Understanding Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants, often referred to as blood thinners, are medications that help prevent blood clots from forming or growing larger. They are crucial for individuals at risk of developing clots, which can lead to serious health issues such as strokes, heart attacks, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Understanding how these medications work and the safety tips when taking anticoagulants is essential for anyone prescribed these drugs.
How Anticoagulants Work
Anticoagulants function by interfering with the body’s natural clotting process. They do not dissolve existing clots but rather prevent new ones from forming. This is achieved by inhibiting certain proteins in the blood that are necessary for clotting. The effectiveness of anticoagulants can vary based on the type of medication, dosage, and individual patient factors.
Why Are Anticoagulants Prescribed?
Doctors prescribe anticoagulants for various reasons, including:
- Preventing Stroke: Particularly in patients with atrial fibrillation, a condition that increases the risk of stroke.
- Treating DVT: To prevent clots from traveling to the lungs, which can cause a pulmonary embolism.
- Post-Surgery: To reduce the risk of clot formation after certain surgeries, especially orthopedic procedures.
While anticoagulants are beneficial, they also come with risks, making it vital to follow safety tips when taking anticoagulants to minimize complications.
Common Anticoagulants Used
There are several types of anticoagulants, each with its specific uses and mechanisms. Here are some of the most commonly prescribed anticoagulants:
1. Warfarin (Coumadin)
Warfarin has been a staple in anticoagulation therapy for decades. It works by inhibiting vitamin K, which is essential for clotting factor production. Patients on warfarin require regular blood tests to monitor their INR (International Normalized Ratio) levels to ensure they remain within a safe range.
2. Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)
DOACs, including apixaban (Eliquis), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), and dabigatran (Pradaxa), have gained popularity due to their ease of use. Unlike warfarin, they do not require frequent blood monitoring and have fewer dietary restrictions. However, they still carry risks, and patients should be aware of potential interactions with other medications.
3. Heparin
Heparin is often used in hospital settings for immediate anticoagulation. It can be administered intravenously or via subcutaneous injection. Patients may transition to oral anticoagulants after their hospital stay.
4. Low Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWH)
LMWHs, such as enoxaparin (Lovenox), are commonly used for DVT prevention and treatment. They are typically given as an injection and have a more predictable response than unfractionated heparin, allowing for less frequent monitoring.
Safety Tips When Taking Anticoagulants
Taking anticoagulants requires careful management to ensure safety and effectiveness. Here are some essential tips to consider:
- Follow Prescriptions: Always take your medication exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Regular Monitoring: If you are on warfarin, ensure you attend all scheduled INR tests to monitor your blood’s clotting ability.
- Be Aware of Interactions: Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and over-the-counter drugs you are taking, as many can interact with anticoagulants.
- Watch for Signs of Bleeding: Be vigilant for unusual bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, or blood in urine or stool, and report these to your doctor immediately.
- Maintain a Consistent Diet: If you are on warfarin, keep your vitamin K intake consistent, as fluctuations can affect your INR levels.
- Stay Active but Cautious: Engage in regular physical activity, but avoid high-risk activities that could lead to injury.
For more detailed information and personalized advice, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, understanding anticoagulants and adhering to safety tips when taking anticoagulants can significantly reduce the risks associated with these medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider for tailored advice and support. Your health is worth it! 💊❤️
Why Anticoagulants Are Prescribed
Anticoagulants, commonly referred to as blood thinners, are medications that play a crucial role in preventing blood clots. These clots can lead to serious health issues, including strokes, heart attacks, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Understanding why anticoagulants are prescribed is essential for anyone taking these medications.
Common Conditions Treated with Anticoagulants
Healthcare providers prescribe anticoagulants for various medical conditions, including:
- Atrial Fibrillation: This irregular heartbeat can increase the risk of blood clots forming in the heart.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, usually in the legs.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A serious condition where a blood clot travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow.
- Heart Valve Replacement: Patients with artificial heart valves are at a higher risk for clot formation.
- Post-Surgery: Anticoagulants may be prescribed after certain surgeries to prevent clotting.
By preventing the formation of clots, anticoagulants help reduce the risk of life-threatening complications. However, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely to ensure safe and effective use of these medications. 🩺
How Anticoagulants Work
Anticoagulants work by interfering with the body’s natural clotting process. They do not dissolve existing clots but rather prevent new ones from forming. There are several types of anticoagulants, including:
- Vitamin K Antagonists: Such as warfarin, which inhibit the action of vitamin K, essential for clotting.
- Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): These include medications like rivaroxaban and apixaban, which target specific clotting factors.
- Heparin: Often used in hospitals, it works quickly to prevent clotting.
Understanding how these medications function can help patients appreciate their importance in managing health conditions. 💊
Potential Side Effects
While anticoagulants are vital for preventing serious health issues, they can also come with potential side effects. Being aware of these can help you recognize any adverse reactions early and seek medical advice when necessary.
Common Side Effects
Some of the most common side effects associated with anticoagulants include:
- Bleeding: This is the most significant risk. Patients may experience unusual bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, or bleeding gums.
- Nausea: Some individuals may feel nauseous or experience gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness can occur, especially if bleeding is present.
It’s crucial to monitor for these side effects and report them to your healthcare provider promptly. ⚠️
Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, anticoagulants can lead to more severe complications, such as:
- Severe Bleeding: This can occur in the brain, stomach, or other vital organs, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Interactions with Other Medications: Anticoagulants can interact with various medications, increasing the risk of side effects.
Always inform your healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements you are taking to avoid dangerous interactions. 🛑
Managing Side Effects
To minimize the risk of side effects while taking anticoagulants, consider the following tips:
- Regular Monitoring: Keep up with regular blood tests as recommended by your doctor to ensure your medication levels are safe.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help maintain overall health and reduce side effects.
- Report Symptoms: If you notice any unusual symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
By staying informed and proactive, you can manage your health effectively while on anticoagulants. Remember, safety is paramount when taking these medications! 🛡️
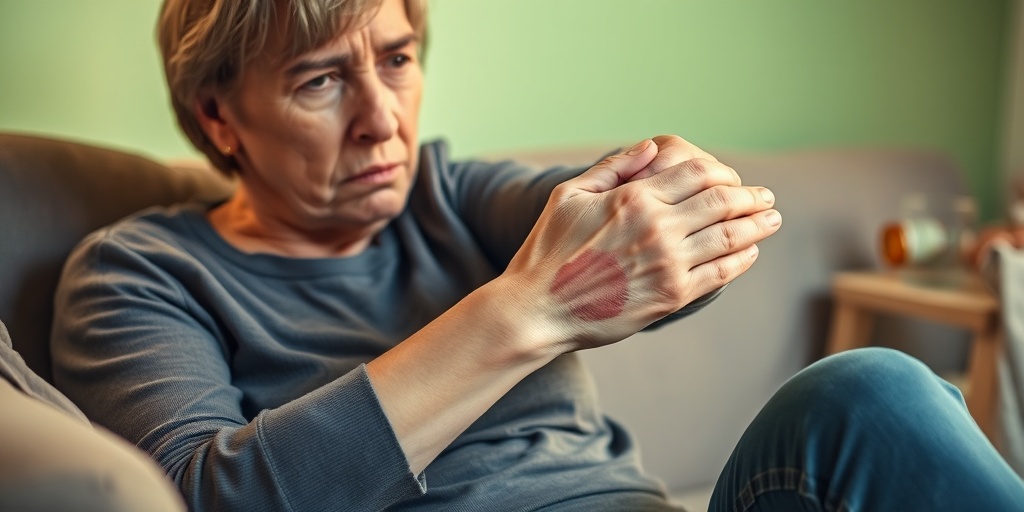

Safety Precautions to Follow
Taking anticoagulants can be a vital part of managing certain health conditions, but it also comes with its own set of risks. Understanding safety tips when taking anticoagulants is crucial to minimize complications and ensure effective treatment. Here are some essential precautions to keep in mind:
1. Regular Monitoring
One of the most important safety tips is to have regular blood tests to monitor your coagulation levels. This is especially true for medications like warfarin, where the International Normalized Ratio (INR) needs to be checked frequently. Keeping your healthcare provider informed about any changes in your health can help adjust your dosage accordingly.
2. Be Aware of Drug Interactions
Anticoagulants can interact with various medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new medication. Some common interactions include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Certain antibiotics
- Herbal supplements like ginkgo biloba
3. Avoid High-Risk Activities
Engaging in activities that increase your risk of injury can be dangerous while on anticoagulants. Activities such as contact sports, climbing, or even vigorous exercise can lead to serious bleeding. Opt for low-impact exercises like walking or swimming to stay active without putting yourself at risk.
4. Inform Healthcare Providers
Always inform any healthcare provider that you are taking anticoagulants before undergoing any procedures, including dental work. This information is crucial for ensuring your safety during treatments.
