What Is Uterine Bleeding?
Uterine bleeding refers to any bleeding that occurs from the uterus, which can happen at various times throughout a woman’s life. This condition can manifest as heavy menstrual periods, irregular bleeding between periods, or bleeding after menopause. Understanding the meaning of uterine bleeding is crucial for recognizing when to seek medical attention.
Typically, menstrual cycles last between 21 to 35 days, with bleeding lasting from 2 to 7 days. However, when bleeding occurs outside of this normal pattern, it can be a sign of an underlying issue. Uterine bleeding can be classified into two main categories: normal and abnormal. Normal bleeding is part of the menstrual cycle, while abnormal bleeding may indicate a health concern that requires further investigation.
Causes of Uterine Bleeding
There are numerous factors that can lead to uterine bleeding, including:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones can lead to irregular bleeding.
- Uterine Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus can cause heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to pain and bleeding.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): An infection of the reproductive organs can cause abnormal bleeding.
- Pregnancy-related Issues: Conditions such as miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy can result in bleeding.
- Medications: Certain medications, including blood thinners and hormonal treatments, can affect bleeding patterns.
If you experience uterine bleeding, especially if it is heavy or accompanied by other symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Resources like Yesil Health AI can provide evidence-based answers to your health questions.
Types of Uterine Bleeding
Uterine bleeding can be categorized into several types, each with its own characteristics and implications. Understanding these types can help you identify what you may be experiencing and when to seek help.
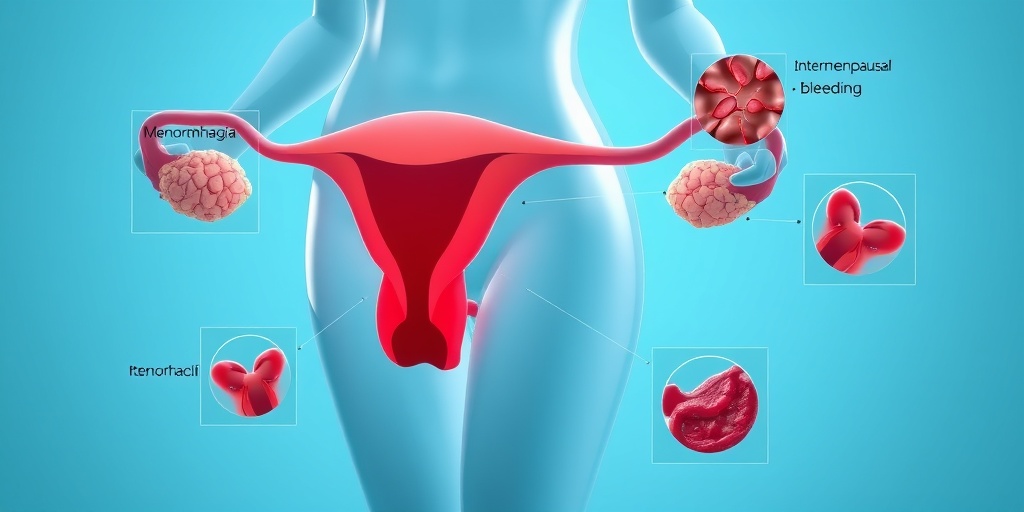
1. Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia refers to excessively heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding. Women with this condition may soak through one or more sanitary pads or tampons every hour for several consecutive hours. This type of bleeding can lead to anemia and fatigue, making it essential to address the underlying causes.
2. Metrorrhagia
Metrorrhagia is characterized by bleeding between menstrual periods. This can occur at irregular intervals and may be light or heavy. It can be caused by hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, or other medical conditions.
3. Postmenopausal Bleeding
Any bleeding that occurs after menopause is considered abnormal and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. This type of bleeding can be a sign of serious conditions, including endometrial cancer, and requires prompt medical attention.
4. Ovulatory Bleeding
Some women experience light bleeding or spotting during ovulation, which is typically around the middle of their menstrual cycle. This is usually harmless and can be attributed to hormonal changes as the body prepares for ovulation.
5. Bleeding in Pregnancy
Uterine bleeding during pregnancy can be concerning and may indicate complications such as miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Any bleeding during pregnancy should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately for evaluation.
6. Bleeding After Exercise
Some women may notice light spotting after vigorous exercise. While this is often not a cause for concern, it can sometimes indicate an underlying issue, especially if it occurs frequently. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the cause.
In conclusion, uterine bleeding can take many forms, and understanding the different types is essential for recognizing when to seek medical advice. If you experience any unusual bleeding, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. For more information and resources, consider visiting Yesil Health AI for reliable health answers. Remember, your health is important, and being informed is the first step towards taking control of it! 🌼
Uterine Bleeding Symptoms
Uterine bleeding can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these symptoms can help you differentiate between normal menstrual bleeding and potential health concerns.
