What Is Pilonidal Disease?
Pilonidal disease is a common yet often misunderstood condition that primarily affects the area at the base of the spine, known as the natal cleft. This condition occurs when hair follicles become clogged with hair, skin debris, and bacteria, leading to the formation of cysts or abscesses. While it can affect anyone, it is most frequently seen in young adults, particularly males, and those who are overweight or have a sedentary lifestyle.
The term “pilonidal” comes from the Latin words “pilus,” meaning hair, and “nidus,” meaning nest. This aptly describes the condition, as it often involves hair trapped beneath the skin. If left untreated, pilonidal disease can lead to recurrent infections and significant discomfort.
Causes of Pilonidal Disease
The exact cause of pilonidal disease is not entirely understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Hair Growth: Excessive hair growth in the natal cleft can lead to the formation of cysts.
- Friction and Pressure: Prolonged sitting or friction in the area can irritate the skin and contribute to the condition.
- Genetics: A family history of pilonidal disease may increase the likelihood of developing it.
- Obesity: Being overweight can create additional pressure on the area, making it more susceptible to cyst formation.
Understanding these causes can help in preventing the condition and seeking timely treatment if symptoms arise.
Pilonidal Disease Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of pilonidal disease is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can vary in severity and may include:
- Pain and Discomfort: The most common symptom is pain in the lower back or tailbone area, especially when sitting.
- Swelling: The affected area may become swollen and tender to the touch.
- Redness and Inflammation: The skin around the cyst may appear red and inflamed.
- Drainage: In some cases, the cyst may drain pus or blood, which can lead to foul-smelling discharge.
- Recurring Infections: Individuals may experience repeated episodes of infection, leading to chronic discomfort.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While pilonidal disease can sometimes resolve on its own, it is important to seek medical attention if:
- The pain becomes severe or persistent.
- You notice signs of infection, such as fever or increased redness.
- There is significant drainage from the cyst.
Healthcare providers may recommend various treatment options, ranging from conservative measures like warm compresses and antibiotics to surgical interventions for more severe cases.
For more information on pilonidal disease, including treatment options and management strategies, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, understanding pilonidal disease and its symptoms is vital for effective management. By being aware of the signs and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can navigate this condition with greater ease and comfort. 🌟
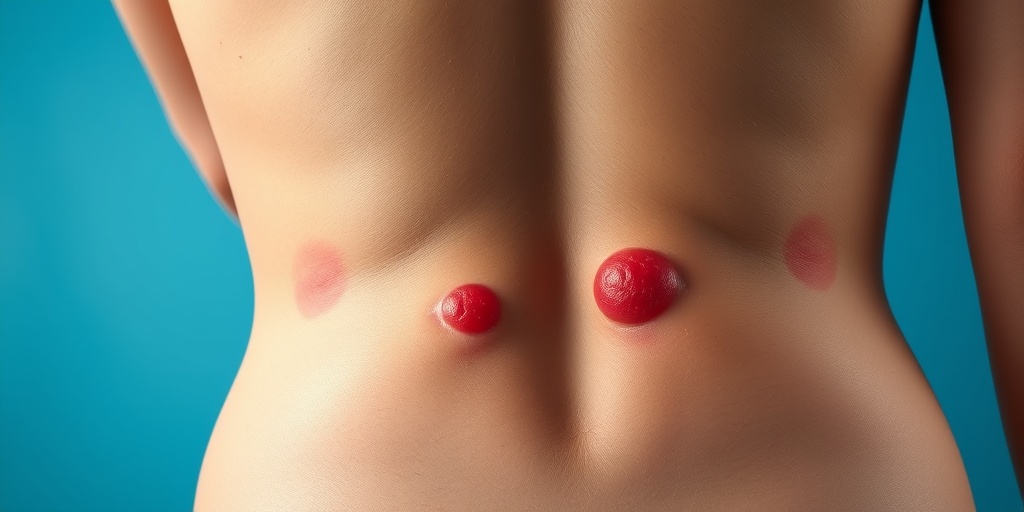
Pilonidal Disease Causes
Pilonidal disease is a condition that primarily affects the area at the base of the spine, known as the natal cleft. Understanding the causes of pilonidal disease is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. While the exact cause remains somewhat elusive, several factors contribute to its development.
Hair Follicle Involvement
One of the primary causes of pilonidal disease is the presence of hair follicles in the natal cleft. When hair follicles become clogged with hair, skin debris, and bacteria, they can form a cyst or abscess. This blockage can lead to inflammation and infection, resulting in the painful symptoms associated with pilonidal disease.
Trauma and Friction
Another significant factor is trauma or friction in the area. Activities that involve prolonged sitting, such as driving or cycling, can irritate the skin and hair follicles, increasing the risk of developing pilonidal disease. This is particularly common in individuals who have a sedentary lifestyle or engage in activities that put pressure on the lower back.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics may also play a role in the development of pilonidal disease. Some individuals may inherit a tendency to develop this condition due to the structure of their hair follicles or skin. If you have a family history of pilonidal disease, you may be at a higher risk.
