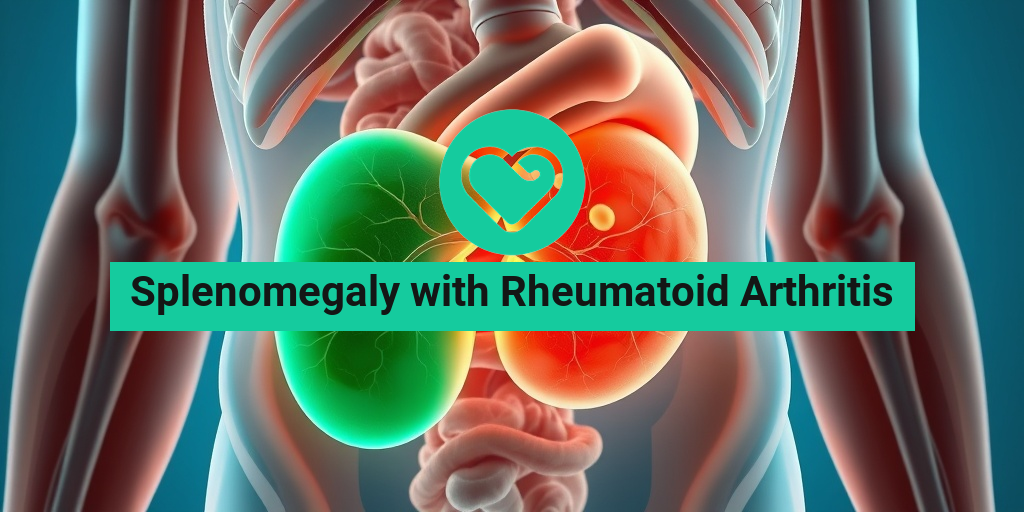
What Is Splenomegaly?
Splenomegaly refers to the enlargement of the spleen, an organ located in the upper left part of the abdomen. The spleen plays a crucial role in filtering blood, recycling iron, and supporting the immune system. When the spleen becomes enlarged, it can indicate various underlying health issues, ranging from infections to blood disorders.
Causes of Splenomegaly
There are several potential causes of splenomegaly, including:
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections can lead to spleen enlargement. Common culprits include mononucleosis and malaria.
- Liver diseases: Conditions like cirrhosis or hepatitis can cause blood flow issues, leading to splenomegaly.
- Blood disorders: Conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, or hemolytic anemia can result in an enlarged spleen.
- Inflammatory diseases: Autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, can also contribute to spleen enlargement.
Understanding the underlying cause of splenomegaly is essential for effective treatment and management. If you suspect you have an enlarged spleen, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Overview
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is primarily due to wear and tear, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary widely among individuals but often include:
- Joint pain and swelling: Typically affects joints on both sides of the body, such as the hands, wrists, and knees.
- Morning stiffness: Many people with RA experience stiffness in the morning that can last for several hours.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is a common complaint among those with RA.
- Fever: Some individuals may experience low-grade fevers during flare-ups.
How Rheumatoid Arthritis Affects the Body
RA is not just a joint disease; it can have systemic effects on the body. Inflammation can lead to complications in various organs, including the heart, lungs, and even the spleen. This is where the connection between splenomegaly and rheumatoid arthritis becomes significant.
Splenomegaly with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may experience splenomegaly due to the chronic inflammation associated with the disease. The immune system’s persistent activation can lead to an enlarged spleen as it works overtime to filter out abnormal cells and manage inflammation.
Moreover, some patients may also experience leukopenia (a decrease in white blood cells) alongside splenomegaly. This condition can further complicate the management of rheumatoid arthritis, as a weakened immune system can increase susceptibility to infections.
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Enlarged Spleen?
While rheumatoid arthritis does not directly cause splenomegaly, the inflammatory processes associated with the disease can lead to spleen enlargement. If you are experiencing symptoms of splenomegaly, such as abdominal discomfort or a feeling of fullness, it is crucial to discuss these with your healthcare provider.
Managing Splenomegaly in RA Patients
Management of splenomegaly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis typically involves addressing the underlying inflammation. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics can help reduce inflammation and manage RA symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can support overall health.
- Regular monitoring: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help track the progression of both RA and splenomegaly.
For more information on managing rheumatoid arthritis and its complications, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between splenomegaly and rheumatoid arthritis is essential for effective management of both conditions. If you have concerns about your health, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance. 🌟

Symptoms of Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly, or an enlarged spleen, can often go unnoticed until it becomes significant enough to cause discomfort or other health issues. When associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the symptoms may vary, and understanding them is crucial for effective management. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
1. Abdominal Discomfort
One of the most common symptoms of splenomegaly is a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the left upper abdomen. This sensation can be due to the spleen pressing against other organs, leading to a sense of pressure or bloating.
