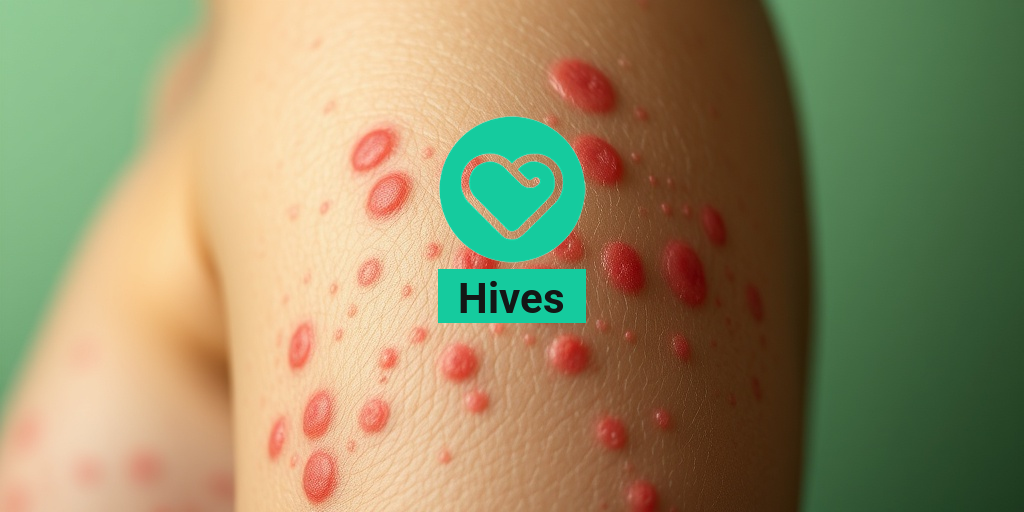
What Are Hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts that can appear on the skin. They can vary in size and shape, often changing rapidly. Hives can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergies, stress, medications, and even certain foods. Understanding what hives are and how they manifest is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Types of Hives
Hives can be classified into two main types:
- Acute Hives: These hives last less than six weeks and are often caused by an allergic reaction to food, medication, or insect stings.
- Chronic Hives: When hives persist for six weeks or longer, they are considered chronic. The exact cause is often harder to determine and may involve autoimmune responses.
Common Triggers
Identifying the triggers of hives is essential for prevention. Some common triggers include:
- Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs)
- Medications (e.g., antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Insect stings or bites
- Environmental factors (e.g., pollen, pet dander)
- Physical stimuli (e.g., pressure, temperature changes)
If you suspect you have hives, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Resources like Yesil Health AI can provide evidence-based answers to your health questions.
Hives Symptoms
The symptoms of hives can vary from person to person, but they typically include:
Itchy Welts
The most characteristic symptom of hives is the presence of itchy welts on the skin. These welts can appear anywhere on the body and may be red or skin-colored. The itching can be intense and may worsen at night, disrupting sleep.
Swelling
In some cases, hives can cause swelling in deeper layers of the skin, known as angioedema. This swelling often occurs around the eyes, lips, and throat, and can be accompanied by pain or discomfort.
Duration and Appearance
Hives can appear suddenly and may last for a few hours to several days. They often change shape and location, which can be confusing for those experiencing them. Some hives may fade while new ones develop, creating a cycle of symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While hives are often harmless, there are instances when medical attention is necessary. Seek immediate help if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat
- Symptoms that persist for more than a few days
These symptoms could indicate a more serious allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis, which requires urgent medical care.
Managing Hives
Managing hives involves identifying and avoiding triggers, as well as using over-the-counter antihistamines to relieve itching and discomfort. In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications or recommend lifestyle changes to help manage symptoms.