Obesity and Poor Hygiene
Obesity is another contributing factor. Excess weight can create additional folds in the skin, making it easier for hair and debris to become trapped. Additionally, poor hygiene practices can exacerbate the problem, as inadequate cleaning can lead to the accumulation of bacteria and dead skin cells in the natal cleft.
Pilonidal Disease Risk Factors
Identifying the risk factors associated with pilonidal disease can help individuals take proactive measures to reduce their chances of developing this condition. Here are some key risk factors to consider:
Age and Gender
Pilonidal disease is most commonly seen in young adults, particularly those between the ages of 15 and 30. Additionally, it is more prevalent in males than females, which may be attributed to differences in hair growth patterns and skin structure.
Occupation and Lifestyle
Certain occupations and lifestyles can increase the risk of pilonidal disease. Jobs that require long periods of sitting, such as truck drivers or office workers, can contribute to the development of this condition. Similarly, athletes who engage in cycling or other activities that put pressure on the lower back may also be at higher risk.
Personal Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good personal hygiene is essential in preventing pilonidal disease. Individuals who neglect regular cleaning of the natal cleft area may find themselves more susceptible to infections and cyst formation. Regular bathing and proper grooming can help minimize the risk.
Body Hair and Skin Type
Individuals with thick or coarse body hair may be more prone to pilonidal disease. The hair can easily become trapped in the skin, leading to cyst formation. Additionally, those with oily skin may also be at a higher risk due to increased clogging of hair follicles.
Obesity
As mentioned earlier, obesity is a significant risk factor. The excess skin folds can create an environment conducive to the development of pilonidal disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help mitigate this risk.
In summary, understanding the causes and risk factors associated with pilonidal disease is essential for prevention and early intervention. By being aware of these factors, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and seek timely treatment if symptoms arise. 🩺✨

Pilonidal Disease Diagnosis
Pilonidal disease is a condition that affects the skin and tissue at the top of the buttocks, often characterized by the formation of cysts or abscesses. Diagnosing this condition can sometimes be straightforward, but it often requires a thorough examination and understanding of the patient’s symptoms.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing pilonidal disease is recognizing its symptoms. Common signs include:
- Pain and Discomfort: Patients often experience pain in the lower back or buttocks, especially when sitting.
- Swelling and Redness: The area may appear swollen and red, indicating inflammation.
- Drainage: In some cases, pus or blood may drain from the cyst, which can be a sign of infection.
- Foul Odor: If the cyst becomes infected, it may emit an unpleasant smell.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will typically conduct a physical examination to assess the area for any signs of cysts or abscesses. During this examination, they will look for:
- Presence of Sinus Tracts: These are small channels that may develop under the skin, leading to the cyst.
- Size and Depth of Cysts: The size and depth can help determine the severity of the condition.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be necessary to evaluate the extent of the disease, especially if there are concerns about deeper tissue involvement. These tests can help visualize:
- Underlying Structures: To rule out any complications or associated conditions.
- Multiple Cysts: To determine if there are more than one cyst present.
Medical History
Understanding a patient’s medical history is crucial in diagnosing pilonidal disease. Factors such as:
- Previous Episodes: Recurring issues may indicate a chronic condition.
- Family History: A family history of pilonidal disease can increase the likelihood of developing it.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the next step is to explore treatment options that can effectively manage the condition.
Pilonidal Disease Treatment Options
Treating pilonidal disease can vary based on the severity of the condition and the presence of any complications. Here are the most common treatment options available:
Conservative Treatments
For mild cases, conservative treatments may be sufficient. These include:
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses can help reduce pain and promote drainage of any cysts.
- Antibiotics: If there is an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear it up.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
Surgical Options
For more severe cases or recurrent pilonidal disease, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgical procedures include:
- Incision and Drainage: This is often the first step for an abscess, where the cyst is opened to allow drainage.
- Excision: Involves removing the cyst and surrounding tissue to prevent recurrence.
- Flap Surgery: This technique involves closing the wound with a flap of nearby tissue, which can reduce the chance of recurrence.
Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, proper care is essential for healing. Patients should:
- Keep the Area Clean: Regular cleaning can prevent infections.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor healing.
- Avoid Sitting for Long Periods: This can help reduce pressure on the surgical site.
Long-Term Management
For individuals prone to pilonidal disease, long-term management strategies may include:
- Maintaining Hygiene: Keeping the area clean and dry can help prevent recurrence.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of developing pilonidal disease.
