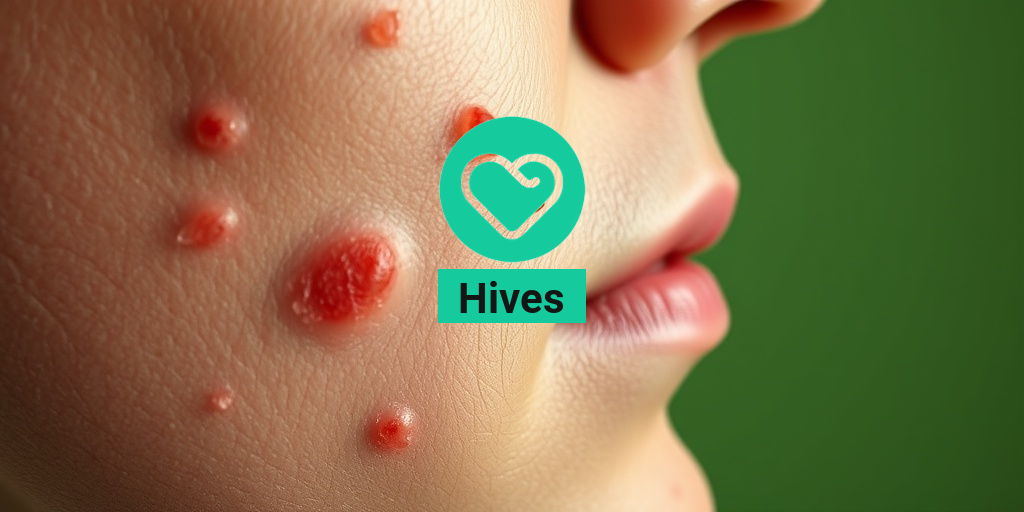
What Are Hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear anywhere on the body and often change in appearance and location within a short period. Hives are typically a reaction of the skin to allergens, irritants, or other triggers, and they can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks).
Understanding the Causes of Hives
The exact cause of hives can be complex, as they can be triggered by a variety of factors. Some common causes include:
- Allergic Reactions: Foods, medications, and insect stings can trigger hives in sensitive individuals.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature changes, sunlight, and pressure on the skin can lead to hives.
- Infections: Viral infections, especially in children, can cause hives as part of the body’s immune response.
- Stress: Emotional stress can also be a contributing factor for some people.
Understanding what triggers your hives is crucial for effective management. Keeping a diary of your symptoms and potential triggers can help you identify patterns and avoid future outbreaks.
Hives Symptoms
The symptoms of hives can vary widely from person to person, but the most common signs include:
Itchy Welts
The hallmark of hives is the presence of itchy welts on the skin. These welts can be small or large, and they often appear suddenly. The itching can range from mild to severe, making it uncomfortable for those affected.
Changes in Appearance
Hives can change in size and shape, often appearing and disappearing within hours. This characteristic makes them distinct from other skin conditions. The welts may also become red or skin-colored, and they can merge to form larger patches.
Swelling
In some cases, hives can cause swelling in deeper layers of the skin, known as angioedema. This can lead to swelling in areas such as the lips, eyes, and throat, which may require immediate medical attention if it affects breathing.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While hives are often harmless and resolve on their own, there are instances when you should seek medical help:
- If you experience difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- If the swelling spreads rapidly or affects your face and throat.
- If hives persist for more than a few days without improvement.
For those looking for reliable information and support regarding hives, Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) is a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. They can provide insights into managing symptoms and understanding potential triggers.
Conclusion
Hives can be an uncomfortable and frustrating condition, but understanding what they are and recognizing their symptoms can empower you to manage them effectively. If you suspect you have hives or are experiencing persistent symptoms, consider consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options. Remember, knowledge is key to managing your health! 🌟

Hives Triggers
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. Understanding the triggers of hives is essential for managing and preventing outbreaks. Let’s explore some common causes that can lead to this uncomfortable condition.
Allergic Reactions
One of the most prevalent triggers of hives is an allergic reaction. This can occur due to:
- Food allergies: Common culprits include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy.
- Medications: Certain antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and even some over-the-counter medications can provoke hives.
- Insect stings or bites: Reactions to bee stings or mosquito bites can also lead to hives.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also play a significant role in triggering hives. These include:
- Temperature changes: Sudden exposure to heat or cold can cause hives to develop.
- Sunlight: Some individuals may experience hives after prolonged sun exposure.
- Pressure: Tight clothing or pressure on the skin can lead to a specific type of hives known as pressure urticaria.
Infections and Illnesses
Infections, particularly viral infections, can also trigger hives. Conditions such as:
- Common colds
- Strep throat
- Mononucleosis
can lead to hives as a symptom. Additionally, autoimmune diseases may also be linked to chronic hives.