In conclusion, understanding hives is essential for effective management. If you experience symptoms, consider consulting a healthcare professional or utilizing resources like Yesil Health AI for reliable health information. Remember, while hives can be bothersome, they are often manageable with the right approach! 🌼
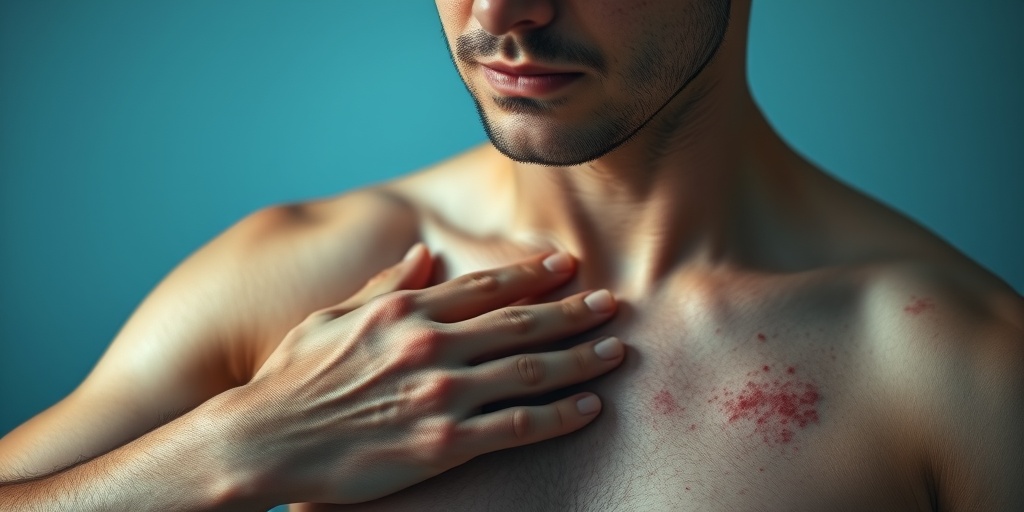

Hives Causes
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear anywhere on the body and often come and go quickly. Understanding the causes of hives is essential for effective management and treatment. Here are some common triggers:
Allergic Reactions
One of the most common causes of hives is an allergic reaction. When your body encounters an allergen, it releases histamines, which can lead to the development of hives. Common allergens include:
- Pollen
- Pet dander
- Food (such as nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy)
- Insect stings or bites
- Medications (like antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also trigger hives. These may include:
- Extreme temperatures (hot or cold)
- Sun exposure
- Pressure on the skin (from tight clothing or sitting for long periods)
Infections
Viral infections, such as the common cold or flu, can lead to hives as well. The body’s immune response to the infection may trigger the release of histamines, resulting in hives. Bacterial infections and parasitic infections can also be culprits.
Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress and anxiety can exacerbate or even trigger hives in some individuals. The body’s stress response can lead to the release of histamines, causing the characteristic welts. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or therapy can help reduce the occurrence of hives.
Chronic Conditions
In some cases, hives can be a symptom of an underlying chronic condition, such as:
- Autoimmune disorders (like lupus or thyroid disease)
- Chronic infections
- Other skin conditions (like eczema)
Hives Risk Factors
While anyone can develop hives, certain factors can increase your risk. Understanding these risk factors can help you take preventive measures and seek timely treatment.
Age and Gender
Hives can affect individuals of any age, but they are more common in young adults and children. Additionally, women are more likely to experience hives than men, particularly during hormonal changes such as menstruation or pregnancy.
Family History
If you have a family history of allergies or hives, you may be at a higher risk of developing them yourself. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in how your body reacts to allergens and environmental triggers.
Existing Allergies
Individuals with existing allergies, such as hay fever or food allergies, are more susceptible to developing hives. If you already have a known allergy, it’s crucial to manage it effectively to reduce the risk of hives.
Chronic Stress
As mentioned earlier, chronic stress can trigger hives. If you are frequently under stress, whether from work, personal life, or other factors, you may be at an increased risk. Finding healthy coping mechanisms is essential for overall well-being.