5. Recognize Signs of Bleeding
Being aware of the signs of bleeding is essential. If you notice any unusual bruising, blood in your urine or stool, or prolonged bleeding from cuts, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Early detection can prevent more serious complications.
Dietary Considerations
Your diet plays a significant role in how anticoagulants work in your body. Making informed dietary choices can enhance the effectiveness of your treatment while minimizing risks. Here are some dietary considerations to keep in mind:
1. Monitor Vitamin K Intake
Vitamin K is crucial for blood clotting, and its levels can significantly affect how anticoagulants work. Foods high in vitamin K include:
- Leafy greens (kale, spinach, broccoli)
- Brussels sprouts
- Green tea
While you don’t need to eliminate these foods entirely, maintaining a consistent intake is key. Sudden increases or decreases in vitamin K can alter your medication’s effectiveness.
2. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and can help your body process medications more effectively. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you are taking medications that can cause dehydration.
3. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can interfere with the effectiveness of anticoagulants and increase the risk of bleeding. It’s advisable to limit your alcohol intake or discuss with your healthcare provider what is safe for you. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation.
4. Be Cautious with Supplements
Many dietary supplements can affect blood clotting. For instance, fish oil and garlic supplements may increase bleeding risk. Always consult your healthcare provider before adding any new supplements to your routine.
5. Balanced Diet for Overall Health
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support your overall health while on anticoagulants. A healthy diet can help manage weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, all of which are important for individuals taking these medications.
By following these safety tips when taking anticoagulants and being mindful of your dietary choices, you can significantly reduce risks and enhance the effectiveness of your treatment. Remember, always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your specific health needs. 🩺🍏

Monitoring and Follow-Up
When you’re prescribed anticoagulants, regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are crucial to ensure your safety and the effectiveness of your treatment. These medications, which help prevent blood clots, require careful management to avoid complications. Here’s what you need to know about monitoring your health while on anticoagulants.
Importance of Regular Blood Tests
One of the primary ways to monitor your anticoagulant therapy is through regular blood tests. These tests help determine how well your blood is clotting and whether your medication dosage needs adjustment. Depending on the type of anticoagulant you are taking, your healthcare provider may recommend:
- INR Testing: For those on warfarin, the International Normalized Ratio (INR) is a critical measure. It indicates how long it takes for your blood to clot compared to a normal range.
- Anti-Xa Testing: If you are on direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), your doctor may use anti-Xa tests to monitor drug levels and effectiveness.
Regular blood tests can help prevent serious complications, such as excessive bleeding or clotting. Make sure to keep a schedule for these tests and communicate any changes in your health to your healthcare provider.
Recognizing Signs of Complications
While on anticoagulants, it’s essential to be vigilant about any signs of complications. Some symptoms to watch for include:
- Unusual Bruising: If you notice bruises that appear without any apparent cause, it could indicate that your blood is not clotting properly.
- Prolonged Bleeding: If you experience bleeding that lasts longer than usual, such as from a cut or during menstruation, contact your doctor.
- Signs of Clots: Symptoms like swelling, pain, or redness in your legs could indicate a deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Being aware of these signs can help you seek timely medical attention, ensuring your safety while on anticoagulants. 🩺
Medication Management
Managing your medications is another critical aspect of monitoring your health. Here are some tips to help you stay on track:
- Keep a Medication Log: Document your medication schedule, dosages, and any side effects you experience. This log can be invaluable during follow-up appointments.
- Communicate with Your Healthcare Provider: Always inform your doctor about any other medications or supplements you are taking, as they can interact with anticoagulants.
- Adhere to Your Schedule: Take your medications exactly as prescribed. Missing doses can increase your risk of clotting or bleeding.
By staying organized and informed, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with anticoagulant therapy.
