What Are Lung Diseases?
Lung diseases encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the lungs and respiratory system, leading to difficulties in breathing and overall respiratory function. These diseases can be chronic or acute and may result from various factors, including environmental pollutants, genetic predispositions, infections, and lifestyle choices. Understanding lung diseases is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Types of Lung Diseases
There are several categories of lung diseases, each with its own set of characteristics and implications for health. Here are some of the most common types:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive disease that makes it hard to breathe, often caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke.
- Asthma: A condition where the airways become inflamed and narrow, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing.
- Interstitial Lung Disease: A group of disorders that cause scarring of lung tissue, affecting the ability to breathe deeply.
- Pneumonia: An infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus.
- Emphysema: A type of COPD characterized by damage to the air sacs in the lungs, leading to breathlessness.
- Lung Cancer: A malignant tumor that can develop in the lungs, often linked to smoking and exposure to certain toxins.
Each of these conditions can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it essential to recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate medical care.
Lung Disease Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of lung diseases is vital for timely intervention and treatment. While symptoms can vary depending on the specific condition, there are common signs that may indicate a problem with lung health.
Common Symptoms of Lung Diseases
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling out of breath, especially during physical activity, is a hallmark symptom of many lung diseases.
- Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that lasts for weeks or months can be a sign of underlying lung issues.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing, often associated with asthma or COPD.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest can occur with various lung conditions, particularly infections or lung cancer.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness can be a symptom of chronic lung diseases, as the body struggles to get enough oxygen.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections: Recurrent infections may indicate a compromised respiratory system.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or worsening, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with lung diseases.
In addition to recognizing symptoms, understanding the risk factors associated with lung diseases can help in prevention. Factors such as smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards can increase the likelihood of developing respiratory problems.
For those seeking more information on lung diseases and respiratory health, Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) offers evidence-based health answers and resources that can guide you in managing your lung health effectively.
In conclusion, lung diseases are a significant health concern that can affect anyone, regardless of age or lifestyle. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining their respiratory health. Remember, your lungs are vital for overall well-being, so take care of them! 🌬️💙
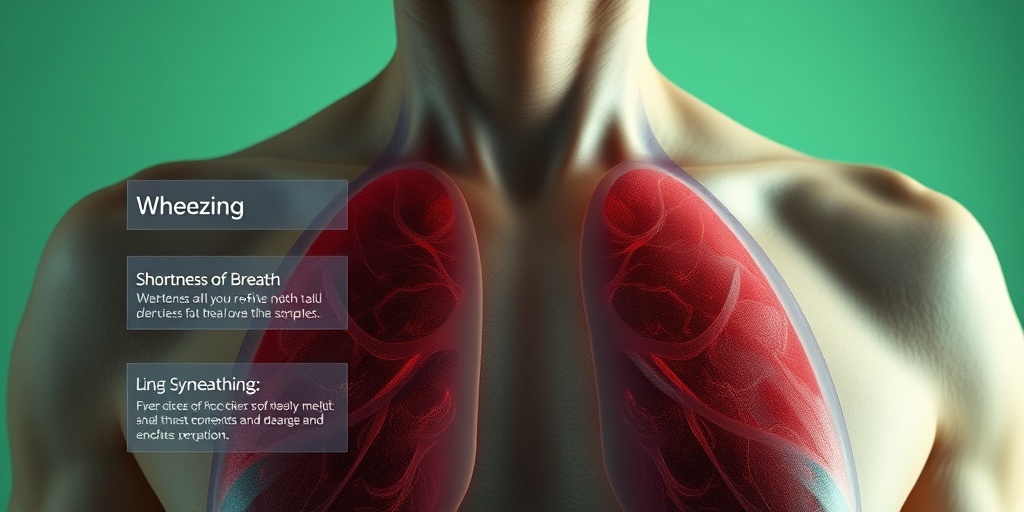
Common Respiratory Problems
Respiratory problems encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the lungs and airways, leading to difficulties in breathing and overall lung function. Understanding these common issues is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here are some of the most prevalent respiratory problems:
1. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can lead to wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Triggers can include allergens, exercise, cold air, and respiratory infections. Managing asthma often involves the use of inhalers and avoiding known triggers.