Exposure to Known Triggers
If you have identified specific triggers that cause your hives, such as certain foods or environmental factors, avoiding these triggers can significantly reduce your risk. Keeping a diary of your hives episodes can help you pinpoint what to avoid.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors of hives is vital for effective management. By identifying triggers and taking preventive measures, you can minimize the impact of hives on your daily life. If you experience persistent or severe hives, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. 🌼

Hives Diagnosis
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear suddenly and may last for a few hours or several days. Diagnosing hives can sometimes be straightforward, but it often requires a thorough understanding of the patient’s history and symptoms. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis of hives.
Understanding Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing hives is recognizing the symptoms. Common signs include:
- Itchy welts: These can be red or skin-colored and may appear anywhere on the body.
- Swelling: In some cases, hives can cause swelling in deeper layers of the skin, known as angioedema.
- Duration: Hives can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks).
Medical History and Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will typically start with a detailed medical history. They may ask questions such as:
- When did the hives first appear?
- Have you experienced any recent illnesses or infections?
- Are there any known allergies?
- What medications are you currently taking?
Following the medical history, a physical examination will be conducted to assess the hives and any associated symptoms. This helps to rule out other skin conditions that may resemble hives.
Allergy Testing
If the cause of the hives is unclear, your doctor may recommend allergy testing. This can include:
- Skin prick tests: Small amounts of allergens are introduced to the skin to see if a reaction occurs.
- Blood tests: These can help identify specific allergens or underlying conditions that may be causing the hives.
Identifying Triggers
Keeping a diary of your symptoms can be beneficial in identifying potential triggers. Note when the hives occur, what you were doing, and any foods or medications you consumed. Common triggers include:
- Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish)
- Insect stings or bites
- Medications (e.g., antibiotics, NSAIDs)
- Environmental factors (e.g., pollen, pet dander)
Hives Treatment Options
Treating hives effectively often depends on understanding their cause. While some cases resolve on their own, others may require medical intervention. Here are the most common treatment options for managing hives.
Over-the-Counter Antihistamines
For mild cases of hives, over-the-counter antihistamines are often the first line of treatment. These medications work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms. Popular options include:
- Loratadine (Claritin)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
These medications can help reduce itching and swelling, providing relief for those suffering from hives. However, it’s essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
Prescription Medications
For more severe or chronic cases of hives, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as:
- Prescription antihistamines: These may be more potent than over-the-counter options.
- Corticosteroids: These can help reduce inflammation and are typically used for short periods.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases where hives are linked to autoimmune conditions, these medications may be necessary.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
One of the most effective ways to manage hives is to identify and avoid triggers. This may involve:
- Working with an allergist to pinpoint specific allergens.
- Avoiding known irritants, such as certain foods or environmental factors.
- Making lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress and avoiding extreme temperatures.
Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, some home remedies may provide relief from hives:
- Cool compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected area can help soothe itching.
- Oatmeal baths: Soaking in an oatmeal bath can provide relief from itching and irritation.
- Calamine lotion: This can help alleviate discomfort and reduce itching.
While hives can be uncomfortable and frustrating, understanding the diagnosis and treatment options can empower individuals to manage their symptoms effectively. If you experience persistent or severe hives, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment. 🌼

Hives Home Remedies
Hives, also known as urticaria, can be an uncomfortable and sometimes distressing condition characterized by itchy, raised welts on the skin. While it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for persistent or severe cases, there are several home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms and provide relief. Here are some effective options:
1. Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the affected areas can help reduce swelling and soothe itching. Simply wrap ice cubes in a clean cloth or use a cold pack, and apply it to the hives for about 10-15 minutes. This method can provide immediate relief and is especially useful during flare-ups. ❄️
2. Oatmeal Baths
Soaking in an oatmeal bath can be incredibly soothing for irritated skin. Oatmeal contains anti-inflammatory properties that can help calm the skin and reduce itching. To prepare an oatmeal bath:
- Grind plain oats into a fine powder.