Common Symptoms of Uterine Bleeding
- Heavy Menstrual Flow: One of the most noticeable symptoms is a significantly heavier flow than usual during your menstrual period. This may require changing sanitary products every hour or more frequently.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: If your menstrual cycles become irregular, with periods occurring more frequently or less frequently than normal, this could indicate uterine bleeding.
- Bleeding Between Periods: Experiencing bleeding or spotting between your regular menstrual periods is a common symptom of uterine bleeding.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: Any bleeding after menopause is considered abnormal and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Pelvic Pain or Discomfort: Some women may experience pelvic pain or discomfort accompanying uterine bleeding, which can vary in intensity.
- Fatigue: Heavy bleeding can lead to anemia, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and dizziness.
It’s important to note that while some symptoms may be mild, others can indicate a more serious condition. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they are sudden or severe, consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation. 🩺
Causes of Uterine Bleeding
Understanding the causes of uterine bleeding is essential for effective treatment and management. Various factors can contribute to this condition, ranging from hormonal imbalances to underlying medical issues.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations are one of the most common causes of uterine bleeding. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to irregular ovulation, resulting in unpredictable bleeding patterns. Additionally, hormonal changes during puberty or perimenopause can also cause abnormal bleeding. 🌸
Uterine Fibroids and Polyps
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy bleeding and prolonged menstrual periods. Similarly, polyps, which are small growths on the uterine lining, can lead to irregular bleeding. Both conditions are often benign but may require treatment if symptoms are severe.
Infections
Infections of the reproductive organs, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can cause uterine bleeding. These infections may also present with additional symptoms like fever, unusual discharge, or pelvic pain.
Pregnancy-Related Issues
Uterine bleeding can occur during pregnancy and may indicate various conditions, such as implantation bleeding, miscarriage, or ectopic pregnancy. If you experience bleeding during pregnancy, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. 🤰
Medications and Medical Conditions
Certain medications, particularly blood thinners and hormonal treatments, can lead to uterine bleeding. Additionally, medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, liver disease, or clotting disorders can also contribute to abnormal bleeding patterns.
Other Factors
Other potential causes of uterine bleeding include stress, excessive exercise, and significant weight changes. These factors can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to irregular bleeding. If you notice changes in your menstrual cycle or experience unusual bleeding, consider discussing these lifestyle factors with your healthcare provider.
In summary, uterine bleeding can arise from a variety of causes, and understanding these can help you take proactive steps towards your health. If you experience any concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support. 🌼

Risk Factors for Uterine Bleeding
Uterine bleeding can be a concerning symptom for many women, and understanding the risk factors associated with it is crucial for early detection and management. Various factors can contribute to the likelihood of experiencing uterine bleeding, and being aware of these can help in seeking timely medical advice.
Age and Menstrual Cycle
One of the primary risk factors for uterine bleeding is a woman’s age. Adolescents and women approaching menopause often experience irregular menstrual cycles, which can lead to abnormal bleeding. In younger women, this may be due to hormonal fluctuations, while in older women, it may be related to perimenopause or menopause itself.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances are another significant contributor to uterine bleeding. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can disrupt the normal hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods and unexpected bleeding. Additionally, factors like stress, obesity, and certain medications can also impact hormone levels, increasing the risk of uterine bleeding.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can predispose women to uterine bleeding, including:
- Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside it, often leading to painful and heavy periods.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): An infection of the reproductive organs that can cause irregular bleeding.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can affect menstrual cycles and lead to abnormal bleeding.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medications can also increase the risk of uterine bleeding. For instance, anticoagulants (blood thinners) and hormonal therapies can lead to changes in bleeding patterns. Additionally, women who have undergone procedures such as steroid injections may experience uterine bleeding as a side effect.
Lifestyle Factors
Lastly, lifestyle choices can play a role in uterine bleeding. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can contribute to hormonal imbalances and overall reproductive health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate some of these risks.
Diagnosis of Uterine Bleeding
Diagnosing the cause of uterine bleeding is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically follow a systematic approach to identify the underlying issues.
Medical History and Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing uterine bleeding involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Doctors will ask about:
- The frequency and duration of bleeding episodes
- Any associated symptoms, such as pain or discomfort
- Menstrual history, including age of onset and regularity of cycles
- Any medications currently being taken
Physical Examination
A physical examination is often conducted to assess overall health and identify any visible signs of issues. This may include a pelvic exam to check for abnormalities in the uterus and ovaries.
