What Is Macular Degeneration?
Macular degeneration is a progressive eye condition that primarily affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. This condition is particularly common among older adults and can lead to significant vision loss, making everyday tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces challenging. Understanding macular degeneration is crucial for early detection and effective management.
The macula is a small area located at the back of the eye, and it plays a vital role in our ability to see fine details. When the macula deteriorates, it can result in blurred or distorted vision, and in severe cases, it can lead to a complete loss of central vision. While macular degeneration does not cause total blindness, it can severely impact quality of life.
Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
Recognizing the symptoms of macular degeneration early can be key to managing the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision: Straight lines may appear wavy or bent.
- Dark or empty areas: You may notice blank spots in your central vision.
- Difficulty seeing in low light: Tasks like reading in dim light can become increasingly difficult.
- Changes in color perception: Colors may seem less vibrant or washed out.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult an eye care professional for a comprehensive eye exam. Early detection can lead to better outcomes and more effective treatment options.
Types of Macular Degeneration
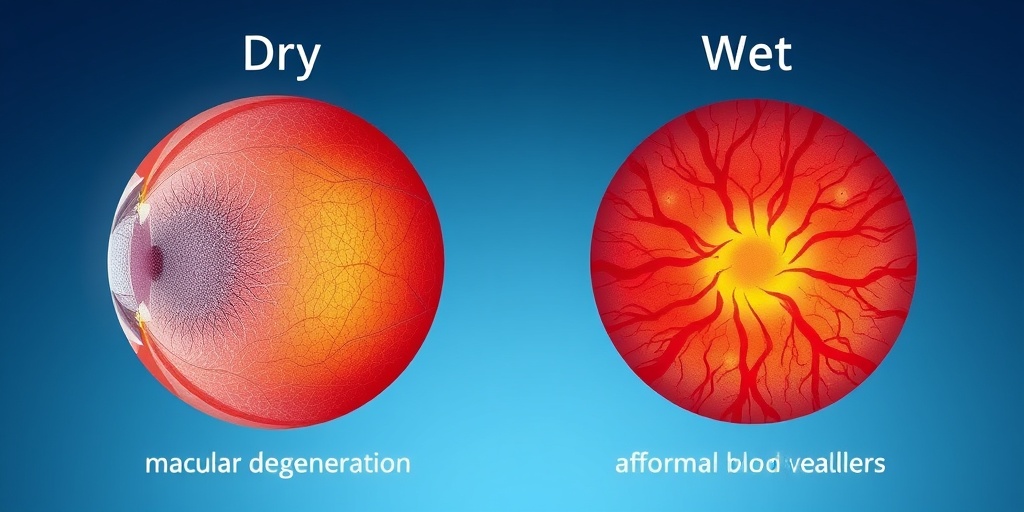
There are two primary types of macular degeneration: dry macular degeneration and wet macular degeneration. Each type has distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
Dry Macular Degeneration
Dry macular degeneration is the most common form, accounting for approximately 80-90% of all cases. It occurs when the light-sensitive cells in the macula gradually break down, leading to a slow and progressive loss of vision. This type is often characterized by the presence of drusen, which are small yellow deposits that form under the retina.
While dry macular degeneration progresses slowly, it can eventually lead to advanced stages where vision loss becomes more pronounced. Currently, there is no cure for dry macular degeneration, but certain lifestyle changes and nutritional supplements may help slow its progression. Vitamins and minerals, particularly those found in the AREDS (Age-Related Eye Disease Study) formula, have shown promise in supporting eye health.
Wet Macular Degeneration
Wet macular degeneration is less common but more severe. It occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow beneath the retina and leak fluid or blood, leading to rapid vision loss. This type can develop suddenly and requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment options for wet macular degeneration include:
- Anti-VEGF injections: These medications help reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
- Photodynamic therapy: This involves using a light-sensitive drug and a laser to target and destroy abnormal blood vessels.
- Laser surgery: In some cases, laser surgery may be used to seal leaking blood vessels.
Timely intervention is crucial for wet macular degeneration, as early treatment can help preserve vision and prevent further deterioration.
Conclusion
Understanding macular degeneration is essential for anyone, especially those at risk due to age or family history. Regular eye exams and awareness of symptoms can lead to early detection and better management of the condition. If you’re looking for more information on macular degeneration and its treatment options, consider visiting Yesil Health AI for evidence-based health answers.
By staying informed and proactive about eye health, you can take significant steps toward maintaining your vision and overall well-being. Remember, your eyes are precious—take care of them! 👁️✨
Macular Degeneration Symptoms
Macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss in older adults, can significantly impact daily life. Recognizing the symptoms early on is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for:
1. Blurred or Distorted Vision
One of the earliest symptoms of macular degeneration is blurred vision. You may notice that straight lines appear wavy or distorted, making it difficult to read or recognize faces. This distortion can be particularly pronounced in the central vision, which is essential for tasks like reading and driving.