- Add the powdered oats to warm bathwater.
- Soak for 15-20 minutes, allowing the skin to absorb the soothing properties.
This natural remedy is not only effective but also a relaxing way to unwind. 🛁
3. Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera is renowned for its healing properties and can be particularly beneficial for hives. Its cooling effect helps to soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the hives and let it dry. This can provide instant relief and promote healing. 🌿
4. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is another popular home remedy for hives. Its natural acidity can help balance the skin’s pH and reduce itching. To use ACV:
- Mix equal parts of apple cider vinegar and water.
- Apply the mixture to the affected areas using a cotton ball.
- Leave it on for about 30 minutes before rinsing off.
Be cautious if you have sensitive skin, as ACV can be potent. 🍏
5. Herbal Teas
Drinking herbal teas like chamomile or peppermint can help calm the body and reduce stress, which may trigger hives in some individuals. These teas have anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in soothing the skin from within. Enjoy a warm cup of tea and let its calming effects work their magic. ☕
Hives Prevention Tips
Preventing hives is often about identifying triggers and making lifestyle adjustments. Here are some practical prevention tips to help you avoid flare-ups:
1. Identify Triggers
Keeping a diary of your hives can help you identify potential triggers. Common culprits include:
- Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs)
- Medications (e.g., antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Environmental factors (e.g., pollen, pet dander, dust mites)
Once you identify your triggers, you can take steps to avoid them. 🕵️♂️
2. Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate hives, so finding effective ways to manage stress is crucial. Consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as:
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Deep breathing exercises
Regular physical activity can also help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. 🧘♀️
3. Wear Loose Clothing
Tight clothing can irritate the skin and trigger hives. Opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics to minimize friction and allow your skin to breathe. Natural fibers like cotton are often the best choice. 👕
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps keep your skin hydrated and can reduce the likelihood of hives. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day, and consider incorporating hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables into your diet. 💧
5. Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience frequent or severe hives, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They can help identify underlying conditions and recommend appropriate treatments or medications to manage your symptoms effectively. 🩺
By implementing these home remedies and prevention tips, you can take proactive steps to manage hives and improve your quality of life. Remember, everyone’s body is different, so what works for one person may not work for another. Always listen to your body and seek professional advice when needed.

Frequently Asked Questions about Hives
What are hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear anywhere on the body and are often a reaction to allergens or irritants.
What causes hives?
There are numerous potential causes of hives, including:
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or insect stings
- Environmental factors such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites
- Physical triggers like heat, cold, or pressure on the skin
- Stress and anxiety
How long do hives last?
The duration of hives can vary. Acute hives may last a few hours to a few days, while chronic hives can persist for six weeks or longer. If hives last more than a few days, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious. They are a reaction of the immune system and cannot be spread from person to person.
What are the symptoms of hives?
The primary symptom of hives is the appearance of itchy welts on the skin. Other symptoms may include:
- Swelling in areas such as the face, lips, or throat
- Burning or stinging sensations
- Flushing or redness of the skin
How can I treat hives at home?
For mild cases of hives, you can try the following home remedies:
- Taking antihistamines to relieve itching
- Applying cool compresses to the affected areas
- Avoiding known triggers and irritants
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or if your hives persist for an extended period, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. These could be signs of a serious allergic reaction.
Can stress cause hives?
Yes, stress can be a trigger for hives. Emotional stress can lead to physical reactions in the body, including the development of hives. Managing stress through relaxation techniques may help reduce outbreaks.
Are there any long-term effects of hives?
In most cases, hives do not have long-term effects. However, chronic hives can lead to ongoing discomfort and may require medical treatment to manage symptoms effectively.
Can certain foods trigger hives?
Yes, certain foods can trigger hives in sensitive individuals. Common food triggers include:
- Nuts
- Shellfish
- Eggs
- Dairy products
If you suspect a food allergy, it is best to consult with a healthcare provider for proper testing and guidance.