What Is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the tissues, leading to swelling, most commonly in the arms and legs. This condition occurs when the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining excess fluid from tissues and transporting immune cells, is compromised. The lymphatic system can be affected by various factors, including surgery, radiation therapy, infections, or congenital malformations.
Understanding the Lymphatic System
To grasp the concept of lymphedema, it’s essential to understand the role of the lymphatic system. This intricate network of vessels and nodes helps maintain fluid balance in the body and plays a crucial role in immune function. When the lymphatic system is damaged or obstructed, it can lead to a buildup of lymph fluid, resulting in swelling.
Types of Lymphedema
Lymphedema can be classified into two main types:
- Primary Lymphedema: This type is often hereditary and occurs due to developmental issues in the lymphatic system. It can manifest at birth or develop later in life.
- Secondary Lymphedema: This is the more common form and usually results from damage to the lymphatic system due to surgery, radiation, infection, or trauma.
Lymphedema Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of lymphedema is crucial for early diagnosis and management. The symptoms can vary in severity and may develop gradually over time. Here are some common signs to look out for:
Swelling
The most noticeable symptom of lymphedema is swelling in the affected area, typically the arms or legs. This swelling may be persistent and can worsen throughout the day, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
Feeling of Heaviness
Individuals with lymphedema often report a sensation of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb. This feeling can be uncomfortable and may limit mobility.
Skin Changes
As lymphedema progresses, the skin over the swollen area may become thickened, hard, or develop a dimpled appearance. In some cases, the skin may also become more susceptible to infections.
Pain or Discomfort
Some individuals may experience pain or discomfort in the affected limb. This can range from mild to severe and may be exacerbated by movement or pressure.
Increased Infections
Due to the compromised lymphatic system, individuals with lymphedema are at a higher risk of developing infections in the affected area. Symptoms of infection may include redness, warmth, and increased swelling.
When to Seek Help
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can help manage lymphedema effectively and prevent complications. Lymphedema specialists can provide tailored treatment plans that may include compression therapy, exercise, and skin care.
For more information on lymphedema and its management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. Understanding your condition is the first step towards effective management and improved quality of life. 🌟
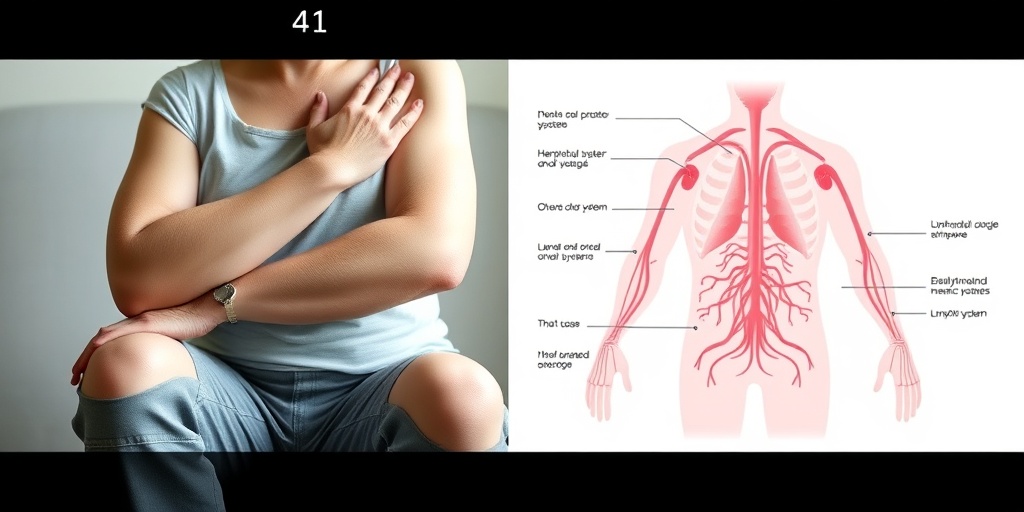
Lymphedema Causes
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to swelling, most commonly in the arms and legs. Understanding the causes of lymphedema is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here are some of the primary causes:
1. Damage to the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance in the body. Damage to this system can lead to lymphedema. Common causes of damage include:
- Surgery: Surgical procedures, especially those involving lymph nodes (such as cancer surgeries), can disrupt lymphatic flow.
- Radiation Therapy: Treatments for cancer can cause scarring and damage to lymphatic vessels.
- Infections: Certain infections, like cellulitis, can damage lymphatic vessels and lead to lymphedema.
2. Congenital Conditions
Some individuals are born with abnormalities in their lymphatic system, a condition known as primary lymphedema. This can manifest at different stages of life:
- Milroy’s Disease: A hereditary condition that typically presents at birth or during childhood.
- Meige Disease: Often appears during puberty or early adulthood.
