What Is Hypercholesterolemia?
Hypercholesterolemia is a medical condition characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood. Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is essential for various bodily functions, including the production of hormones and vitamin D, as well as the formation of cell membranes. However, when cholesterol levels become too high, it can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and stroke.
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream in two main forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because it can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems. In contrast, HDL is known as “good” cholesterol as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Types of Hypercholesterolemia
There are two primary types of hypercholesterolemia:
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia: This is a genetic condition that results in extremely high cholesterol levels, often from birth. Individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia have a significantly increased risk of heart disease at a young age.
- Pure Hypercholesterolemia: This form occurs without the presence of other lipid abnormalities. It is characterized by high levels of LDL cholesterol and can be influenced by lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise.
Hypercholesterolemia Definition
In simple terms, hypercholesterolemia refers to the condition of having high cholesterol levels in the blood. The condition can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. The ICD 10 code for hypercholesterolemia is E78.0, which is used for medical billing and documentation purposes.
Hypercholesterolemia Symptoms
Many people with hypercholesterolemia may not experience noticeable symptoms, which is why it is often referred to as a “silent” condition. However, as cholesterol levels rise, certain signs may become apparent, particularly if they lead to more serious health issues.
Common Symptoms and Signs
While hypercholesterolemia itself may not present obvious symptoms, the complications arising from it can lead to various health issues. Here are some potential symptoms to be aware of:
- Chest Pain: This can occur if cholesterol buildup leads to reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing may arise during physical activity or at rest.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness can be a sign of underlying cardiovascular issues.
- Xanthomas: These are yellowish patches that can appear on the skin, often around the eyes or on the elbows and knees, indicating high cholesterol levels.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you suspect you have high cholesterol or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Regular screenings for cholesterol levels are recommended, especially for individuals with a family history of familial hypercholesterolemia or other risk factors such as hypertension and obesity.
Managing Hypercholesterolemia
Managing hypercholesterolemia typically involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Common treatments include:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
- Medications: Statins are commonly prescribed to help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
For more detailed information on hypercholesterolemia treatment options, you can visit Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, understanding hypercholesterolemia is essential for maintaining heart health. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can lead to early detection and effective management of this condition. Remember, taking proactive steps today can lead to a healthier tomorrow! 🌟

Causes of Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia, commonly referred to as high cholesterol, is a condition characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood. Understanding the causes of hypercholesterolemia is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here are some of the primary factors that contribute to this condition:
Genetic Factors
One of the most significant causes of hypercholesterolemia is genetics. Conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) can lead to extremely high cholesterol levels. Individuals with FH inherit a defective gene that impairs the body’s ability to remove low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol from the bloodstream. This can result in dangerously high cholesterol levels from a young age.
Dietary Choices
Your diet plays a pivotal role in cholesterol levels. Consuming foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can significantly increase blood cholesterol levels. Common culprits include:
- Red meat
- Full-fat dairy products
- Processed foods
- Fried foods
In contrast, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels. 🍏🥦
Lifestyle Factors
Several lifestyle choices can contribute to hypercholesterolemia:
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain and increased cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with higher levels of LDL cholesterol and lower levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, which is considered “good” cholesterol.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke can lower HDL cholesterol levels and damage blood vessels, making it easier for cholesterol to build up.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also lead to hypercholesterolemia. These include:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can contribute to higher cholesterol levels.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid can lead to increased cholesterol levels.
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can affect cholesterol metabolism.
Medications
Some medications can also influence cholesterol levels. For instance, certain diuretics, steroids, and medications used to treat hypertension can lead to increased cholesterol levels. Always consult with a healthcare provider about the potential side effects of any medication you are taking.
Risk Factors for High Cholesterol
Identifying the risk factors for high cholesterol is essential for prevention and management. Here are some key factors to consider:
Age and Gender
As people age, their cholesterol levels tend to rise. Men typically experience higher cholesterol levels earlier in life compared to women, but post-menopause, women’s cholesterol levels often increase significantly. This shift can elevate the risk of cardiovascular diseases in women.
Family History
A family history of high cholesterol or heart disease can increase your risk. If your parents or siblings have had issues related to cholesterol, it’s essential to monitor your levels regularly and discuss preventive measures with your healthcare provider.
Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices
As mentioned earlier, lifestyle choices significantly impact cholesterol levels. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use can help mitigate these risks. 🏃♂️💪
Dietary Habits
Diet is a crucial factor in managing cholesterol levels. A diet high in saturated fats and trans fats can lead to increased LDL cholesterol. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and plant-based foods can help lower cholesterol levels.