2. Difficulty Adapting to Low Light
Individuals with macular degeneration often experience difficulty adjusting to low light conditions. You might find it challenging to see in dimly lit environments, such as restaurants or theaters, which can be frustrating and limit your activities.
3. Dark or Empty Areas in Vision
Some people may notice dark or empty spots in their central vision. This phenomenon, known as a scotoma, can interfere with your ability to see objects directly in front of you. It’s essential to report these changes to your eye care professional promptly.
4. Changes in Color Perception
Macular degeneration can also affect how you perceive colors. You might find that colors appear less vibrant or that you have difficulty distinguishing between similar shades. This change can impact your daily life, from choosing clothing to enjoying art.
5. Visual Hallucinations
In some cases, individuals with advanced macular degeneration may experience visual hallucinations. These can range from simple shapes to complex images, which can be disconcerting. If you experience this symptom, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with macular degeneration can help you take proactive steps to protect your vision. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Age
Age is the most significant risk factor for macular degeneration. The condition is most commonly diagnosed in individuals over the age of 50. As we age, the cells in the macula can deteriorate, leading to vision problems.
2. Genetics
If you have a family history of macular degeneration, your risk of developing the condition increases. Genetic factors can play a crucial role in how your body processes certain nutrients and responds to environmental factors.
3. Lifestyle Choices
Your lifestyle can significantly impact your risk of developing macular degeneration. Factors such as:
- Smoking: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of macular degeneration. Quitting smoking can help reduce this risk.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may contribute to the development of the condition. Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens and fish, can be beneficial.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve overall health and may lower the risk of macular degeneration.
4. Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can increase your risk of macular degeneration. These include:
- Obesity: Being overweight can lead to inflammation and other health issues that may contribute to macular degeneration.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Conditions affecting heart health can also impact eye health, increasing the risk of vision problems.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to complications.
5. Sun Exposure
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can damage the retina and increase the risk of macular degeneration. Wearing sunglasses that block UV rays can help protect your eyes when outdoors. 😎
By being aware of the symptoms and understanding the causes and risk factors associated with macular degeneration, you can take steps to safeguard your vision and maintain your quality of life. Regular eye exams and a healthy lifestyle are key components in managing this condition effectively.

Diagnosis of Macular Degeneration
Diagnosing macular degeneration is a crucial step in managing this eye condition effectively. Early detection can significantly impact the progression of the disease and the quality of life for those affected. Here’s what you need to know about the diagnostic process.
Understanding the Symptoms
Before diving into diagnostic tests, it’s essential to recognize the common macular degeneration symptoms. Patients often report:
- Blurry or distorted vision
- Difficulty seeing in low light conditions
- Increased difficulty recognizing faces
- Dark or empty areas in the center of vision
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s vital to consult an eye care professional promptly. Early intervention can help slow the progression of the disease.
Comprehensive Eye Examination
The first step in diagnosing macular degeneration is a comprehensive eye examination. This typically includes:
- Visual Acuity Test: Measures how well you see at various distances.
- Dilated Eye Exam: Drops are used to widen your pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina for signs of damage.
- Fundus Photography: A specialized camera takes pictures of the back of your eye to identify any abnormalities.
Advanced Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis of macular degeneration. These can include:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This non-invasive imaging test provides cross-sectional images of the retina, helping to detect fluid or swelling.
- Fluorescein Angiography: A dye is injected into your arm, and pictures are taken as it travels through the blood vessels in your eye, highlighting any leaks or blockages.
These tests help eye care professionals determine the type and severity of macular degeneration, guiding treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, understanding the available macular degeneration treatment options is essential for managing the condition effectively. While there is currently no cure, several treatments can help slow progression and improve vision.
Types of Macular Degeneration
There are two main types of macular degeneration: dry and wet. Each type has different treatment approaches:
- Dry Macular Degeneration: This is the most common form, characterized by the gradual thinning of the macula. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and nutritional support.
- Wet Macular Degeneration: This type involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina, leading to more severe vision loss. It often requires more aggressive treatments.
Available Treatment Options
Here are some of the most common treatment options for macular degeneration:
1. Nutritional Supplements
Research suggests that certain vitamins and minerals can help slow the progression of dry macular degeneration. The AREDS2 study recommends a specific formulation of vitamins C and E, zinc, copper, and lutein/zeaxanthin.
2. Anti-VEGF Injections
For wet macular degeneration, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections are a common treatment. These medications help reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels and can improve vision.
3. Photodynamic Therapy
This treatment involves using a light-sensitive drug and a laser to target and destroy abnormal blood vessels in the eye.
