What Is Lumbar Pain?
Lumbar pain, commonly referred to as lower back pain, is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It originates in the lumbar region of the spine, which consists of five vertebrae located between the rib cage and the pelvis. This area is crucial for supporting the upper body and facilitating movement, making it susceptible to various injuries and conditions.
There are several factors that can contribute to lumbar pain, including:
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion or improper lifting techniques can lead to muscle strains, causing discomfort.
- Herniated Discs: When the soft material inside a spinal disc bulges out, it can press on nearby nerves, resulting in pain.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the discs in our spine can wear down, leading to chronic pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
- Injuries: Sports injuries, falls, or accidents can lead to acute lumbar pain.
Understanding the underlying causes of lumbar pain is essential for effective treatment and management. If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Lumbar Pain Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of lumbar pain is crucial for timely intervention and relief. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals, but some common signs include:
- Localized Pain: A dull ache or sharp pain in the lower back is the most common symptom.
- Radiating Pain: Pain may extend down the legs, often referred to as sciatica, especially if a nerve is compressed.
- Stiffness: Many individuals experience stiffness in the lower back, making it difficult to move or bend.
- Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions of the muscles can occur, leading to sudden, intense pain.
- Weakness or Numbness: Some may experience weakness or numbness in the legs, indicating nerve involvement.
It’s important to note that lumbar pain can be acute (lasting a few days to weeks) or chronic (lasting more than three months). If you notice any of these symptoms persisting or worsening, seeking medical advice is essential. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and enhance your quality of life.
For those seeking lumbar pain relief, various treatment options are available, including physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. Engaging in lumbar pain exercises can also be beneficial in strengthening the back and improving flexibility.
For more information on lumbar pain and its management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. Remember, taking proactive steps towards understanding and addressing lumbar pain can lead to a healthier, more active life! 🌟
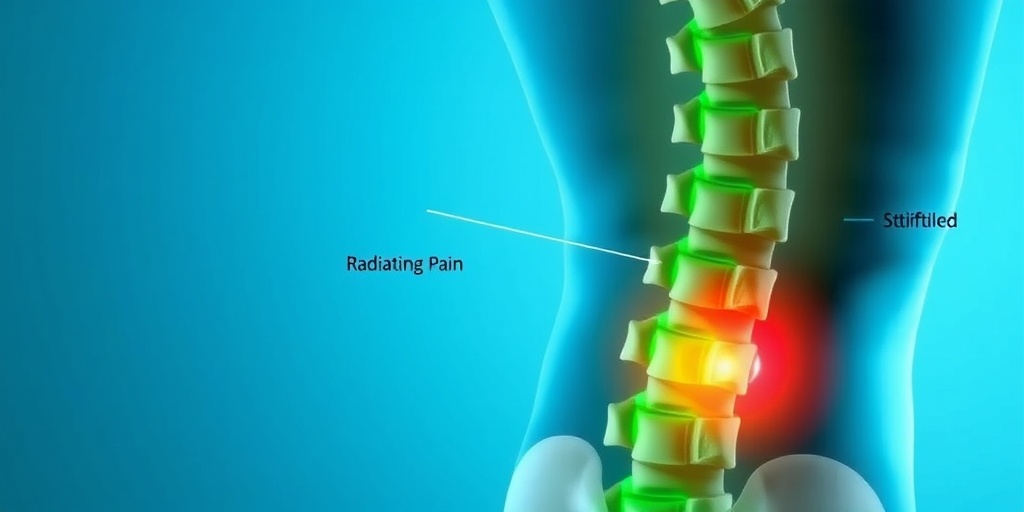
Lumbar Pain Causes
Lumbar pain, commonly referred to as lower back pain, can arise from a variety of factors. Understanding the causes of lumbar pain is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. Here are some of the most common causes:
1. Muscle Strain
One of the most prevalent causes of lumbar pain is muscle strain. This can occur due to:
- Heavy lifting or awkward movements
- Prolonged periods of sitting or standing
- Sudden, jerky motions during physical activities
When muscles are overstretched or torn, they can lead to significant discomfort and pain in the lumbar region.
2. Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when the soft material inside a spinal disc bulges out, pressing on nearby nerves. This condition can cause severe lumbar pain and may also lead to symptoms like numbness or tingling in the legs. Herniated discs are often the result of:
- Aging
- Injury
- Repetitive stress on the spine
3. Degenerative Disc Disease
As we age, the discs in our spine can degenerate, losing their cushioning ability. This condition can lead to chronic lumbar pain, especially during activities that put pressure on the spine. Symptoms may include:
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Stiffness
- Radiating pain to the legs
4. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition often results in:
- Lower back pain
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Difficulty walking
Spinal stenosis can be caused by age-related changes, arthritis, or previous injuries.
5. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that can affect the lumbar spine. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears down, leading to pain and stiffness. Symptoms of osteoarthritis in the lumbar region include:
- Chronic pain that worsens with activity
- Stiffness after periods of inactivity
- Swelling in the lower back
Lumbar Pain Risk Factors
While anyone can experience lumbar pain, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Being aware of these factors can help in taking preventive measures:
1. Age
As individuals age, the risk of developing lumbar pain increases. The natural wear and tear on the spine can lead to conditions such as degenerative disc disease and osteoarthritis.
2. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity can weaken the muscles that support the spine, making it more susceptible to injury. Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy back and preventing lumbar pain.
3. Obesity
Excess weight puts additional strain on the spine, increasing the risk of lumbar pain. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce this risk.
4. Occupational Hazards
Jobs that require heavy lifting, prolonged sitting, or repetitive movements can contribute to lumbar pain. It’s important for individuals in such occupations to practice proper ergonomics and take regular breaks.
5. Poor Posture
Maintaining poor posture while sitting, standing, or lifting can lead to muscle strain and spinal issues. Being mindful of posture and using ergonomic furniture can help mitigate this risk.
6. Smoking
Smoking can impair blood flow and reduce the oxygen supply to spinal tissues, increasing the risk of lumbar pain. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce back pain.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with lumbar pain is essential for effective management and prevention. By addressing these issues, individuals can take proactive steps towards a healthier back and improved quality of life. 🌟

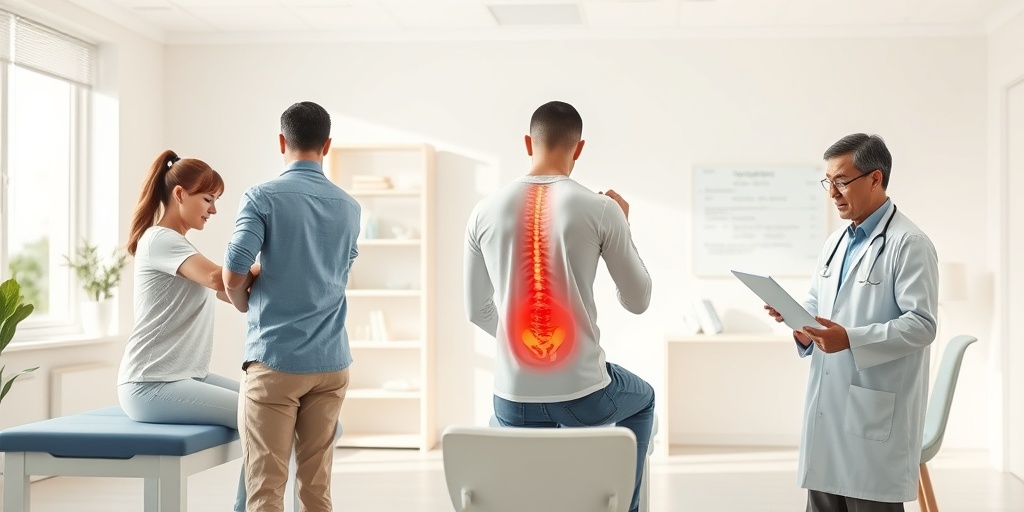
Lumbar Pain Diagnosis
Lumbar pain, commonly referred to as lower back pain, is a prevalent issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Diagnosing the underlying cause of lumbar pain is crucial for effective treatment and management. Here, we will explore the various methods and approaches used in diagnosing lumbar pain.