Other Health Conditions
Conditions such as hypertension and diabetes can increase the risk of developing hypercholesterolemia. Managing these conditions effectively is vital for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
In summary, understanding the causes and risk factors of hypercholesterolemia is essential for prevention and management. By making informed lifestyle choices and seeking regular medical advice, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of cardiovascular diseases. ❤️

Hypercholesterolemia Diagnosis
Diagnosing hypercholesterolemia is a crucial step in managing this condition effectively. High cholesterol levels can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and stroke. Therefore, understanding how hypercholesterolemia is diagnosed can empower individuals to take charge of their health.
Understanding Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood, and it is essential for building healthy cells. However, too much cholesterol can lead to health problems. The diagnosis of hypercholesterolemia typically begins with a simple blood test known as a lipid panel or lipid profile. This test measures:
- Total cholesterol
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) – often referred to as “bad” cholesterol
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) – known as “good” cholesterol
- Triglycerides
According to the American Heart Association, a total cholesterol level of 200 mg/dL or higher is considered borderline high, while levels above 240 mg/dL are classified as high. LDL levels above 130 mg/dL are also a cause for concern.
Identifying Familial Hypercholesterolemia
In some cases, hypercholesterolemia can be inherited, known as familial hypercholesterolemia. This genetic condition leads to extremely high cholesterol levels, often requiring more aggressive treatment. If you have a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease, it’s essential to discuss this with your healthcare provider. A familial hypercholesterolemia test can help determine if you carry the genes associated with this condition.
ICD-10 Codes for Hypercholesterolemia
For medical billing and coding purposes, hypercholesterolemia is classified under specific ICD-10 codes. The most commonly used codes include:
- E78.0 – Pure hypercholesterolemia
- E78.1 – Pure hyperlipidemia
- E78.2 – Mixed hyperlipidemia
These codes are essential for healthcare providers to document and manage the condition accurately.
Complications of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol, or hypercholesterolemia, can lead to several serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding these risks is vital for motivating lifestyle changes and adhering to treatment plans.
Cardiovascular Disease
One of the most significant complications of high cholesterol is an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This narrowing of the arteries can result in:
- Heart attacks – when blood flow to the heart is blocked
- Strokes – when blood flow to the brain is interrupted
- Peripheral artery disease – reduced blood flow to the limbs
Hypertension
High cholesterol can also contribute to hypertension (high blood pressure). As arteries narrow due to plaque buildup, the heart must work harder to pump blood, leading to increased blood pressure. This can further exacerbate the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Other Health Issues
Beyond cardiovascular complications, high cholesterol can lead to other health issues, including:
- Gallstones – cholesterol can crystallize and form stones in the gallbladder
- Pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas due to high triglyceride levels
- Osteoporosis – some studies suggest a link between high cholesterol and bone health
Recognizing the potential complications of hypercholesterolemia is essential for proactive health management. Regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce these risks. 🩺
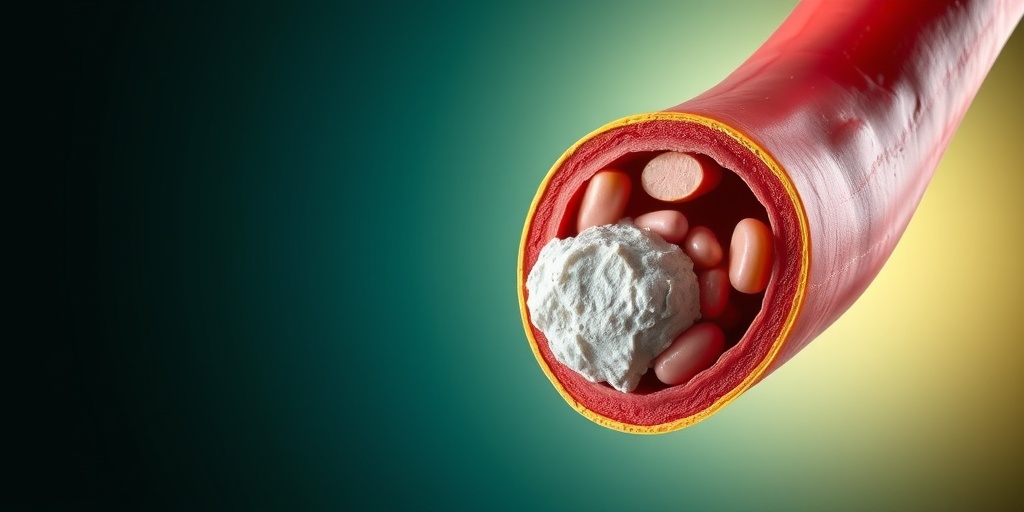
Hypercholesterolemia Treatment Options
Hypercholesterolemia, commonly referred to as high cholesterol, is a condition characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood. This can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and stroke. Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available to manage this condition.