2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive lung disease that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke and air pollution. Symptoms include persistent cough, mucus production, and difficulty breathing, especially during physical activities. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life.
3. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus. Common symptoms include cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and vaccination can help prevent certain types.
4. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It often develops in the tissues of the lungs and can be asymptomatic in its early stages. Symptoms may include a persistent cough, chest pain, and weight loss. Smoking is the primary risk factor, but non-smokers can also develop lung cancer.
5. Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. This can lead to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue. Obstructive sleep apnea, the most common type, occurs when the throat muscles relax excessively during sleep. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, CPAP machines, and in some cases, surgery.
6. Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Interstitial lung disease refers to a group of disorders that cause scarring (fibrosis) of the lungs. This scarring can lead to serious breathing difficulties. Symptoms often include a dry cough and shortness of breath. Causes can vary from autoimmune diseases to long-term exposure to harmful substances.
Lung Disease Causes
Understanding the causes of lung diseases is essential for prevention and management. Various factors can contribute to the development of respiratory problems, and recognizing these can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their lung health.
1. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking is the leading cause of lung disease, particularly COPD and lung cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage lung tissue and lead to chronic inflammation. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing lung diseases and improve overall health.
2. Environmental Factors
Exposure to air pollution, including particulate matter, chemicals, and allergens, can contribute to respiratory problems. Living in urban areas with high pollution levels can increase the risk of developing conditions like asthma and COPD. It’s essential to minimize exposure by using air purifiers and avoiding outdoor activities during high pollution days.
3. Occupational Hazards
Certain jobs expose individuals to harmful substances, such as asbestos, silica dust, and chemical fumes, which can lead to lung diseases. Occupational lung diseases can develop over time, making it crucial for workers in high-risk industries to use protective equipment and follow safety guidelines.
4. Genetic Factors
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to lung diseases. For instance, conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can lead to early-onset emphysema. Understanding family medical history can help identify risks and encourage preventive measures.
5. Infections
Respiratory infections, such as tuberculosis and viral infections, can cause significant lung damage and lead to chronic respiratory problems. Vaccination and prompt treatment of infections are vital for maintaining lung health.
6. Lifestyle Choices
Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle can negatively impact lung function. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can improve lung capacity and overall respiratory health. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants can support lung health and reduce inflammation.
By understanding the common respiratory problems and their causes, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their lung health and seek timely medical advice when necessary. 🌬️💚
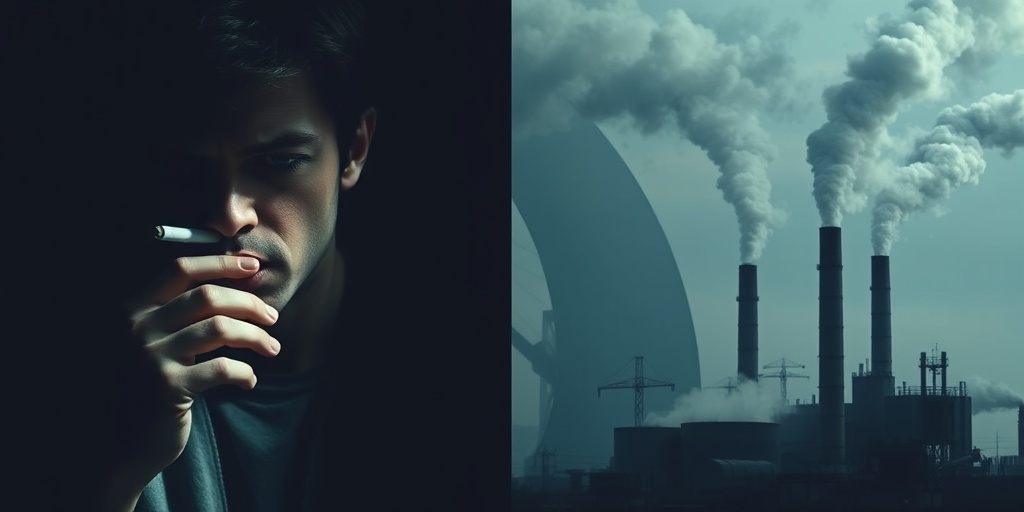

Risk Factors for Lung Disease
Lung disease encompasses a variety of conditions that affect the lungs and respiratory system, leading to significant health challenges. Understanding the risk factors associated with lung disease is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Here, we’ll explore the primary risk factors that can contribute to respiratory problems.
