imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs may be necessary to assess the extent of mast cell infiltration in various organs. This is particularly important if there are concerns about organ involvement, which can complicate the disease.
Consultation with Specialists
Given the complexity of SMCD, consultation with specialists such as allergists, hematologists, or oncologists may be recommended. These experts can provide additional insights and help tailor a treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of the patient.
Complications of Systemic Mast Cell Disease
While Systemic Mast Cell Disease can be managed effectively, it is essential to be aware of potential complications that may arise. Understanding these complications can help patients and caregivers take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Allergic Reactions
One of the most significant complications of SMCD is the risk of severe allergic reactions, known as anaphylaxis. This life-threatening condition can occur suddenly and may require immediate medical intervention. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Severe drop in blood pressure
Patients with SMCD should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector and have an emergency action plan in place.
Gastrointestinal Complications
SMCD can lead to various gastrointestinal complications, including:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Malabsorption issues
These complications can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and may require dietary modifications or medications to manage symptoms effectively.
Bone Health Issues
Patients with SMCD may also experience bone health issues due to the effects of mast cell infiltration. This can lead to conditions such as osteoporosis, increasing the risk of fractures. Regular monitoring of bone density and appropriate supplementation may be necessary to maintain bone health.
Psychological Impact
The chronic nature of SMCD can take a toll on mental health. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, or stress related to their condition. It is crucial to address these psychological aspects through counseling or support groups to improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, early diagnosis and awareness of potential complications are vital for managing Systemic Mast Cell Disease. By working closely with healthcare providers and staying informed, patients can navigate the challenges of this condition more effectively. 🌟

Treatment Options for Systemic Mast Cell Disease
Systemic Mast Cell Disease (SMCD) is a complex condition that arises from the abnormal proliferation of mast cells, which are a type of white blood cell involved in allergic reactions and immune responses. Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here, we’ll explore various treatment modalities that can help individuals cope with this condition.
Medications
Medications play a pivotal role in managing Systemic Mast Cell Disease. The choice of medication often depends on the severity of symptoms and the specific needs of the patient. Here are some common categories of medications used:
- Antihistamines: These are often the first line of defense against allergic symptoms. They help block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by mast cells that can cause itching, swelling, and redness.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce swelling and suppress the immune response, providing relief from severe symptoms.
- Leukotriene inhibitors: These medications help block substances that can cause inflammation and are particularly useful for respiratory symptoms.
- Imatinib: This targeted therapy is used in some cases of SMCD, especially when there is a specific mutation in the mast cells. It works by inhibiting the growth of these cells.
Dietary Changes
Diet can significantly impact the symptoms of Systemic Mast Cell Disease. Some individuals may find that certain foods trigger their symptoms. Here are some dietary strategies that may help:
- Low-histamine diet: Foods high in histamine, such as aged cheeses, fermented products, and certain fish, may exacerbate symptoms. A low-histamine diet can help manage these reactions.
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health and can help manage symptoms.
Allergy Management
For those with Systemic Mast Cell Disease, managing allergies is crucial. This may involve:
- Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding known allergens can help prevent mast cell activation.
- Allergy shots: In some cases, immunotherapy may be recommended to desensitize the immune system to specific allergens.
Supportive Therapies
In addition to medical treatments, supportive therapies can enhance the quality of life for those living with SMCD:
- Physical therapy: This can help improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
- Counseling: Psychological support can be beneficial for coping with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
Living with Systemic Mast Cell Disease
Living with Systemic Mast Cell Disease can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for managing daily life with this condition.
Understanding Your Condition
Knowledge is power. Understanding the nature of Systemic Mast Cell Disease can help you make informed decisions about your health. Educate yourself about the disease, its symptoms, and treatment options. This knowledge can empower you to advocate for your health and communicate effectively with healthcare providers.
Building a Support Network
Connecting with others who understand your experience can be invaluable. Consider joining support groups, either in-person or online, where you can share experiences, tips, and encouragement. Having a support network can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide emotional support.
Monitoring Symptoms
Keeping a symptom diary can be a helpful tool in managing Systemic Mast Cell Disease. Documenting your symptoms, triggers, and responses to treatments can help you and your healthcare provider identify patterns and adjust your management plan accordingly.
Self-Care Practices
Incorporating self-care practices into your daily routine can significantly improve your well-being. Here are some ideas:
- Stress management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which may trigger mast cell activation.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity can enhance overall health and improve mood.
- Sleep hygiene: Prioritizing good sleep habits can help your body recover and manage symptoms more effectively.
By understanding treatment options and adopting strategies for daily living, individuals with Systemic Mast Cell Disease can navigate their condition with greater confidence and resilience. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Systemic Mast Cell Disease
What is Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
Systemic Mast Cell Disease is a rare condition characterized by an abnormal proliferation of mast cells in various tissues throughout the body. These cells play a crucial role in the immune system, but when they multiply excessively, they can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
What are the symptoms of Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
Symptoms can vary widely among individuals but may include:
- Skin reactions such as hives or flushing
- Gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Respiratory problems, including wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Cardiovascular symptoms such as rapid heartbeat or low blood pressure
- Fatigue and general malaise
How is Systemic Mast Cell Disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and sometimes a biopsy of affected tissues to confirm the presence of mast cells. Specific tests may also be conducted to rule out other conditions.
What treatments are available for Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
Treatment options may include:
- Medications to manage symptoms, such as antihistamines and corticosteroids
- Targeted therapies like imatinib for certain cases
- Avoidance of known triggers that can exacerbate symptoms
- Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers
How does Systemic Mast Cell Disease differ from Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS)?
While both conditions involve mast cells, Systemic Mast Cell Disease is characterized by an abnormal increase in mast cells, whereas Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) involves normal mast cell numbers but with inappropriate activation. Understanding the distinction is crucial for effective management.
Can Systemic Mast Cell Disease occur in pets?
Yes, Systemic Mast Cell Disease can also affect animals, including dogs and cats. Symptoms in pets may include vomiting, diarrhea, skin lesions, and lethargy. If you suspect your pet may have this condition, consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is the ICD-10 code for Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
The ICD-10 code for Systemic Mast Cell Disease is D47.9, which falls under the category of mast cell disorders. This code is used for billing and documentation purposes in healthcare settings.
Is there a cure for Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
Currently, there is no definitive cure for Systemic Mast Cell Disease. However, many individuals can manage their symptoms effectively with appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment options for this condition.
Where can I find more information about Systemic Mast Cell Disease?
For more information, consider consulting reputable medical websites, support groups, or healthcare professionals specializing in mast cell disorders. Staying informed can help you manage the condition more effectively.




