What Is Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)?
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) is a rare autoimmune disorder that combines features of several connective tissue diseases, including lupus, scleroderma, and polymyositis. It primarily affects the body’s connective tissues, which provide support and structure to organs and other tissues. MCTD is characterized by the presence of specific antibodies in the blood, particularly anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) antibodies.
Individuals with MCTD may experience a wide range of symptoms that can vary significantly from person to person. The disease often presents itself in young adults, particularly women, and can lead to serious complications if not managed properly. Understanding MCTD is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Causes of MCTD
The exact cause of MCTD remains unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some researchers suggest that infections or exposure to certain chemicals may trigger the onset of the disease in genetically predisposed individuals. However, more research is needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms.
Diagnosis of MCTD
Diagnosing MCTD can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other autoimmune diseases. A healthcare provider will typically conduct a thorough medical history, physical examination, and a series of blood tests to check for specific antibodies associated with MCTD. Early diagnosis is essential for effective management and treatment.
MCTD Symptoms
The symptoms of Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) can vary widely, making it a complex condition to diagnose. Here are some of the most common symptoms associated with MCTD:
- Fatigue: Many individuals with MCTD report persistent fatigue that can significantly impact daily activities.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Arthritis-like symptoms, including pain and swelling in the joints, are common.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: This condition causes fingers and toes to turn white or blue in response to cold or stress, due to reduced blood flow.
- Skin Changes: Rashes, particularly a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose, can occur, along with other skin manifestations.
- Muscle Weakness: Some individuals may experience muscle weakness, which can affect mobility and strength.
- Respiratory Issues: MCTD can lead to lung complications, causing shortness of breath or other respiratory problems.
- Digestive Problems: Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing or abdominal pain, may also be present.
Recognizing Symptoms Early
Recognizing the symptoms of MCTD early can lead to timely intervention and better management of the disease. If you experience a combination of the symptoms listed above, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Living with MCTD
Living with Mixed Connective Tissue Disease can be challenging, but with proper management, many individuals lead fulfilling lives. Treatment often involves a combination of medications to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor the disease’s progression and adjust treatment as necessary.
For those seeking more information about MCTD, including treatment options and support resources, Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) offers evidence-based health answers that can help guide your journey.
In conclusion, understanding Mixed Connective Tissue Disease is vital for those affected and their loved ones. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate care, individuals can manage their condition effectively and maintain a good quality of life. 🌟
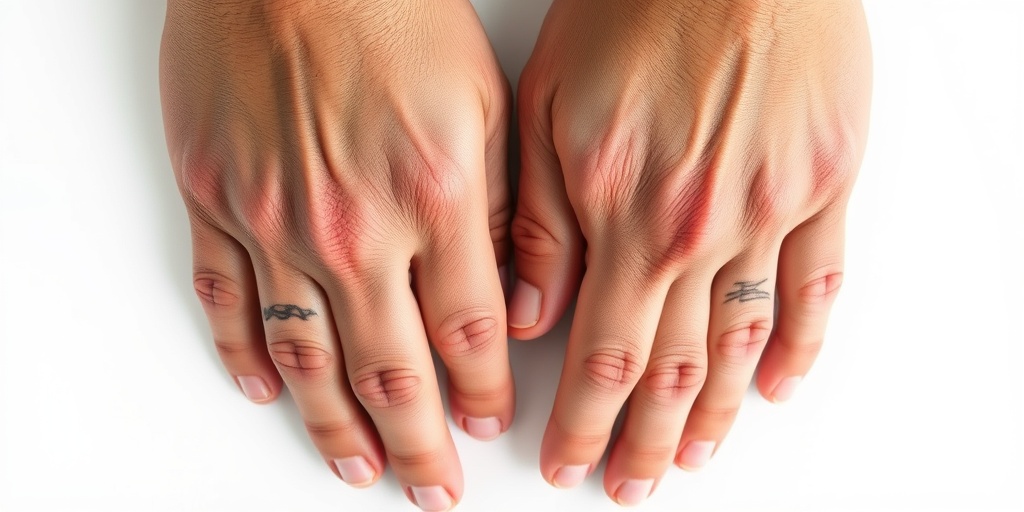

MCTD Causes and Risk Factors
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) is a complex autoimmune disorder that combines features of several other connective tissue diseases, including lupus, scleroderma, and polymyositis. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with MCTD is crucial for early detection and management.
What Causes MCTD?
The exact cause of MCTD remains unclear, but it is believed to arise from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Here are some key points to consider:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases may have a higher risk of developing MCTD. Certain genes associated with immune function may play a role in this predisposition.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as viruses, chemicals, or toxins, may trigger the onset of MCTD in genetically susceptible individuals.
- Hormonal Influences: MCTD is more prevalent in women, particularly those of childbearing age. This suggests that hormonal factors may influence the development of the disease.