2. Pain in the Left Side
Individuals may experience pain or tenderness in the left side of the abdomen. This pain can range from mild to severe and may worsen with certain movements or activities.
3. Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic fatigue is a common symptom in those with RA, but when combined with splenomegaly, it can become more pronounced. The body’s efforts to manage inflammation and the enlarged spleen can lead to increased feelings of tiredness and weakness.
4. Frequent Infections
The spleen plays a vital role in the immune system, filtering blood and helping to fight infections. An enlarged spleen may not function optimally, leading to a higher susceptibility to infections. If you notice frequent illnesses, it may be worth discussing with your healthcare provider.
5. Anemia
Splenomegaly can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells. Symptoms of anemia include pale skin, shortness of breath, and dizziness. If you have RA and notice these symptoms, it’s essential to consult your doctor.
6. Leukopenia
In some cases, splenomegaly can cause leukopenia, which is a decrease in white blood cells. This condition can further compromise your immune system, making it crucial to monitor your blood counts regularly.
Causes of Splenomegaly in RA
Understanding the causes of splenomegaly in the context of rheumatoid arthritis is essential for effective treatment and management. Here are some of the primary factors that contribute to this condition:
1. Inflammatory Response
Rheumatoid arthritis is primarily an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation. This inflammation can extend beyond the joints, affecting various organs, including the spleen. The body’s immune response can lead to swelling and enlargement of the spleen as it works to filter out damaged cells and pathogens.
2. Medications
Certain medications used to treat RA, such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and corticosteroids, can impact spleen size. While these medications are essential for managing RA, they can sometimes lead to side effects that include splenomegaly.
3. Hematological Disorders
Patients with RA may also develop hematological disorders, such as anemia or leukopenia, which can contribute to splenomegaly. The spleen may enlarge as it attempts to compensate for the decreased blood cell counts, leading to further complications.
4. Infections
Individuals with RA are at a higher risk for infections due to their compromised immune systems. Infections can lead to splenomegaly as the spleen works to fight off pathogens. Conditions like splenomegaly with rheumatoid arthritis and leukopenia can arise when the body is overwhelmed by infections.
5. Other Autoimmune Conditions
RA can sometimes coexist with other autoimmune diseases, which may also contribute to splenomegaly. Conditions such as lupus or Sjögren’s syndrome can exacerbate the inflammatory response, leading to an enlarged spleen.
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of splenomegaly in the context of rheumatoid arthritis is vital for effective management. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. 🩺
Diagnosing Splenomegaly
Diagnosing splenomegaly, or an enlarged spleen, particularly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), involves a comprehensive approach. The spleen plays a crucial role in the immune system, and its enlargement can indicate various underlying health issues. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically diagnose this condition.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing splenomegaly is a thorough clinical evaluation. During a physical examination, a doctor will:
- Palpate the abdomen to check for any enlargement of the spleen.
- Assess for any associated symptoms such as pain in the left upper abdomen, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss.
- Review the patient’s medical history, focusing on any history of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Imaging Studies
If splenomegaly is suspected, imaging studies are often the next step. Common imaging techniques include:
- Ultrasound: This is a non-invasive method that uses sound waves to create images of the spleen, helping to determine its size and any abnormalities.
- CT Scan: A computed tomography scan provides detailed cross-sectional images of the spleen and surrounding organs, offering more insight into potential causes of enlargement.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging may be used in certain cases to provide additional information about the spleen’s structure.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are essential in diagnosing the underlying causes of splenomegaly, especially in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. These tests may include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test can reveal abnormalities such as leukopenia (low white blood cell count), which is often associated with RA.
- Liver Function Tests: These tests help assess the liver’s health, as liver diseases can also lead to splenomegaly.
- Autoimmune Panels: Specific tests can help determine the presence of autoimmune markers that may indicate rheumatoid arthritis or other related conditions.
In summary, diagnosing splenomegaly in the context of rheumatoid arthritis requires a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Treatment Options for Splenomegaly
Once diagnosed, the treatment of splenomegaly associated with rheumatoid arthritis focuses on addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms. Here are some common treatment options:
Medications
For patients with rheumatoid arthritis, managing the underlying autoimmune condition is key. Treatment options may include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with RA.
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): Medications like methotrexate can slow the progression of RA and potentially reduce splenomegaly.
- Biologics: Targeted therapies that specifically address the immune response can be effective for patients who do not respond to traditional DMARDs.
Monitoring and Lifestyle Changes
In some cases, if splenomegaly is mild and not causing significant symptoms, a doctor may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular monitoring through follow-up appointments and imaging studies can help track any changes. Additionally, lifestyle changes can support overall health:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support immune function.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity can help improve overall well-being and manage RA symptoms.