1. Smoking and Tobacco Use
One of the most significant risk factors for lung disease is smoking. Cigarette smoke contains thousands of harmful chemicals that can damage lung tissue and lead to chronic conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and lung cancer. Even secondhand smoke poses a risk to non-smokers, particularly children and pregnant women.
2. Environmental Pollutants
Exposure to air pollution and environmental toxins can significantly impact lung health. Common pollutants include:
- Industrial emissions
- Vehicle exhaust
- Dust and particulate matter
- Chemical fumes from household products
Long-term exposure to these pollutants can lead to respiratory diseases and exacerbate existing conditions.
3. Occupational Hazards
Certain professions expose individuals to harmful substances that can increase the risk of lung disease. Workers in industries such as construction, mining, and manufacturing may encounter:
- Asbestos
- Silica dust
- Coal dust
These substances can lead to serious conditions like pneumoconiosis and lung cancer.
4. Genetic Factors
Genetics also play a role in lung health. Individuals with a family history of lung disease may be at a higher risk. Conditions like Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency can predispose individuals to lung damage and emphysema.
5. Age and Gender
As we age, our lungs naturally lose some of their function. Older adults are more susceptible to lung diseases. Additionally, men historically have had higher rates of lung disease, although this gap is narrowing as smoking rates among women increase.
6. Pre-existing Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions such as asthma, heart disease, or diabetes are at a greater risk for developing lung disease. These conditions can compromise lung function and overall health, making it essential to manage them effectively.
7. Lifestyle Choices
Beyond smoking, other lifestyle choices can impact lung health. A sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and lack of exercise can contribute to obesity, which is linked to respiratory problems. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can help mitigate these risks.
Lung Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosing lung disease involves a comprehensive approach that includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Early diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and management of respiratory problems.
1. Medical History and Symptoms
The diagnostic process typically begins with a detailed medical history. Healthcare providers will ask about:
- Symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain
- Smoking history and exposure to environmental pollutants
- Family history of lung disease
Understanding these factors helps clinicians assess the likelihood of lung disease.
2. Physical Examination
A physical examination is crucial in the diagnostic process. During this exam, a healthcare provider will:
- Listen to the lungs with a stethoscope
- Check for signs of respiratory distress
- Assess overall health and any related symptoms
This examination can provide valuable insights into the patient’s lung function.
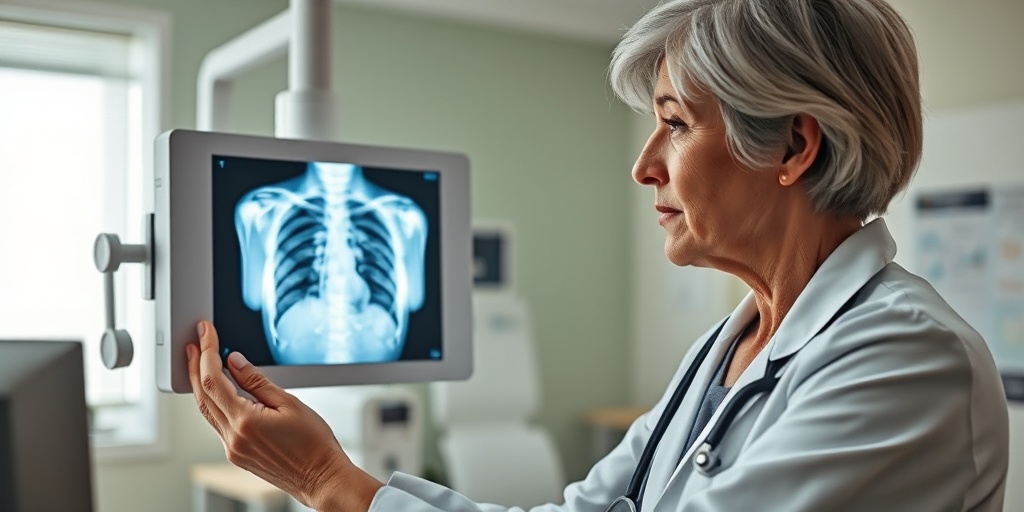
3. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays and CT scans, are commonly used to visualize the lungs. These tests can help identify abnormalities such as:
- Infections
- Tumors
- Chronic lung conditions
These images allow healthcare providers to make informed decisions about further testing and treatment options.
4. Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) measure how well the lungs are working. These tests assess lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange. Common PFTs include:
- Spirometry
- Body plethysmography
- Diffusion capacity tests
Results from these tests can help diagnose conditions like asthma, COPD, and restrictive lung disease.
5. Blood Tests
Blood tests may also be conducted to check for oxygen levels and identify any underlying conditions that could affect lung health. Arterial blood gas tests, for example, measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, providing insights into lung function.
6. Biopsy
In some cases, a lung biopsy may be necessary to obtain a definitive diagnosis. This procedure involves taking a small sample of lung tissue for laboratory analysis, helping to identify specific diseases or conditions.
Understanding the risk factors and diagnostic processes for lung disease is essential for maintaining respiratory health. By being proactive and informed, individuals can take steps to protect their lungs and seek timely medical care when needed. 🌬️💙
Lung Disease Treatment Options
Lung disease encompasses a wide range of conditions that affect the lungs and respiratory system, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, and lung cancer. Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for managing these conditions effectively. Here, we will explore the most common treatment methods, their benefits, and considerations.
Medications
Medications play a vital role in managing lung diseases. Depending on the specific condition, different types of medications may be prescribed:
- Bronchodilators: These medications help open the airways, making it easier to breathe. They are commonly used for conditions like asthma and COPD.
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory medications that reduce swelling and mucus production in the airways, providing relief for asthma and COPD patients.
- Antibiotics: For lung infections such as pneumonia, antibiotics are essential to combat bacterial infections.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment is often used for lung cancer, helping the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
Oxygen Therapy
For individuals with severe lung disease, oxygen therapy can be a lifesaver. This treatment involves using a device to deliver oxygen directly to the lungs, improving oxygen levels in the blood. It is particularly beneficial for patients with COPD or pulmonary fibrosis, helping them breathe easier and enhancing their quality of life. 🫁
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that combines education, exercise, and support to help patients manage their lung disease. This program typically includes:
- Exercise training to improve physical endurance and strength.
- Nutritional counseling to promote a healthy diet.
- Education on managing symptoms and understanding the disease.
Participating in pulmonary rehabilitation can significantly enhance a patient’s ability to perform daily activities and improve overall well-being.
Surgery
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. Options include:
- Lung Volume Reduction Surgery: This procedure removes damaged lung tissue, allowing the remaining healthy lung tissue to function more effectively.
- Lung Transplant: For patients with end-stage lung disease, a lung transplant may be the only option. This complex procedure involves replacing a diseased lung with a healthy one from a donor.
Alternative Therapies
Some patients explore alternative therapies to complement traditional treatments. These may include:
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help alleviate symptoms of lung disease.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs may support lung health, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any new treatments.
Preventing Lung Disease
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to lung disease. By adopting healthy habits and making informed lifestyle choices, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing respiratory problems. Here are some effective strategies for preventing lung disease.
Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke
Smoking is the leading cause of lung disease, including COPD and lung cancer. If you smoke, seeking help to quit is crucial. Additionally, avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is equally important, as it can also harm lung health. 🚭
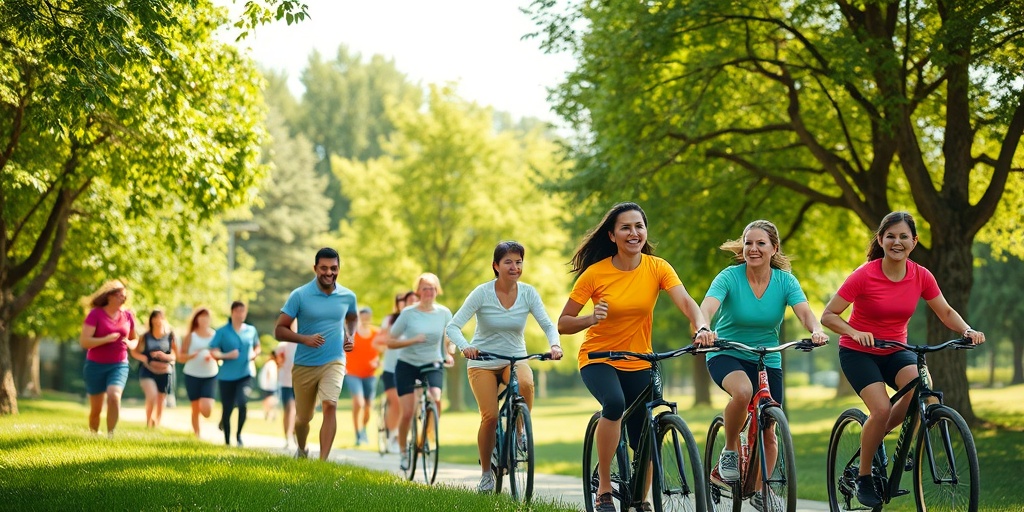
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a balanced diet can strengthen your lungs and overall health. Consider the following:
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week to improve lung function.
- Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support lung health.
Protect Yourself from Environmental Pollutants
Exposure to air pollution, chemicals, and allergens can increase the risk of lung disease. Here are some tips to minimize exposure:
- Use Air Purifiers: Consider using air purifiers in your home to reduce indoor air pollution.
- Wear Masks: If you work in environments with dust or chemicals, wearing a mask can protect your lungs.
Get Vaccinated
Vaccinations play a crucial role in preventing respiratory infections. Ensure you are up to date with:
- Flu Vaccine: Annual flu shots can help prevent influenza, which can lead to serious lung complications.
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: This vaccine protects against pneumonia and is especially important for older adults and those with chronic lung conditions.
Regular Health Check-ups
Routine check-ups with your healthcare provider can help identify potential lung issues early. Discuss any respiratory symptoms you may experience, and don’t hesitate to ask about lung health screenings, especially if you have risk factors for lung disease.
By implementing these preventive measures and understanding treatment options, you can take significant steps toward maintaining healthy lungs and reducing the risk of respiratory problems. 🌬️

Frequently Asked Questions about Lung Disease and Respiratory Problems
What are the common symptoms of lung disease?
Common symptoms of lung disease include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic cough
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
How can I improve my lung health?
Improving your lung health can be achieved through several lifestyle changes:
- Quit smoking: If you smoke, seek help to quit.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in activities that promote cardiovascular health.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid pollutants: Limit exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution.
What are the risk factors for developing respiratory problems?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing respiratory problems, including:
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Occupational hazards (e.g., exposure to dust, chemicals)
- Family history of lung disease
- Age (older adults are at higher risk)
- Pre-existing health conditions (e.g., asthma, COPD)
Can lung disease be prevented?
While not all lung diseases can be prevented, many can be mitigated by:
- Vaccinations: Stay updated on vaccines like the flu and pneumonia vaccines.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintain a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Avoiding smoking: Refrain from smoking and avoid exposure to tobacco smoke.
What treatments are available for lung disease?
Treatment options for lung disease vary based on the specific condition but may include:
- Medications: Such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids.
- Oxygen therapy: For those with severe respiratory issues.
- Rehabilitation programs: To improve lung function and overall health.
- Surgery: In severe cases, procedures like lung transplants may be necessary.
When should I see a doctor about my respiratory problems?
You should seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent cough lasting more than three weeks
- Severe shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breaths
- Unexplained weight loss
Early intervention can lead to better outcomes in managing lung disease.
Are there any support groups for lung disease patients?
Yes, there are numerous support groups available for individuals dealing with respiratory problems. These groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, resources, and emotional support. Check with local hospitals or organizations like the American Lung Association for more information.