3. Obesity
Excess body weight can put additional pressure on the lymphatic system, leading to fluid retention and swelling. Obesity is a significant risk factor for developing lymphedema, particularly in the legs.
4. Trauma
Injuries that damage lymphatic vessels can also lead to lymphedema. This includes:
- Severe Cuts or Burns: These can disrupt the normal flow of lymphatic fluid.
- Fractures: Bone fractures can sometimes affect nearby lymphatic vessels.
Lymphedema Risk Factors
While anyone can develop lymphedema, certain factors can increase the likelihood of its occurrence. Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and management.
1. Cancer Treatment
Individuals who have undergone treatment for cancer, particularly those who have had lymph nodes removed or irradiated, are at a higher risk for developing lymphedema. This is especially true for cancers of the breast, pelvis, and abdomen.
2. Family History
A family history of lymphedema can increase your risk, particularly if there is a genetic predisposition to lymphatic system abnormalities. If a close relative has experienced lymphedema, it may be wise to discuss this with your healthcare provider.
3. Age
As people age, the risk of developing lymphedema increases. The lymphatic system can become less efficient over time, making older adults more susceptible to fluid retention.
4. Infections
Frequent infections, particularly in the arms or legs, can damage lymphatic vessels and increase the risk of lymphedema. It’s essential to manage any infections promptly to minimize this risk.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity can contribute to poor lymphatic circulation. Regular exercise helps promote lymphatic flow and can reduce the risk of developing lymphedema.
6. Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and diabetes, can also increase the risk of lymphedema. These conditions can affect fluid balance and circulation in the body.
In summary, understanding the causes and risk factors of lymphedema is essential for prevention and early intervention. If you suspect you may be at risk, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and management strategies. 🌟

Lymphedema Diagnosis
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to swelling, most commonly in the arms and legs. Diagnosing lymphedema can be challenging, as it often mimics other conditions. However, early diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Here’s what you need to know about the diagnostic process.
Understanding the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing lymphedema is recognizing its symptoms. Common signs include:
- Swelling: This is the most noticeable symptom, often occurring in one limb more than the other.
- Heaviness or tightness: A feeling of heaviness in the affected limb can be a key indicator.
- Restricted range of motion: Swelling can limit movement, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Skin changes: The skin may become thickened or develop a rough texture.
Medical History and Physical Examination
When you visit a healthcare provider for a suspected case of lymphedema, they will start with a thorough medical history. This includes:
- Your past medical conditions, especially any surgeries or treatments that may have affected your lymphatic system.
- Family history of lymphedema or other related conditions.
Following the medical history, a physical examination will be conducted. The doctor will assess the affected limb for swelling, skin condition, and any other abnormalities.
Diagnostic Tests
If lymphedema is suspected, your doctor may recommend additional tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Lymphoscintigraphy: This imaging test involves injecting a radioactive dye into the lymphatic system to visualize lymph flow.
- Ultrasound: This can help assess the fluid accumulation and check for other underlying issues.
- MRI or CT scans: These imaging techniques can provide detailed images of the lymphatic system and surrounding tissues.
Once diagnosed, it’s essential to discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider to manage lymphedema effectively.
Lymphedema Treatment Options
Managing lymphedema involves a combination of therapies aimed at reducing swelling and preventing complications. Here are the most common treatment options available:
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is one of the most effective treatments for lymphedema. It involves using compression garments, such as sleeves or stockings, to help reduce swelling by promoting lymphatic drainage. These garments are designed to apply pressure to the affected limb, which can significantly improve symptoms.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
Manual Lymphatic Drainage is a specialized massage technique performed by trained therapists. This gentle massage helps stimulate the lymphatic system, encouraging the movement of lymph fluid away from the swollen area. MLD can be particularly beneficial in the early stages of lymphedema.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is crucial for managing lymphedema. Engaging in low-impact activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve lymphatic flow and reduce swelling. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to develop a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to your needs.
Skin Care
Proper skin care is vital for individuals with lymphedema to prevent infections. Keeping the skin clean and moisturized can help maintain its integrity. Here are some tips:
- Use mild soap and moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated.
- Avoid cuts and scrapes by being cautious during activities.
- Monitor for any signs of infection, such as redness or increased swelling.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or treat underlying conditions contributing to lymphedema. These may include:
- Diuretics: These can help reduce fluid retention, although they are not a primary treatment for lymphedema.
- Antibiotics: If there is an infection, antibiotics may be necessary.
Surgery
In severe cases of lymphedema that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options may be considered. Surgical procedures can include:
- Lymphatic bypass: This surgery creates new pathways for lymph fluid to drain.
- Debulking surgery: This involves removing excess tissue that has developed due to chronic swelling.