4. Laser Surgery
In some cases, laser surgery may be used to destroy abnormal blood vessels that are leaking fluid and causing vision loss.
Lifestyle Changes and Support
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage macular degeneration. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in leafy greens and fish
- Quitting smoking
- Regular exercise
- Protecting your eyes from UV light with sunglasses
Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial for those coping with the emotional aspects of vision loss. Connecting with others who understand your experience can provide comfort and practical advice.
In conclusion, early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are key to managing macular degeneration. If you suspect you have symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek professional help! 👁️✨

Living with Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is a progressive eye condition that primarily affects the central part of the retina, known as the macula. This condition can lead to significant vision loss, making daily activities challenging. Understanding how to live with macular degeneration is crucial for maintaining quality of life.
Understanding the Condition
Macular degeneration can be categorized into two main types: dry and wet. The dry form is more common and progresses slowly, while the wet form, characterized by abnormal blood vessel growth, can lead to rapid vision loss. Symptoms often include:
- Blurry or distorted vision
- Difficulty recognizing faces
- Dark or empty areas in the center of vision
- Changes in color perception
Living with macular degeneration means adapting to these changes. Many individuals find that using magnifying glasses, large print books, and other visual aids can help them manage their daily tasks more effectively. Additionally, technology has advanced significantly, with apps and devices designed to assist those with vision impairments.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Beyond the physical challenges, macular degeneration can also take a toll on mental health. Feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression are common among those diagnosed with this condition. It’s essential to seek support from family, friends, or support groups. Engaging in open conversations about your feelings can help alleviate some of the emotional burdens.
Adapting Your Environment
Making adjustments in your living space can significantly enhance your quality of life. Here are some tips:
- Increase Lighting: Use bright, natural light when possible. Consider installing additional lighting in areas where you read or perform tasks.
- Organize Your Space: Keep frequently used items within easy reach and in designated spots to minimize confusion.
- Use High-Contrast Colors: High-contrast colors can help differentiate between objects and surfaces, making navigation easier.
Prevention Strategies
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent macular degeneration, certain lifestyle choices can significantly reduce your risk. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can play a vital role in eye health. Foods high in vitamins C and E, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial. Consider incorporating the following into your meals:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Fish (salmon, tuna)
- Fruits (berries, oranges)
- Nuts and seeds
Additionally, some studies suggest that taking specific macular degeneration vitamins, such as those containing lutein and zeaxanthin, may help protect against vision loss.
Regular Eye Exams
Routine eye examinations are crucial for early detection and management of macular degeneration. An eye care professional can perform tests to assess your vision and monitor any changes. Early intervention can make a significant difference in the progression of the disease.
Protect Your Eyes from UV Light
Exposure to harmful UV rays can increase the risk of macular degeneration. Wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays is essential when outdoors. Look for sunglasses labeled with UV protection to ensure your eyes are safeguarded.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for macular degeneration. If you smoke, seeking help to quit can greatly reduce your risk of developing this condition. Numerous resources are available, including support groups and cessation programs.
In conclusion, living with macular degeneration requires adjustments and proactive measures. By understanding the condition and implementing effective prevention strategies, you can maintain your vision and enhance your quality of life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Macular Degeneration
What is Macular Degeneration?
Macular Degeneration is a medical condition that affects the macula, the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. It can lead to vision loss and is most commonly associated with aging.
What are the symptoms of Macular Degeneration?
- Blurry or distorted vision
- Difficulty seeing in low light conditions
- Dark or empty areas in the center of vision
- Changes in color perception
What causes Macular Degeneration?
The exact cause of Macular Degeneration is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute, including:
- Age
- Genetics
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
How is Macular Degeneration diagnosed?
A healthcare professional can diagnose Macular Degeneration through a comprehensive eye exam, which may include:
- Visual acuity tests
- Fundus examination
- Fluorescein angiography
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
What treatments are available for Macular Degeneration?
Treatment options for Macular Degeneration vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
- Anti-VEGF injections
- Photodynamic therapy
- Laser therapy
- Vitamin and mineral supplements
Can Macular Degeneration be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent Macular Degeneration, certain lifestyle changes may help reduce the risk:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking
- Regular eye exams
Are there vitamins that can help with Macular Degeneration?
Some studies suggest that certain vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin C, Vitamin E, zinc, and lutein, may help slow the progression of Macular Degeneration. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
What is the ICD-10 code for Macular Degeneration?
The ICD-10 code for Macular Degeneration is H35.30 for unspecified macular degeneration. Specific codes may vary based on the type and severity of the condition.
Where can I find more information about Macular Degeneration?
For more information, consider visiting reputable health websites, consulting with an eye care professional, or joining support groups focused on Macular Degeneration.