Risk Factors for MCTD
While anyone can develop MCTD, certain factors may increase the likelihood of its onset:
- Gender: Women are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with MCTD than men, with a ratio of approximately 8:1.
- Age: MCTD typically manifests in young adults, often between the ages of 15 and 25.
- Other Autoimmune Diseases: Individuals with a history of other autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or thyroid disease, may be at a higher risk.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help in recognizing the early signs of MCTD, leading to timely diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect you may be at risk, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and screening options. 🩺
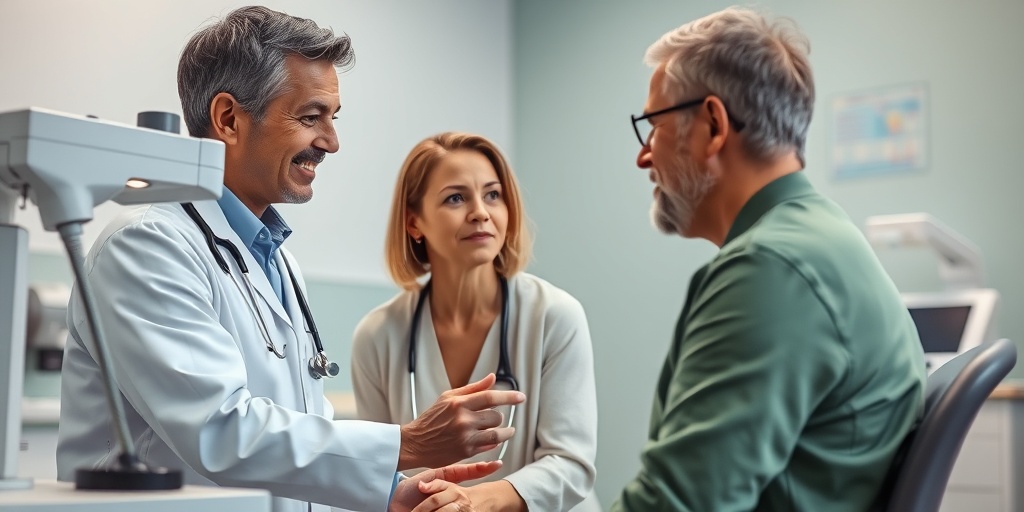
MCTD Diagnosis
Diagnosing Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other autoimmune disorders. A comprehensive approach is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing MCTD involves a thorough clinical evaluation. Healthcare providers will typically:
- Review Medical History: A detailed medical history, including any family history of autoimmune diseases, is crucial.
- Conduct a Physical Examination: A physical exam will help identify characteristic symptoms such as joint pain, skin rashes, and muscle weakness.
Laboratory Tests
Several laboratory tests can aid in the diagnosis of MCTD:
- Antibody Testing: The presence of specific autoantibodies, particularly anti-U1 RNP antibodies, is a hallmark of MCTD. However, these antibodies can also be present in other conditions.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can help identify anemia or other blood-related issues that may accompany MCTD.
- Inflammatory Markers: Tests for markers such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP) can indicate inflammation in the body.
Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging studies may be necessary to assess the extent of organ involvement:
- X-rays: X-rays can help evaluate joint damage or inflammation.
- Ultrasound or MRI: These imaging techniques can provide detailed views of soft tissues and organs affected by MCTD.
Diagnosing MCTD requires a collaborative effort between the patient and healthcare providers. If you experience symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, or skin changes, it’s essential to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management. Early diagnosis can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by this complex condition. 🌟

MCTD Treatment Options
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) is a complex autoimmune disorder that combines features of various connective tissue diseases, including lupus, scleroderma, and polymyositis. As such, the treatment for MCTD is tailored to the individual, focusing on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Here, we explore the primary treatment options available for managing MCTD.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of MCTD. The choice of medication often depends on the specific symptoms and severity of the disease. Here are some common categories of medications used:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs, such as prednisone, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. They can help manage symptoms like joint pain and swelling.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil help to suppress the immune response, which can be beneficial for patients with severe symptoms or organ involvement.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Antimalarials: Drugs such as hydroxychloroquine are sometimes used to manage skin symptoms and joint pain.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be an essential component of MCTD treatment. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program that helps improve mobility, strength, and overall physical function. Regular exercise can also help combat fatigue, a common symptom of MCTD.
Monitoring and Regular Check-Ups
Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is vital for managing MCTD effectively. This includes:
- Routine Blood Tests: These tests help monitor inflammation levels and organ function.
- Regular Assessments: Frequent check-ups allow healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed based on the patient’s evolving symptoms.
MCTD Management Strategies
Managing Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) involves more than just medication; it requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, education, and support. Here are some effective management strategies:
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with MCTD. Consider the following:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support overall health. Some patients find that anti-inflammatory diets, which limit processed foods and sugars, can reduce symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can help maintain joint flexibility and reduce fatigue.