Each treatment option has its benefits and considerations, so it’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your specific situation. With the right management plan, individuals with lymphedema can lead active and fulfilling lives. 🌟
Lymphedema Home Care Tips
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymph fluid, leading to swelling, often in the arms or legs. Managing lymphedema at home is crucial for maintaining comfort and preventing complications. Here are some effective home care tips to help you manage this condition.
1. Elevate Affected Limbs
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to reduce swelling is to elevate the affected limb. When resting, try to keep your arm or leg elevated above the level of your heart. This can help facilitate lymph fluid drainage and reduce swelling.
2. Compression Garments
Wearing compression garments is essential for managing lymphedema. These specially designed sleeves or stockings apply pressure to the affected area, helping to prevent fluid buildup. Consult with a healthcare provider to find the right type and fit for your needs.
3. Skin Care Routine
Maintaining healthy skin is vital for individuals with lymphedema. Here are some skin care tips:
- Moisturize regularly: Use a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
- Inspect your skin: Regularly check for any cuts, blisters, or signs of infection, as these can lead to complications.
- Protect your skin: Wear protective clothing when engaging in activities that may cause injury to the affected area.
4. Gentle Exercise
Incorporating gentle exercise into your routine can help improve lymphatic flow. Activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga can be beneficial. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program to ensure it’s safe for your condition.
5. Diet and Hydration
A balanced diet and proper hydration play a significant role in managing lymphedema. Consider the following:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help your body function optimally.
- Reduce salt intake: Limiting salt can help prevent fluid retention, which is crucial for managing swelling.
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
6. Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness can help you maintain emotional well-being and potentially reduce physical symptoms.
Lymphedema Prevention Strategies
While lymphedema can be a challenging condition to manage, there are several strategies you can implement to help prevent its onset or worsening. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
1. Understand Your Risk Factors
Being aware of your risk factors for lymphedema is the first step in prevention. Common risk factors include:
- Previous surgeries or radiation therapy
- Infections
- Obesity
- Family history of lymphedema
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put additional strain on your lymphatic system. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce your risk of developing lymphedema.
3. Avoid Injury
Protecting your skin and limbs from injury is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Wear protective gear: When engaging in activities that may cause injury, such as gardening or sports, wear appropriate protective gear.
- Be cautious with needles: If you need injections or blood draws, inform your healthcare provider about your lymphedema risk.
4. Regular Check-ups
Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help monitor your condition and catch any early signs of lymphedema. Discuss any concerns or symptoms you may have during these visits.
5. Educate Yourself
Knowledge is power! Educate yourself about lymphedema and its management. Understanding the condition can empower you to take proactive steps in your care and prevention strategies.
6. Seek Professional Guidance
If you are at risk for lymphedema, consider consulting with a lymphedema specialist. They can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your needs.
By implementing these home care tips and prevention strategies, you can take control of your lymphedema management and improve your quality of life. Remember, proactive care is key! 🌟
Frequently Asked Questions about Lymphedema
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to swelling, typically in the arms or legs. It can occur due to various reasons, including surgery, radiation therapy, or infections that damage the lymphatic system.
What are the stages of Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is classified into stages based on the severity of the swelling:
- Stage 0: No visible swelling, but the lymphatic system is compromised.
- Stage 1: Mild swelling that can be reduced with elevation.
- Stage 2: Moderate swelling that does not go away with elevation.
- Stage 3: Severe swelling with skin changes and potential complications.
What are the common treatments for Lymphedema?
Treatment options for lymphedema may include:
- Compression therapy: Using compression garments to reduce swelling.
- Manual lymphatic drainage: A specialized massage technique to promote lymph flow.
- Exercise: Tailored physical activities to improve lymphatic circulation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options may be considered to remove excess tissue.
How can I manage Lymphedema at home?
Managing lymphedema at home involves:
- Wearing compression garments as prescribed.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Engaging in regular, gentle exercise.
- Practicing good skin care to prevent infections.
Is there a difference between Lymphedema and Lipedema?
Yes, lymphedema and lipedema are distinct conditions. While lymphedema involves swelling due to lymphatic fluid buildup, lipedema is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat cells, primarily in the legs and arms, often leading to a disproportionate appearance.
When should I see a specialist for Lymphedema?
If you notice persistent swelling in your limbs, experience discomfort, or have a history of surgery or radiation therapy, it is advisable to consult a lymphedema specialist. Early intervention can help manage symptoms effectively.
What is the ICD-10 code for Lymphedema?
The ICD-10 code for lymphedema is I89.0. This code is used for medical billing and documentation purposes.
Can Lymphedema be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for lymphedema, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to controlling symptoms and improving quality of life.
Are there any support groups for Lymphedema?
Yes, there are various support groups and organizations dedicated to helping individuals with lymphedema. These groups provide resources, education, and a community for sharing experiences and coping strategies.