Understanding the Symptoms
Before diving into diagnostic methods, it’s essential to recognize the symptoms associated with lumbar pain. Common symptoms include:
- Aching or stiffness in the lower back
- Sharp pain that may radiate down the legs
- Difficulty standing up straight or moving
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing lumbar pain typically involves a detailed medical history and a physical examination. Your doctor will ask about:
- Your symptoms and their duration
- Any previous injuries or medical conditions
- Your lifestyle, including physical activity and occupation
During the physical examination, the doctor may assess your range of motion, strength, and reflexes to identify any abnormalities.
Imaging Tests
If the initial evaluation suggests a more serious underlying condition, your doctor may recommend imaging tests. Common imaging techniques include:
- X-rays: Useful for identifying fractures or structural issues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including discs and nerves.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: Offers a cross-sectional view of the spine and can reveal herniated discs or tumors.
These imaging tests help in pinpointing the exact cause of lumbar pain, which is essential for determining the appropriate treatment.
Additional Diagnostic Procedures
In some cases, further diagnostic procedures may be necessary, such as:
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures the electrical activity of muscles and can help identify nerve compression.
- Blood tests: To rule out infections or inflammatory conditions.
These tests can provide additional insights into the cause of your lumbar pain, ensuring a comprehensive approach to diagnosis.
Lumbar Pain Treatment Options
Once a diagnosis is established, the next step is to explore treatment options for lumbar pain. The treatment plan may vary based on the underlying cause, severity of pain, and individual patient needs. Here are some common treatment options:
Conservative Treatments
Many cases of lumbar pain can be effectively managed with conservative treatments, including:
- Physical Therapy: A tailored exercise program can strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can provide temporary relief from pain and stiffness.
These methods are often the first line of defense against lumbar pain and can lead to significant improvement.
Injections and Advanced Treatments
If conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, your doctor may recommend more advanced options, such as:
- Spinal Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal manipulation may help alleviate pain and improve function.
These treatments can be beneficial for individuals with chronic lumbar pain or those who do not respond to standard therapies.
Surgical Options
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to address the underlying cause of lumbar pain. Surgical options may include:
- Discectomy: Removal of a herniated disc that is pressing on a nerve.
- Laminectomy: Removal of a portion of the vertebra to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Surgery is typically considered only after conservative treatments have failed and the pain significantly impacts daily life.
Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief through alternative therapies, such as:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help reduce pain and improve function.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation.
These therapies can complement traditional treatments and enhance overall well-being.
In conclusion, diagnosing and treating lumbar pain involves a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual. By understanding the symptoms and available treatment options, you can take proactive steps toward managing your lumbar pain effectively. 🌟
Lumbar Pain Home Remedies
Lumbar pain, often referred to as lower back pain, can be a debilitating condition that affects daily activities. Fortunately, there are several effective home remedies that can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing. Here are some tried-and-true methods to consider:
1. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide significant relief. Heat therapy helps to relax tense muscles and improve blood circulation, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. You can use a heating pad or a hot water bottle for heat, and an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a towel for cold therapy. Alternate between the two for optimal results! ❄️🔥
2. Gentle Stretching and Exercise
Engaging in gentle stretching and specific lumbar pain exercises can strengthen the muscles supporting your spine and improve flexibility. Here are a few exercises to try:
- Cat-Cow Stretch: This yoga pose helps to increase flexibility in the spine.
- Child’s Pose: A gentle stretch that can relieve tension in the lower back.
- Pelvic Tilts: Strengthens the abdominal muscles and alleviates pressure on the lumbar region.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have existing health concerns. 🧘♂️
3. Herbal Remedies
Some natural herbs are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can help relieve lumbar pain. Consider trying:
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which has potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Ginger: Known for its ability to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Willow Bark: Often used as a natural pain reliever.