- Regular Check-Ups: Staying in touch with a healthcare provider can help catch any issues early.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for pilonidal disease is crucial for effective management and recovery. If you suspect you have this condition, consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options. 🩺

Pilonidal Disease Home Care
Pilonidal disease can be a painful and uncomfortable condition, often affecting the area at the base of the spine. If you or someone you know is dealing with this issue, understanding how to manage it at home can significantly improve comfort and promote healing. Here are some effective home care strategies for pilonidal disease.
Understanding Pilonidal Disease
Pilonidal disease occurs when hair and skin debris become trapped in a small pit or cyst near the tailbone, leading to inflammation and infection. Symptoms may include:
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Swelling and redness around the cyst
- Drainage of pus or blood from the cyst
- Foul odor from the infected area
Home Care Strategies
Managing pilonidal disease at home involves a combination of hygiene practices, pain management, and monitoring for complications. Here are some tips:
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
Keeping the area clean is crucial. Here’s how:
- Daily Cleaning: Gently wash the area with mild soap and water. Avoid harsh soaps that can irritate the skin.
- Dry Thoroughly: After washing, ensure the area is completely dry to prevent moisture buildup, which can worsen the condition.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress can help reduce pain and promote drainage if there is an abscess.
2. Pain Management
Managing pain is essential for comfort. Consider the following:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Positioning: Sit on soft surfaces and avoid prolonged sitting to minimize pressure on the affected area.
3. Monitor for Complications
Keep an eye on the symptoms. If you notice any of the following, seek medical attention:
- Increased redness or swelling around the cyst
- Fever or chills
- Increased drainage or foul odor
Pilonidal Disease Prevention Tips
Preventing pilonidal disease is often possible with some lifestyle adjustments and awareness of risk factors. Here are some effective prevention tips to keep in mind:
Understanding Risk Factors
Before diving into prevention strategies, it’s essential to understand the risk factors associated with pilonidal disease. These include:
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase pressure on the tailbone area.
- Prolonged Sitting: Occupations or activities that require long periods of sitting can contribute to the development of pilonidal disease.
- Hair Type: Individuals with thick or coarse hair may be more prone to developing this condition.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Here are some practical tips to help prevent pilonidal disease:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Keeping your weight in check can reduce pressure on the tailbone area. Consider a balanced diet and regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight. 🍏🏃♂️
2. Practice Good Hygiene
Regularly cleaning the area around the tailbone can help prevent hair and debris buildup. Shower daily and consider using a gentle exfoliating scrub to keep the skin smooth.
3. Avoid Prolonged Sitting
If your job requires long hours of sitting, take regular breaks to stand up and move around. Consider using a cushion designed to relieve pressure on the tailbone.
4. Hair Removal Techniques
For those prone to pilonidal disease, consider hair removal methods such as:
- Shaving: Regularly shaving the area can help reduce hair buildup.
- Laser Hair Removal: This long-term solution can significantly reduce hair growth in the area.
By implementing these home care strategies and prevention tips, you can effectively manage and reduce the risk of pilonidal disease. Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment. 🩺✨

Frequently Asked Questions about Pilonidal Disease
What is Pilonidal Disease?
Pilonidal disease is a condition that occurs when hair and skin debris become trapped in a small pocket or cyst near the tailbone. This can lead to inflammation, infection, and the formation of a painful abscess.
What are the common symptoms of Pilonidal Disease?
- Pain and discomfort near the tailbone
- Swelling in the affected area
- Redness and irritation
- Drainage of pus or blood
- Foul odor from the cyst
What causes Pilonidal Disease?
The exact cause of pilonidal disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to:
- Hair growth in the area
- Friction from sitting for long periods
- Obesity and lack of physical activity
- Genetic factors
How is Pilonidal Disease treated?
Treatment options for pilonidal disease may include:
- Antibiotics for infection
- Drainage of abscesses
- Surgery to remove the cyst
- Wound care and hygiene practices
What is the cost of Pilonidal Disease surgery?
The cost of surgery for pilonidal disease can vary widely based on factors such as location, the complexity of the procedure, and whether you have insurance. On average, it can range from $3,000 to $10,000.
How does Pilonidal Disease differ from a cyst?
Pilonidal disease specifically refers to the condition involving the cyst near the tailbone, while a cyst can occur in various parts of the body and may not necessarily be associated with hair follicles or infection.
Are there any pictures available for Pilonidal Disease?
Yes, there are many medical resources and websites that provide images of pilonidal disease to help individuals understand the condition better. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
What is the ICD-10 code for Pilonidal Disease?
The ICD-10 code for pilonidal disease is L05.9, which is used for billing and insurance purposes.
Can Pilonidal Disease be prevented?
While it may not be entirely preventable, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding prolonged sitting, and managing weight can help reduce the risk of developing pilonidal disease.
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience symptoms such as persistent pain, swelling, or drainage from the area near your tailbone, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.




