What is Oophorectomy?
Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of one or both ovaries in women. The ovaries are the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone. The procedure is usually performed to treat various medical conditions, including ovarian cancer, ovarian cysts, and endometriosis.
In some cases, oophorectomy may be performed as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer in women with a high risk of developing the disease, such as those with a family history of ovarian cancer or those who have a genetic mutation that increases their risk.
The procedure can be performed through open surgery, where a large incision is made in the abdomen, or through laparoscopic surgery, where several small incisions are made, and a camera and specialized instruments are used to remove the ovaries.
Oophorectomy can have significant effects on a woman’s reproductive and hormonal health. Removal of the ovaries can lead to menopause, even if the woman has not yet reached menopause naturally. This can cause symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
However, oophorectomy can also provide relief from symptoms such as pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, and infertility associated with certain medical conditions. It’s essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks of oophorectomy with a healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right option for individual circumstances.
Types of Oophorectomy
There are several types of oophorectomy, including:
Unilateral Oophorectomy
This type of oophorectomy involves the removal of one ovary. This procedure is usually performed when a problem is detected in one ovary, such as a tumor or cyst, and the other ovary is healthy.
Bilateral Oophorectomy
This type of oophorectomy involves the removal of both ovaries. This procedure is usually performed when both ovaries are affected by a medical condition, such as ovarian cancer, or when the risk of ovarian cancer is high.
Salpingo-Oophorectomy
This type of oophorectomy involves the removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This procedure is usually performed when there is a problem with the fallopian tubes, such as an ectopic pregnancy or a tumor.
Prophylactic Oophorectomy
This type of oophorectomy involves the removal of the ovaries as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer in women with a high risk of developing the disease.
It’s essential to discuss the type of oophorectomy that’s right for individual circumstances with a healthcare provider. They can help determine the best course of treatment based on the underlying medical condition and overall health.
If you’re considering oophorectomy or have questions about the procedure, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance and support throughout the process. Additionally, resources like Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) can provide evidence-based health answers and support to help you make informed decisions about your health. 💊
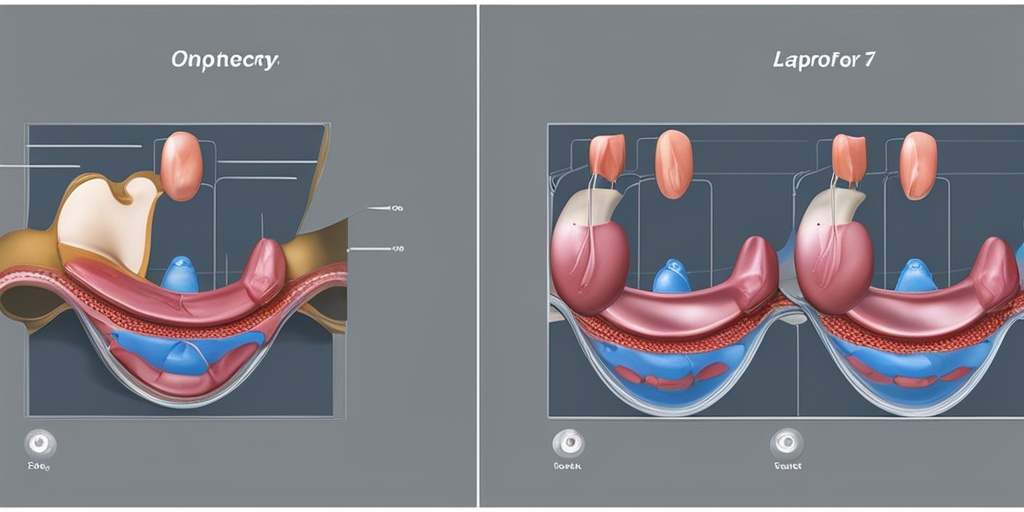
Why is Oophorectomy Performed?
Oophorectomy, the surgical removal of one or both ovaries, is a medical procedure performed to treat various gynecological conditions and cancers. The decision to undergo oophorectomy is often made after careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. So, why is oophorectomy performed?
Ovarian Cancer Treatment
Oophorectomy is often performed as a treatment for ovarian cancer. In this case, the surgery aims to remove the cancerous tumor and any affected ovarian tissue. The procedure can be performed as part of a larger treatment plan, which may include chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Reducing Cancer Risk
In some cases, oophorectomy may be performed as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer in women with a high genetic risk. This is often the case for women with a family history of ovarian cancer or those who have tested positive for genetic mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2.
Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain
Oophorectomy may also be performed to treat severe endometriosis, a condition in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, leading to pelvic pain and other symptoms. Removing the ovaries can help reduce the production of estrogen, which can contribute to the growth of endometrial tissue.
Other Conditions
In some cases, oophorectomy may be performed to treat other conditions, such as ovarian cysts or torsion, which can cause severe abdominal pain and other symptoms.
Oophorectomy Risks and Complications
While oophorectomy can be an effective treatment for various gynecological conditions, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure.
Immediate Risks
As with any surgical procedure, oophorectomy carries immediate risks, including:
- Bleeding and hemorrhage: Excessive bleeding during or after the procedure can lead to serious complications.
- Infection: Bacterial or viral infections can occur at the surgical site or elsewhere in the body.
- Adhesions: The formation of scar tissue can lead to bowel obstruction or other complications.
Long-term Complications
In addition to immediate risks, oophorectomy can also lead to long-term complications, including:
- Menopause symptoms: Removing the ovaries can induce menopause, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
- Hormonal imbalance: The removal of the ovaries can disrupt hormone levels, leading to a range of symptoms and potential health issues.
- Osteoporosis: The loss of estrogen production can increase the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures.
It’s essential to discuss the potential risks and complications of oophorectomy with your healthcare provider to determine if the procedure is right for you. 💊
Preparing for Oophorectomy Surgery
Are you scheduled to undergo an oophorectomy, a surgical procedure to remove one or both ovaries? 🤕 Preparing for the surgery can help reduce anxiety and ensure a smooth recovery. In this section, we’ll guide you through the essential steps to take before the operation.
Understanding Your Diagnosis
Before we dive into the preparation process, it’s crucial to understand why you need an oophorectomy. Your doctor may have recommended the surgery to treat conditions such as ovarian cancer, endometriosis, or ovarian cysts. Take the time to discuss your diagnosis with your healthcare provider and ask questions about the procedure.
Medications and Supplements
Your doctor may advise you to stop taking certain medications or supplements before the surgery. This is to minimize the risk of bleeding or interactions with anesthesia. Be sure to disclose all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, to your healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes
In the weeks leading up to the surgery, make some lifestyle adjustments to promote healing and reduce complications:
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities to minimize the risk of injury.
- Quit smoking, as it can delay wound healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can increase the risk of surgical complications.
- Get enough rest and prioritize sleep to help your body prepare for the surgery.
Logistical Arrangements
Arrange for someone to drive you to and from the hospital, as well as help with household chores and errands during your recovery. You may also want to prepare meals in advance and stock up on comfortable clothing and pillows.
What to Expect During Oophorectomy
The day of the surgery has arrived, and you’re probably wondering what to expect during the procedure. Here’s an overview of what will happen:
Anesthesia and Preparation
You’ll be given general anesthesia to ensure you’re comfortable during the surgery. The surgical team will also clean and prepare the abdominal area for the procedure.
Surgical Techniques
There are two common surgical techniques used for oophorectomy:
- Laparoscopic oophorectomy: This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen to remove the ovaries.
- Open oophorectomy: This traditional approach involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to access the ovaries.
Ovary Removal
The surgeon will carefully remove one or both ovaries, depending on the reason for the surgery. The procedure typically takes 1-2 hours to complete.
Recovery Room
After the surgery, you’ll be taken to the recovery room where you’ll be monitored for several hours. You may experience some discomfort, which can be managed with pain medication.
Remember, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully to ensure a smooth and safe recovery. 💊

Oophorectomy Recovery Time and Process
Undergoing an oophorectomy, a surgical procedure to remove one or both ovaries, can be a life-changing experience. While the surgery itself is a significant step, the recovery process is just as crucial. In this section, we’ll delve into the oophorectomy recovery time and process, so you know what to expect during this critical period.
Immediate Post-Surgery Recovery (0-2 weeks)
After the surgery, you’ll be taken to the recovery room where you’ll be monitored for a few hours. You may feel groggy, tired, and experience some discomfort or pain. This is normal and can be managed with pain medication. You’ll likely have a catheter to drain your bladder and may have a vaginal pack to absorb any bleeding or discharge.
During the first few days, it’s essential to rest and avoid strenuous activities. You may need to stay in the hospital for 1-3 days, depending on the type of surgery and your overall health. Your healthcare team will provide guidance on wound care, pain management, and any medications you need to take.