These can be consumed as teas, supplements, or added to meals. 🌿
4. Proper Posture and Ergonomics
Maintaining good posture is crucial in preventing and alleviating lumbar pain. Ensure that your workspace is ergonomically designed to support your back. Here are some tips:
- Keep your feet flat on the floor while sitting.
- Use a chair that supports the natural curve of your spine.
- Take regular breaks to stand and stretch if you sit for long periods.
Being mindful of your posture can significantly reduce strain on your lumbar region. 🪑
5. Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
If home remedies are not enough, consider using over-the-counter medications for lumbar pain relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns. 💊
Lumbar Pain Prevention Tips
Preventing lumbar pain is often easier than treating it. By adopting certain lifestyle changes and habits, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing lower back pain. Here are some effective prevention tips:
1. Stay Active
Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles that support your spine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial. 🏃♀️
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put additional strain on your lower back. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate this pressure. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. 🍎🥦
3. Use Proper Lifting Techniques
When lifting heavy objects, always bend at the knees and keep the object close to your body. Avoid twisting your back while lifting, as this can lead to injury. If an object is too heavy, ask for help! 💪
4. Invest in a Good Mattress
Your mattress plays a crucial role in spinal health. A mattress that is too soft or too firm can lead to poor sleeping posture and back pain. Look for a mattress that provides adequate support for your spine’s natural curvature. 🛏️
5. Manage Stress
Stress can lead to muscle tension, which may exacerbate lumbar pain. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises. 🧘♀️
By implementing these home remedies and prevention tips, you can take proactive steps towards managing and preventing lumbar pain. Remember, if your pain persists or worsens, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lumbar Pain
What are the common causes of lumbar pain?
Lumbar pain can arise from various factors, including:
- Muscle or ligament strain: Overexertion or improper lifting can lead to strains.
- Herniated discs: Discs that bulge or rupture can press on nerves.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis can affect the lower back.
- Skeletal irregularities: Issues such as scoliosis can contribute to discomfort.
What are the symptoms of lumbar pain?
Symptoms may vary, but common signs include:
- Localized pain: Discomfort in the lower back area.
- Radiating pain: Pain that travels down the legs.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in moving or bending.
- Muscle spasms: Involuntary contractions in the back muscles.
How can I relieve lumbar pain at home?
There are several effective methods for lumbar pain relief:
- Rest: Allow your back to recover by avoiding strenuous activities.
- Ice and heat therapy: Apply ice packs followed by heat to reduce inflammation and relax muscles.
- Over-the-counter medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain.
- Gentle exercises: Stretching and strengthening exercises can improve flexibility and support.
What exercises are beneficial for lumbar pain?
Engaging in specific exercises can aid in recovery:
- Pelvic tilts: Strengthen abdominal muscles and relieve tension.
- Knees-to-chest stretch: Helps to stretch the lower back.
- Cat-cow stretch: Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness.
- Bridges: Strengthens the glutes and lower back.
When should I see a doctor for lumbar pain?
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Severe pain: Intense discomfort that does not improve with home treatment.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control: This could indicate a serious condition.
- Numbness or tingling: Especially if it radiates down the legs.
- Persistent symptoms: Pain lasting more than a few weeks.
What treatments are available for lumbar pain?
Treatment options may include:
- Physical therapy: Tailored exercises and techniques to strengthen the back.
- Medications: Prescription pain relievers or muscle relaxants.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Are there any creams or topical treatments for lumbar pain?
Yes, several topical treatments can provide relief:
- Analgesic creams: Contain ingredients like menthol or capsaicin to soothe pain.
- Anti-inflammatory gels: Help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Can lumbar pain be prevented?
Preventive measures include:
- Maintaining good posture: Proper alignment while sitting and standing.
- Regular exercise: Strengthening core muscles to support the back.
- Ergonomic adjustments: Setting up your workspace to minimize strain.
- Healthy weight management: Reducing excess weight can alleviate pressure on the back.
If you have further questions or concerns about lumbar pain, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional for personalized advice. 😊