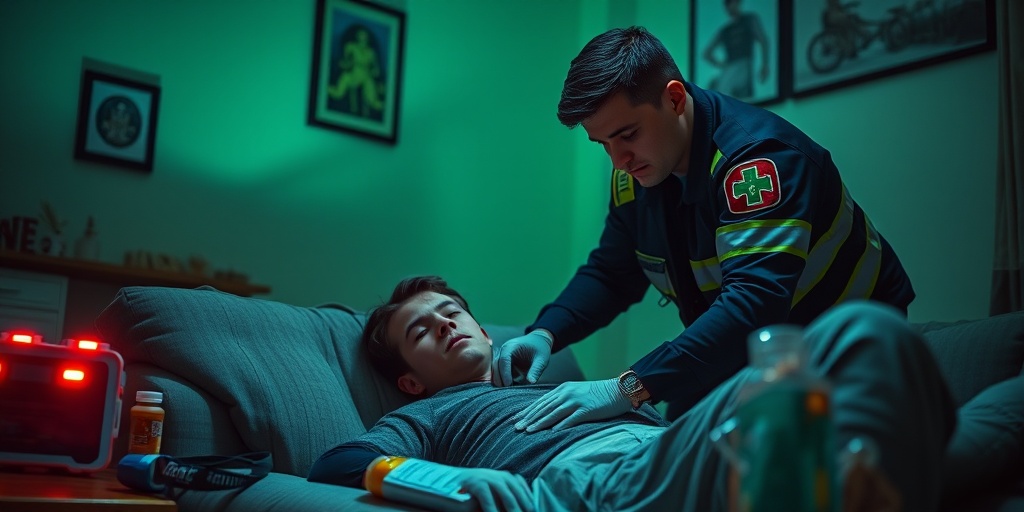
Emergency Situations and Anticoagulants
Understanding how to handle emergency situations while on anticoagulants is vital for your safety. Whether it’s a minor injury or a more serious health issue, knowing what to do can make all the difference.
What to Do in Case of Bleeding
One of the most significant risks associated with anticoagulants is bleeding. If you experience any of the following, it’s essential to act quickly:
- Minor Cuts: Apply direct pressure to the wound for at least 10 minutes. If bleeding doesn’t stop, seek medical attention.
- Severe Bleeding: If you have a deep cut or are bleeding heavily, call emergency services immediately. Do not hesitate!
Always carry a medical alert card or wear a bracelet that indicates you are on anticoagulants. This information can be crucial for first responders in an emergency. 🚑
Recognizing Signs of a Stroke or Heart Attack
Anticoagulants can help prevent strokes and heart attacks, but they can also complicate these emergencies. Be aware of the signs:
- Stroke Symptoms: Look for sudden numbness, confusion, difficulty speaking, or loss of balance. Remember the acronym FAST: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties, Time to call emergency services.
- Heart Attack Symptoms: Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, or jaw. Don’t ignore these signs!
In both cases, time is of the essence. Quick action can save lives, so don’t hesitate to seek help if you suspect a serious issue.
Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies can help you feel more secure while on anticoagulants. Here are some steps to consider:
- Emergency Contacts: Keep a list of emergency contacts, including your healthcare provider, family members, and friends who can assist you.
- First Aid Kit: Have a well-stocked first aid kit at home and in your car, including items like bandages, antiseptic wipes, and gauze.
- Know Your Medications: Be familiar with your anticoagulant, including its effects and potential interactions with other medications.
By taking these precautions, you can navigate emergencies more confidently while on anticoagulants. Stay safe and informed! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are anticoagulants and why are they prescribed?
Anticoagulants are medications that help prevent blood clots from forming. They are often prescribed for individuals with conditions such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or those who have undergone certain surgeries. Safety tips when taking anticoagulants are crucial to ensure effective treatment and minimize risks.
What are some safety tips when taking anticoagulants?
- Always take your medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Be aware of potential interactions with other medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Maintain a consistent diet, especially regarding vitamin K intake, as it can affect how anticoagulants work.
- Regularly monitor your blood levels as advised by your doctor.
- Report any unusual bleeding or bruising to your healthcare provider immediately.
Can I take over-the-counter medications while on anticoagulants?
Some over-the-counter medications can interact with anticoagulants, increasing the risk of bleeding. Always consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking any new medications, including pain relievers and cold medications. 💊
What should I do if I miss a dose of my anticoagulant?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your regular schedule. Never double up on doses. If you have concerns, contact your healthcare provider for guidance.
Are there any lifestyle changes I should consider while taking anticoagulants?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes can enhance your safety while on anticoagulants. These include:
- Engaging in regular, moderate exercise to improve circulation.
- Avoiding activities that increase the risk of injury or falls.
- Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet.
- Limiting alcohol consumption, as it can increase bleeding risk.
How can I manage potential side effects of anticoagulants?
Common side effects may include bleeding, bruising, or gastrointestinal issues. To manage these:
- Keep a close watch on any signs of excessive bleeding.
- Discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider, who may adjust your dosage or suggest alternatives.
- Stay informed about your condition and treatment plan.
When should I seek medical attention while on anticoagulants?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe or uncontrollable bleeding.
- Signs of a stroke, such as sudden numbness or weakness.
- Severe headache or dizziness.
Being proactive about your health is essential when taking anticoagulants. Always prioritize safety and communicate openly with your healthcare team. 🩺