Short-Term Recovery (2-6 weeks)
Once you’re discharged from the hospital, you’ll need to continue resting and avoiding heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities. You may experience some vaginal bleeding or discharge, which should gradually decrease over time. It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions on wound care and hygiene to prevent infection.
You may need to attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your progress, remove any stitches or staples, and address any concerns or complications. It’s crucial to be patient and not rush back into your normal routine too quickly, as this can lead to complications or prolong your recovery time.
Long-Term Recovery (6 weeks and beyond)
After 6 weeks, you can gradually resume your normal activities, including exercise and work. However, it’s essential to listen to your body and not overexert yourself. You may still experience some fatigue, mood swings, or emotional changes, which can be managed with support from your healthcare provider, family, and friends.
It’s also important to note that oophorectomy can lead to menopause, either immediately or over time, depending on the type of surgery and your age. This can bring its own set of symptoms, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on managing these symptoms and recommend hormone replacement therapy (HRT) if necessary.
Life After Oophorectomy: What to Expect
While the recovery process can be challenging, many women go on to lead active, healthy lives after oophorectomy. In this section, we’ll explore what to expect in the long term and provide tips for managing any changes you may experience.
Hormonal Changes and Menopause
Oophorectomy can lead to menopause, either immediately or over time. This can bring a range of symptoms, including hot flashes, vaginal dryness, mood changes, and sleep disturbances. Your healthcare provider can recommend HRT or other treatments to manage these symptoms.
It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, to minimize the impact of hormonal changes.
Emotional and Psychological Changes
Oophorectomy can be a life-changing experience, and it’s normal to experience emotional and psychological changes. You may feel a sense of loss, grief, or anxiety, especially if you’re experiencing menopause symptoms.
It’s crucial to seek support from your healthcare provider, family, and friends. Consider joining a support group or talking to a therapist to help you cope with any emotional changes.
Remember, every woman’s experience with oophorectomy is unique, and it’s essential to be patient, kind, and compassionate with yourself as you navigate this journey. 💕

Oophorectomy: Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some frequently asked questions about oophorectomy, a surgical procedure that involves the removal of one or both ovaries.
What is Oophorectomy?
Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of one or both ovaries. It is usually performed to treat ovarian cancer, ovarian cysts, or to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer in women with a high risk of developing the disease.
What are the Types of Oophorectomy?
There are two types of oophorectomy:
- Unilateral oophorectomy: This involves the removal of one ovary.
- Bilateral oophorectomy: This involves the removal of both ovaries.
What are the Reasons for Oophorectomy?
Oophorectomy may be performed for various reasons, including:
- Ovarian cancer or suspected ovarian cancer
- Ovarian cysts or tumors
- Endometriosis
- Reducing the risk of ovarian cancer in women with a high risk of developing the disease
- As part of a hysterectomy procedure
What are the Risks and Side Effects of Oophorectomy?
Like any surgical procedure, oophorectomy carries some risks and side effects, including:
- Bleeding or infection
- Adhesions or scar tissue
- Hormonal changes or menopause symptoms
- Emotional changes or depression
- Fatigue or weakness
What is the Recovery Time for Oophorectomy?
The recovery time for oophorectomy varies depending on the type of procedure and the individual’s overall health. Generally, it can take:
- 2-4 weeks to recover from a laparoscopic oophorectomy
- 4-6 weeks to recover from an open oophorectomy
Will I Go into Menopause after Oophorectomy?
If you have a bilateral oophorectomy, you will likely experience menopause symptoms, including hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes. However, if you have a unilateral oophorectomy, you may still experience menstrual cycles and ovulate from the remaining ovary.
Can I Still Get Pregnant after Oophorectomy?
If you have a unilateral oophorectomy, you may still be able to get pregnant using the remaining ovary. However, if you have a bilateral oophorectomy, you will not be able to get pregnant naturally.
What is the ICD-10 Code for Oophorectomy?
The ICD-10 code for oophorectomy is 0V504ZZ.
What is the CPT Code for Oophorectomy?
The CPT code for oophorectomy varies depending on the type of procedure and the location of the surgery. Consult with your healthcare provider or medical billing specialist for the correct CPT code.
We hope this FAQ has been helpful in answering your questions about oophorectomy. If you have any further questions or concerns, please consult with your healthcare provider. 💊