- Avoiding Alcohol: Limiting alcohol intake can reduce stress on the liver and spleen.
Surgical Options
In rare cases where splenomegaly is severe and causing complications, surgical intervention may be necessary. A splenectomy, or surgical removal of the spleen, may be considered. However, this is typically a last resort due to the spleen’s important role in the immune system.
In conclusion, treating splenomegaly in the context of rheumatoid arthritis involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on managing the underlying condition, monitoring symptoms, and making lifestyle adjustments. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized treatment options. 🌟

Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints but can also have systemic effects, including splenomegaly (enlargement of the spleen). Managing RA effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Understanding how RA interacts with other conditions, such as splenomegaly, is crucial for effective management.
Understanding the Connection Between RA and Splenomegaly
Many individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may wonder, “Does rheumatoid arthritis cause an enlarged spleen?” The answer is not straightforward. While RA itself does not directly cause splenomegaly, the inflammation associated with RA can lead to various complications, including splenic enlargement. This can occur due to the body’s immune response and the medications used to treat RA.
Medications for Managing RA
Effective management of rheumatoid arthritis often involves a combination of medications. Here are some common types:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Medications like methotrexate can slow disease progression.
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: These can quickly reduce inflammation but are used cautiously due to potential side effects.
It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best medication regimen, especially if splenomegaly is present. Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor liver function and blood cell counts, as RA and its treatments can affect these parameters.
Regular Monitoring and Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a rheumatologist are vital for managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. During these visits, your doctor will assess your symptoms, evaluate the effectiveness of your treatment plan, and monitor for any complications, including leukopenia (low white blood cell count), which can occur alongside splenomegaly in some RA patients.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatment, making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve the quality of life for those with rheumatoid arthritis. Here are some effective strategies:
Dietary Adjustments
A well-balanced diet can help manage inflammation and support overall health. Consider incorporating the following:
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation.
- Fruits and Vegetables: A variety of colorful fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice and quinoa can help maintain energy levels and support digestive health.
Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day to help your body function optimally. 🥤
Physical Activity
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining joint function and overall health. Low-impact activities such as:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Yoga
can be particularly beneficial. These activities help improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce stiffness. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have splenomegaly or other complications.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine can be beneficial. Consider:
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help reduce stress and improve mental clarity.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: These can help calm the mind and body.
- Gentle Stretching: Incorporating stretching into your daily routine can help alleviate tension.
Finding activities that bring you joy, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones, can also contribute to better emotional health. 😊
In conclusion, managing rheumatoid arthritis, especially when accompanied by splenomegaly, requires a multifaceted approach. By combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes and home remedies, individuals can improve their quality of life and manage their symptoms more effectively.

Frequently Asked Questions about Splenomegaly with Rheumatoid Arthritis
What is splenomegaly and how is it related to rheumatoid arthritis?
Splenomegaly refers to the enlargement of the spleen, which can occur in various medical conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In patients with RA, the immune system is overactive, which can lead to inflammation and enlargement of the spleen as it works to filter out abnormal cells and produce immune responses.
Can rheumatoid arthritis cause an enlarged spleen?
Yes, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to an enlarged spleen. The chronic inflammation associated with RA may stimulate the spleen to increase in size as it plays a role in the immune response. This condition is often referred to as splenomegaly with rheumatoid arthritis.
How does rheumatoid arthritis affect the spleen?
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect the spleen by causing it to become enlarged due to increased immune activity. This can lead to symptoms such as discomfort or pain in the left upper abdomen, fatigue, and a feeling of fullness. Additionally, the spleen may become more active in filtering blood and producing immune cells, which can impact overall health.
What are the symptoms of splenomegaly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
- Pain or discomfort in the left upper abdomen
- Feeling of fullness or pressure
- Fatigue
- Frequent infections
- Leukopenia (low white blood cell count)
Can rheumatoid arthritis lead to spleen problems?
Yes, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to various spleen problems, including splenomegaly and potential complications such as hypersplenism, where the spleen becomes overactive and removes blood cells at an increased rate. This can result in conditions like anemia or leukopenia.
What should I do if I suspect I have splenomegaly with rheumatoid arthritis?
If you suspect you have splenomegaly with rheumatoid arthritis, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They may perform physical examinations, imaging tests, or blood tests to assess your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Is there a treatment for splenomegaly associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
Treatment for splenomegaly associated with rheumatoid arthritis typically focuses on managing the underlying RA. This may include medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), corticosteroids, or biologics. In some cases, if the spleen is severely enlarged or causing significant symptoms, surgical intervention may be considered.
Can lifestyle changes help manage splenomegaly with rheumatoid arthritis?
While lifestyle changes alone may not directly reduce splenomegaly, they can help manage rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can contribute to overall health and potentially reduce inflammation.