Stress and Emotional Factors
Believe it or not, stress can be a significant trigger for hives. Emotional stress can lead to physical reactions in the body, including the development of hives. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress levels and potentially reduce the occurrence of hives.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can also trigger hives. Many women report outbreaks during:
- Menstrual cycles
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
These hormonal changes can affect the skin’s sensitivity and lead to hives.
Hives Diagnosis
Diagnosing hives can sometimes be straightforward, but it may require a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis of hives.
Medical History Review
The first step in diagnosing hives is a comprehensive review of your medical history. Your doctor will ask about:
- Symptoms: When did the hives start? How long do they last? Are they itchy?
- Triggers: Have you noticed any specific foods, medications, or activities that seem to provoke the hives?
- Family history: Is there a history of allergies or hives in your family?
Physical Examination
A physical examination is crucial in diagnosing hives. Your doctor will inspect the affected areas of your skin to assess:
- Appearance: The size, shape, and distribution of the hives.
- Duration: How long the hives have been present.
Allergy Testing
If an allergic reaction is suspected, your doctor may recommend allergy testing. This can include:
- Skin prick tests: Small amounts of allergens are introduced to the skin to see if a reaction occurs.
- Blood tests: These can help identify specific allergens or immune responses.
Additional Tests
In some cases, further testing may be necessary to rule out other conditions. This could include:
- Blood tests: To check for underlying infections or autoimmune disorders.
- Skin biopsy: Rarely, a biopsy may be performed to examine the skin tissue.
Understanding the triggers and diagnosis of hives is essential for effective management. If you experience persistent or severe hives, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and treatment plan. 🌟
Hives Treatment Options
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can be triggered by various factors, including allergies, stress, and certain medications. If you’re experiencing hives, it’s essential to explore effective treatment options to alleviate discomfort and prevent future outbreaks. Here are some common treatment options:
Over-the-Counter Antihistamines
One of the most common treatments for hives is the use of over-the-counter antihistamines. These medications work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms. Popular options include:
- Loratadine (Claritin)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
These antihistamines can help reduce itching and swelling, providing relief from hives. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Prescription Medications
For more severe cases of hives, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications. These can include:
- Prescription antihistamines – These may be more potent than over-the-counter options.
- Corticosteroids – These medications can help reduce inflammation and are typically used for short-term treatment.
- Immunosuppressants – In chronic cases, medications that suppress the immune system may be necessary.
It’s crucial to discuss the potential side effects and benefits of these medications with your healthcare provider.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Understanding what triggers your hives is vital for effective management. Common triggers include:
- Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish)
- Insect stings or bites
- Medications (e.g., antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Environmental factors (e.g., pollen, pet dander)
Keeping a hives diary can help you track outbreaks and identify patterns related to your triggers. Once you know what causes your hives, you can take steps to avoid these triggers and reduce the likelihood of future episodes.
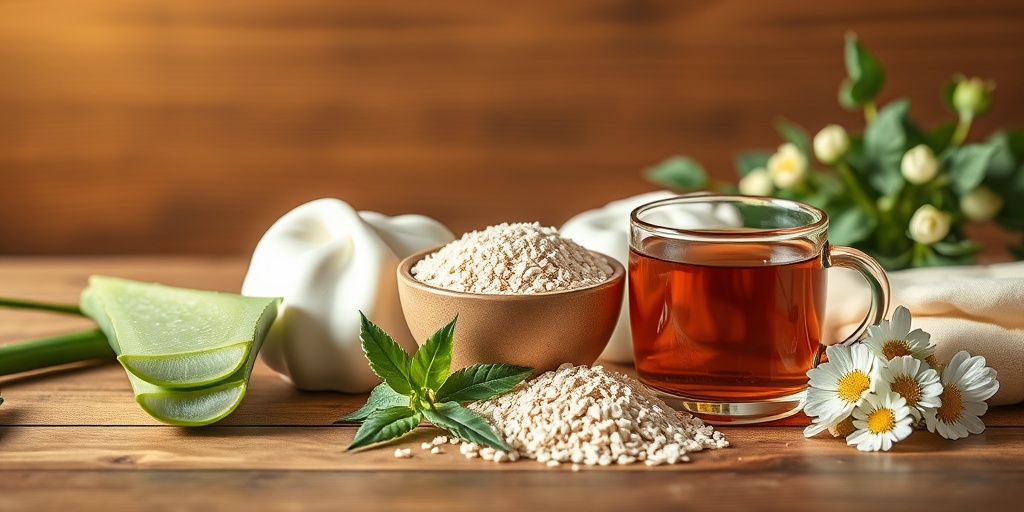
Hives Home Remedies
If you’re looking for natural ways to alleviate the discomfort of hives, several home remedies may provide relief. While these remedies may not replace medical treatment, they can complement your overall management strategy.
Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the affected areas can help soothe itching and reduce swelling. Simply wrap ice in a cloth or use a cold pack and apply it to the hives for 10-15 minutes. This can provide immediate relief and help calm the skin. ❄️
Oatmeal Baths
Soaking in an oatmeal bath can be incredibly soothing for itchy skin. Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce irritation. To prepare an oatmeal bath:
- Grind plain oats into a fine powder.