Medications for Hypercholesterolemia
One of the most common approaches to treating hypercholesterolemia is through medication. Here are some of the primary types of medications used:
- Statins: These are the most widely prescribed medications for lowering cholesterol. Statins work by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for cholesterol production in the liver. Popular statins include atorvastatin, simvastatin, and rosuvastatin.
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: These medications help remove cholesterol from the bloodstream by binding to bile acids in the intestine. Examples include cholestyramine and colesevelam.
- Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors: Ezetimibe is a medication that reduces the absorption of cholesterol from the diet, helping to lower overall cholesterol levels.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: These are newer medications that can significantly lower LDL cholesterol levels. They are typically used for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia or those who have not responded to other treatments.
Understanding Familial Hypercholesterolemia
For some individuals, hypercholesterolemia is genetic, known as familial hypercholesterolemia. This condition requires more aggressive treatment strategies, often involving a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Genetic testing can help identify those at risk, allowing for early intervention.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is crucial for anyone undergoing treatment for hypercholesterolemia. Your healthcare provider will typically recommend routine blood tests to assess your cholesterol levels and adjust your treatment plan as necessary. The ICD 10 code for hypercholesterolemia is E78.0, which is used for billing and documentation purposes.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Cholesterol
In addition to medication, making lifestyle changes can significantly impact cholesterol levels and overall heart health. Here are some effective strategies:
Dietary Modifications
What you eat plays a vital role in managing hypercholesterolemia. Consider the following dietary changes:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, lentils, and fruits, can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Replace saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy with healthier fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
- Limit Trans Fats: Avoid processed foods that contain trans fats, as they can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3s, which can improve heart health.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise is another key component in managing cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, and swimming can help raise HDL (good cholesterol) and lower LDL (bad cholesterol).
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing hypercholesterolemia. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can lead to significant improvements in cholesterol levels. Consider working with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to develop a personalized weight management plan.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
If you smoke, quitting can improve your HDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, limiting alcohol intake can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of hypertension.
By combining medication with these lifestyle changes, individuals with hypercholesterolemia can effectively manage their cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of cardiovascular diseases. Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your treatment plan or lifestyle. 🩺💪

Frequently Asked Questions about Hypercholesterolemia
What is Hypercholesterolemia?
Hypercholesterolemia refers to an elevated level of cholesterol in the blood. It is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Understanding its causes and implications is crucial for effective management.
What are the symptoms of Hypercholesterolemia?
Many individuals with hypercholesterolemia may not experience noticeable symptoms. However, some potential signs can include:
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Yellowish patches on the skin (xanthomas)
What is Familial Hypercholesterolemia?
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic condition that results in extremely high cholesterol levels. It is often inherited and can lead to early heart disease if not treated properly. Testing for this condition is essential for affected individuals and their families.
How is Hypercholesterolemia diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a blood test to measure cholesterol levels. The ICD 10 code for hypercholesterolemia is E78.0, which healthcare providers use for billing and documentation purposes.
What are the treatment options for Hypercholesterolemia?
Treatment for hypercholesterolemia may include lifestyle changes and medications. Common approaches include:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet
- Regular physical activity
- Medications such as statins
Is there a difference between Hypercholesterolemia and Hyperlipidemia?
Yes, while hypercholesterolemia specifically refers to high cholesterol levels, hyperlipidemia is a broader term that encompasses elevated levels of all types of lipids in the blood, including triglycerides.
What lifestyle changes can help manage Hypercholesterolemia?
To manage hypercholesterolemia, consider the following lifestyle changes:
- Eating a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding tobacco smoke
Can Hypercholesterolemia lead to other health issues?
Yes, untreated hypercholesterolemia can lead to serious health problems, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Regular monitoring and management are essential to prevent these complications.
What is the ICD 10 code for Hypercholesterolemia?
The ICD 10 code for hypercholesterolemia is E78.0. This code is used by healthcare providers for diagnosis and billing purposes.
Are there any specific tests for Familial Hypercholesterolemia?
Yes, genetic testing can confirm familial hypercholesterolemia. A healthcare provider may recommend this test if there is a family history of high cholesterol or early heart disease.
What should I do if I suspect I have Hypercholesterolemia?
If you suspect you have hypercholesterolemia, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform the necessary tests and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.