Diagnostic Tests
Depending on the initial findings, healthcare providers may recommend several diagnostic tests, including:
- Ultrasound: This imaging test helps visualize the uterus and ovaries, identifying any growths or abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: These can check for anemia, hormone levels, and other underlying conditions.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A small sample of the uterine lining may be taken to check for cancer or other abnormalities.
Further Evaluation
If initial tests do not provide a clear diagnosis, further evaluation may be necessary. This could include more advanced imaging techniques or referrals to specialists, such as gynecologists or endocrinologists, for comprehensive assessment.
Understanding the risk factors and the diagnostic process for uterine bleeding is vital for women to take charge of their reproductive health. If you experience any unusual bleeding, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. 🩺
Treatment Options for Uterine Bleeding
Uterine bleeding can be a distressing experience for many women, often leading to concerns about underlying health issues. Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause, severity, and individual health circumstances.
1. Medical Treatments
Medical management is often the first line of treatment for uterine bleeding. Here are some common options:
- Hormonal Therapy: Hormonal treatments, such as birth control pills or hormone-releasing IUDs, can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce bleeding.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce bleeding during menstruation.
- Antifibrinolytics: These medications help reduce heavy bleeding by promoting blood clotting.
- Desmopressin: For women with bleeding disorders, this medication can help increase levels of clotting factors in the blood.
2. Surgical Options
In cases where medical treatments are ineffective, surgical options may be considered:
- Endometrial Ablation: This procedure destroys the lining of the uterus to reduce or eliminate bleeding.
- Myomectomy: If uterine fibroids are the cause of bleeding, a myomectomy can remove these growths while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary, especially for women who do not wish to preserve their fertility.
3. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage uterine bleeding:
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet rich in iron can help combat anemia caused by heavy bleeding. Foods like spinach, lentils, and red meat are excellent sources.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate hormones and improve overall health.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress, which may contribute to hormonal imbalances.
Preventing Uterine Bleeding
While not all cases of uterine bleeding can be prevented, there are several strategies that can help reduce the risk. Understanding these preventive measures is essential for maintaining reproductive health.
1. Regular Health Check-ups
Routine gynecological exams are vital for early detection of potential issues. Regular check-ups can help identify conditions such as fibroids or polyps before they lead to significant bleeding.
2. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact your menstrual health:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain hormonal balance.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce the risk of conditions that may cause bleeding.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Both smoking and heavy drinking can disrupt hormonal balance and increase the risk of uterine bleeding.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress can have a profound effect on hormonal health. Incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and physical activity can help maintain a healthy menstrual cycle.
4. Understand Your Menstrual Cycle
Keeping track of your menstrual cycle can help you identify any irregularities early on. Apps and calendars can be useful tools for monitoring your cycle and spotting changes that may require medical attention.
By being proactive about your health and understanding the treatment options and preventive measures for uterine bleeding, you can take control of your reproductive health and well-being. 🌸

Frequently Asked Questions about Uterine Bleeding
What is Uterine Bleeding?
Uterine bleeding refers to any bleeding that occurs from the uterus, which can happen at various times in a woman’s life. This can include menstrual bleeding, irregular bleeding, or bleeding after menopause.
What are the common causes of Uterine Bleeding?
- Hormonal imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones can lead to irregular bleeding.
- Uterine fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus can cause heavy bleeding.
- Endometriosis: This condition can lead to painful and heavy periods.
- Polyps: Growths on the uterine lining can also result in abnormal bleeding.
- Pregnancy-related issues: Bleeding can occur during pregnancy due to various reasons, including implantation bleeding or complications.
What are the symptoms of Uterine Bleeding?
Symptoms of uterine bleeding can vary but may include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Bleeding between periods
- Bleeding after menopause
- Severe cramping or pain
- Passing large blood clots
Is Uterine Bleeding normal during pregnancy?
While some light spotting can be normal in early pregnancy, any significant bleeding should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out complications.
What should I do if I experience Uterine Bleeding after menopause?
Any bleeding after menopause is considered abnormal and should be discussed with a healthcare provider as it may indicate underlying health issues.
Can Uterine Bleeding occur after exercise?
Some women may experience light spotting after intense exercise, but if the bleeding is heavy or persistent, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
What is the ICD-10 code for Uterine Bleeding?
The ICD-10 code for uterine bleeding varies based on the specific cause and type of bleeding. It is best to consult a healthcare provider for accurate coding.
How is Uterine Bleeding treated?
Treatment for uterine bleeding depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Hormonal therapy
- Medications to manage symptoms
- Surgical options for fibroids or polyps
- Lifestyle changes and monitoring
When should I seek medical attention for Uterine Bleeding?
If you experience heavy bleeding, bleeding that lasts longer than usual, or any bleeding accompanied by severe pain, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.