- Add the powdered oats to warm bathwater.
- Soak for 15-20 minutes.
This natural remedy can help relieve itching and provide a calming effect on the skin. 🛁
Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera is well-known for its soothing properties and can be applied directly to hives. It helps hydrate the skin and reduce inflammation. Simply apply fresh aloe vera gel to the affected areas and let it dry. This can provide a cooling sensation and help alleviate discomfort. 🌿
Apple Cider Vinegar
Some people find relief from hives by using apple cider vinegar. It can be diluted with water and applied topically or added to a bath. Its anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce itching and redness. However, always do a patch test first to ensure you don’t have a reaction. 🍏
While these home remedies can be helpful, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional if your hives persist or worsen. They can help determine the best course of action tailored to your specific needs.

Hives Prevention Tips
Hives, also known as urticaria, can be an uncomfortable and sometimes distressing condition characterized by raised, itchy welts on the skin. While it’s essential to know how to treat hives, understanding how to prevent them can significantly improve your quality of life. Here are some effective hives prevention tips to help you avoid outbreaks.
Identify and Avoid Triggers
One of the most effective ways to prevent hives is to identify what triggers your outbreaks. Common triggers include:
- Food Allergies: Certain foods like nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy can cause hives.
- Medications: Some medications, including antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may lead to hives.
- Environmental Factors: Pollen, pet dander, and dust mites can trigger allergic reactions.
- Temperature Changes: Sudden changes in temperature, such as hot showers or cold weather, can provoke hives.
Keeping a hives diary can help you track your outbreaks and identify patterns related to your triggers. 📝
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can bolster your immune system and reduce the likelihood of hives. Here are some tips:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support your overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress and improve your immune function.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin health and can prevent dryness, which may exacerbate hives.
Manage Stress Effectively
Stress is a known trigger for many skin conditions, including hives. Implementing stress management techniques can be beneficial:
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness can help you stay calm and reduce stress levels.
- Yoga: This ancient practice combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, which can help alleviate stress.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing techniques can help you relax and manage anxiety.
Use Hypoallergenic Products
When it comes to skincare and household products, opting for hypoallergenic options can minimize the risk of hives. Look for:
- Fragrance-Free Soaps and Lotions: These products are less likely to irritate your skin.
- Non-Irritating Laundry Detergents: Choose detergents that are free from dyes and fragrances.
Hives: When to See a Doctor
While many cases of hives are mild and can be managed at home, there are instances when you should seek medical attention. Knowing when to see a doctor can help prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Persistent or Severe Symptoms
If your hives last longer than six weeks or are accompanied by severe symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Symptoms that warrant a visit include:
- Difficulty Breathing: This could indicate a serious allergic reaction.
- Swelling of the Face or Throat: This may also signal anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition.
- Widespread Rash: If the rash covers a large area of your body or is spreading rapidly, seek medical help.
Signs of Infection
In some cases, hives can become infected. Look for signs such as:
- Increased Redness: If the area around the hives becomes more inflamed.
- Pus or Drainage: Any discharge from the hives may indicate an infection.
- Fever: A fever accompanying hives could suggest an underlying infection.
Unexplained Hives
If you experience hives without a known cause, it’s crucial to consult a doctor. They may perform tests to determine if there’s an underlying condition, such as:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like lupus or thyroid disease can manifest as hives.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections may trigger hives in some individuals.
Understanding hives and knowing when to seek medical advice can empower you to manage this condition effectively. Remember, your health is paramount, and timely intervention can make all the difference! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Hives
What are hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear anywhere on the body and are often a reaction to allergens or irritants.
What causes hives?
Hives can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or insect stings
- Environmental factors such as pollen or pet dander
- Physical stimuli like heat, cold, or pressure
- Stress or infections
How long do hives last?
The duration of hives can vary. Acute hives may last a few hours to a few days, while chronic hives can persist for six weeks or longer. If hives last more than a few days, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious. They are a skin reaction and cannot be spread from person to person.
How can I treat hives at home?
For mild cases of hives, you can try the following home remedies:
- Apply a cool compress to the affected area
- Take antihistamines to relieve itching
- Avoid known triggers and irritants
- Wear loose-fitting clothing to minimize irritation
When should I see a doctor for hives?
If you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or if your hives persist for an extended period, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. 🚑
Can hives appear on the face?
Yes, hives can appear on the face as well as other parts of the body. Facial hives can be particularly concerning due to their visibility and potential for swelling.
What does it mean if I have chronic hives?
Chronic hives may indicate an underlying health issue or persistent exposure to a trigger. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help with hives?
Yes, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage hives:
- Maintain a healthy diet to avoid food triggers
- Practice stress management techniques
- Stay hydrated and get enough sleep
Can medications cause hives?
Yes, certain medications can trigger hives as a side effect. If you suspect a medication is causing your hives, consult your doctor for alternatives.