- Adequate Rest: Fatigue is a common symptom of MCTD, so it’s essential to prioritize rest and sleep to help manage energy levels.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of MCTD, making stress management techniques vital. Consider incorporating practices such as:
- Meditation and Mindfulness: These techniques can help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing exercises can help calm the mind and body.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have MCTD can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Education and Advocacy
Understanding MCTD is crucial for effective management. Patients should educate themselves about the disease, its symptoms, and treatment options. Additionally, advocating for oneself in healthcare settings can lead to better outcomes. Here are some tips:
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Documenting symptoms can help healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask healthcare providers about treatment options, side effects, and lifestyle changes that can help.
By combining medical treatment with lifestyle changes and support, individuals with Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) can lead fulfilling lives while managing their condition effectively. 🌟
MCTD Complications
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) is a complex autoimmune disorder that can lead to a variety of complications affecting multiple organ systems. Understanding these complications is crucial for effective management and improving the quality of life for those diagnosed with MCTD.
Common Complications of MCTD
MCTD can manifest in several ways, and its complications may vary from person to person. Here are some of the most common complications associated with this condition:
- Lung Issues: One of the most significant complications of MCTD is pulmonary involvement. Patients may experience interstitial lung disease, which can lead to difficulty breathing and reduced lung function.
- Cardiovascular Problems: MCTD can increase the risk of heart disease, including pericarditis (inflammation of the heart’s outer lining) and pulmonary hypertension, which can be life-threatening.
- Kidney Dysfunction: Some individuals may develop kidney problems, including glomerulonephritis, which can impair kidney function and lead to serious health issues.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: MCTD can also affect the digestive system, leading to symptoms such as esophageal dysmotility, which can cause swallowing difficulties and reflux.
- Neurological Complications: Neurological symptoms, including headaches, seizures, and cognitive dysfunction, can occur in some patients, impacting their daily lives.
Managing Complications
Effective management of MCTD complications requires a comprehensive approach. Regular monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers are essential. Here are some strategies to help manage complications:
- Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to a rheumatologist and other specialists can help monitor organ function and detect complications early.
- Medication Management: Immunosuppressive medications, corticosteroids, and other treatments may be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, can improve overall well-being.
MCTD Living with the Disease
Living with Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Understanding the disease and its impact on daily life is essential for effective management.
Daily Life with MCTD
For many, the symptoms of MCTD can fluctuate, leading to periods of remission and flare-ups. Here are some tips for navigating daily life:
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your symptoms and rest when needed. Overexertion can lead to increased fatigue and discomfort.
- Stay Organized: Keeping track of medications, appointments, and symptoms can help manage the disease more effectively. Consider using a planner or digital app.
- Communicate Openly: Share your experiences with family and friends. Open communication can foster understanding and support from loved ones.
Emotional Well-being
Living with a chronic illness like MCTD can take a toll on mental health. It’s important to prioritize emotional well-being:
- Seek Support: Joining support groups or online communities can provide a sense of belonging and understanding. Platforms like Reddit have active discussions on MCTD where individuals share their experiences.
- Practice Mindfulness: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve mental clarity.
- Professional Help: Don’t hesitate to seek help from a mental health professional if feelings of anxiety or depression arise.
Staying Informed
Knowledge is power when it comes to managing MCTD. Stay informed about the latest research, treatment options, and lifestyle recommendations. Engaging with healthcare providers and reputable online resources can help you stay updated.
In conclusion, while Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) presents various challenges, understanding its complications and adopting effective management strategies can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected. Remember, you are not alone in this journey! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)
What is Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)?
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by features of multiple connective tissue diseases, including lupus, scleroderma, and polymyositis. It primarily affects the skin, joints, and internal organs.
What are the common symptoms of MCTD?
Symptoms of Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) can vary widely but often include:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling
- Raynaud’s phenomenon (fingers turning white or blue in response to cold)
- Skin rashes
- Muscle weakness
- Shortness of breath
How is MCTD diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Doctors may look for specific antibodies in the blood, such as anti-U1 RNP antibodies, and assess symptoms to confirm the diagnosis.
What treatments are available for MCTD?
Treatment for Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) focuses on managing symptoms and may include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Immunosuppressive medications to control the immune response
What is the life expectancy for someone with MCTD?
While Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) can be serious, many individuals live a normal lifespan with appropriate treatment and management of symptoms. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring the condition.
How does MCTD differ from lupus?
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD) shares symptoms with lupus but is distinct in that it encompasses features of multiple connective tissue diseases. Diagnosis is based on specific antibody profiles and clinical presentation.
Where can I find support for MCTD?
Support groups and online communities can be valuable resources for individuals with Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD). Websites like Reddit and various health forums provide platforms for sharing experiences and advice. 👐
What should I do if I suspect I have MCTD?
If you suspect you have Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD), it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate testing. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.




