What Are Hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear anywhere on the body and often change location within a short period. Hives are typically a reaction of the skin to allergens, stress, or other triggers, and they can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks). Understanding what hives are and their underlying causes can help you manage and treat them effectively.
How Do Hives Develop?
Hives occur when the body releases histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream. This release can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Common allergens include foods (like nuts, shellfish, and eggs), medications (such as antibiotics), and insect stings.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature changes, sunlight, and pressure on the skin can also lead to hives.
- Stress: Emotional stress can trigger hives in some individuals, leading to a cycle of itching and discomfort.
- Infections: Viral infections, particularly in children, can cause hives as a symptom.
While hives can be uncomfortable and distressing, they are usually not serious and often resolve on their own. However, in some cases, they can indicate a more severe allergic reaction, especially if accompanied by symptoms like difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Hives Symptoms
The primary symptom of hives is the appearance of welts on the skin. These welts can vary in size and may be surrounded by redness. Here are some common symptoms associated with hives:
Itchy Skin
One of the most bothersome symptoms of hives is intense itching. The itchiness can range from mild to severe, leading to scratching that may worsen the condition. It’s essential to avoid scratching, as this can lead to skin damage and potential infections.
Welts of Varying Sizes
Hives can appear as small bumps or large patches, and they may merge to form larger areas of raised skin. The welts can change shape and location rapidly, often disappearing and reappearing within hours.
Color Changes
The welts may appear red or skin-colored and can be surrounded by a halo of redness. The color and appearance can vary based on the individual’s skin tone and the severity of the reaction.
Duration of Symptoms
Acute hives typically last less than six weeks, with individual welts often disappearing within 24 hours. Chronic hives, on the other hand, can persist for months or even years, requiring ongoing management and treatment.
Associated Symptoms
In some cases, hives may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Swelling: Angioedema, or swelling beneath the skin, can occur, particularly around the eyes, lips, and throat.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Some individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain if the hives are related to a food allergy.
- Respiratory Symptoms: In severe cases, hives can be part of an anaphylactic reaction, leading to difficulty breathing or swallowing.
If you notice any of these associated symptoms, especially difficulty breathing or swelling of the throat, it is crucial to seek emergency medical help.
For those dealing with hives, understanding the symptoms and potential triggers can be invaluable. If you’re looking for more information on managing hives or other health-related queries, consider visiting Yesil Health AI for evidence-based answers and resources. 🌿

Hives Triggers
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. Understanding the triggers of hives is essential for managing and preventing outbreaks. These triggers can be diverse, ranging from environmental factors to dietary choices. Let’s explore some of the most common triggers that can lead to hives.
Allergic Reactions
One of the primary causes of hives is an allergic reaction. When your immune system reacts to a substance it perceives as harmful, it releases histamines, leading to the characteristic welts. Common allergens include:
- Food: Shellfish, nuts, eggs, and dairy are frequent culprits.
- Medications: Antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and certain pain relievers can trigger hives.
- Insect Stings: Bee or wasp stings can cause severe allergic reactions, resulting in hives.
Environmental Factors
Environmental triggers can also play a significant role in the development of hives. These include:
- Temperature Changes: Sudden changes in temperature, such as exposure to heat or cold, can provoke hives.
- Sunlight: Some individuals may develop hives in response to sunlight exposure, a condition known as solar urticaria.
- Pressure: Physical pressure on the skin, such as from tight clothing or sitting for long periods, can lead to hives.
Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress is another significant trigger for hives. Emotional stress can lead to the release of histamines, causing outbreaks. If you notice that your hives flare up during stressful situations, it may be beneficial to explore stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises. 🧘♀️
Infections
Viral infections, particularly in children, can also lead to hives. Conditions like the common cold or other viral illnesses may trigger an immune response that results in hives. If you suspect an infection is causing your hives, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment.
Chronic Conditions
Some chronic conditions can lead to persistent hives. For example, autoimmune disorders like lupus or thyroid disease may cause chronic urticaria. If you experience hives regularly, it’s essential to discuss this with your doctor to rule out underlying health issues.
Hives Diagnosis
Diagnosing hives can sometimes be straightforward, but in other cases, it may require a thorough investigation. Understanding how healthcare professionals diagnose hives can help you navigate the process more effectively.
Medical History and Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing hives typically involves a detailed medical history. Your doctor will ask about:
- Onset and Duration: When did the hives start, and how long do they last?
- Associated Symptoms: Are there any other symptoms accompanying the hives, such as swelling or difficulty breathing?
- Potential Triggers: Have you noticed any specific triggers that seem to provoke your hives?
Physical Examination
A physical examination is crucial in diagnosing hives. Your doctor will inspect the welts and may ask you to describe their characteristics, such as:
- Size and Shape: Are the hives large or small? Are they round or irregularly shaped?
- Color: Are the hives red, pale, or a different color?
- Location: Where on your body do the hives appear most frequently?
Allergy Testing
If your doctor suspects that allergies are the cause of your hives, they may recommend allergy testing. This can include:
- Skin Prick Tests: Small amounts of allergens are introduced to your skin to see if a reaction occurs.
- Blood Tests: These tests can measure specific antibodies in your blood that indicate an allergic response.
Additional Tests
In some cases, further testing may be necessary to rule out other conditions. This could include:
- Patch Testing: Used to identify delayed allergic reactions.
- Biopsy: Rarely, a skin biopsy may be performed to examine the skin and rule out other skin conditions.
Understanding the triggers and diagnosis of hives is crucial for effective management. If you experience hives, consider keeping a diary to track your symptoms and potential triggers, which can be invaluable during your medical consultations. 📝

Hives Treatment Options
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can be triggered by various factors, including allergies, stress, and certain medications. If you’re experiencing hives, it’s essential to explore effective treatment options to alleviate your symptoms. Here are some common treatments:
1. Antihistamines
One of the most common treatments for hives is the use of antihistamines. These medications work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic reactions. Over-the-counter options like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and cetirizine (Zyrtec) can provide quick relief from itching and swelling. For chronic hives, your doctor may prescribe stronger antihistamines or a combination of medications.
2. Corticosteroids
In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. These medications can be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the severity of the hives. It’s important to use corticosteroids under medical supervision, as long-term use can lead to side effects.
3. Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial in managing hives. Common triggers include:
- Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish)
- Insect stings
- Medications (e.g., antibiotics, NSAIDs)
- Stress and anxiety
- Temperature changes (heat or cold)
Keeping a hives diary can help you track your symptoms and identify potential triggers.
4. Immunotherapy
For individuals with chronic hives that do not respond to standard treatments, immunotherapy may be an option. This treatment involves gradually exposing the patient to the allergen in controlled doses, helping the immune system build tolerance over time. Consult with an allergist to determine if this approach is suitable for you.
5. Epinephrine Auto-Injectors
In cases where hives are accompanied by severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, carrying an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) is essential. This device can quickly reverse the symptoms of a severe allergic reaction and is a critical tool for those with known severe allergies.
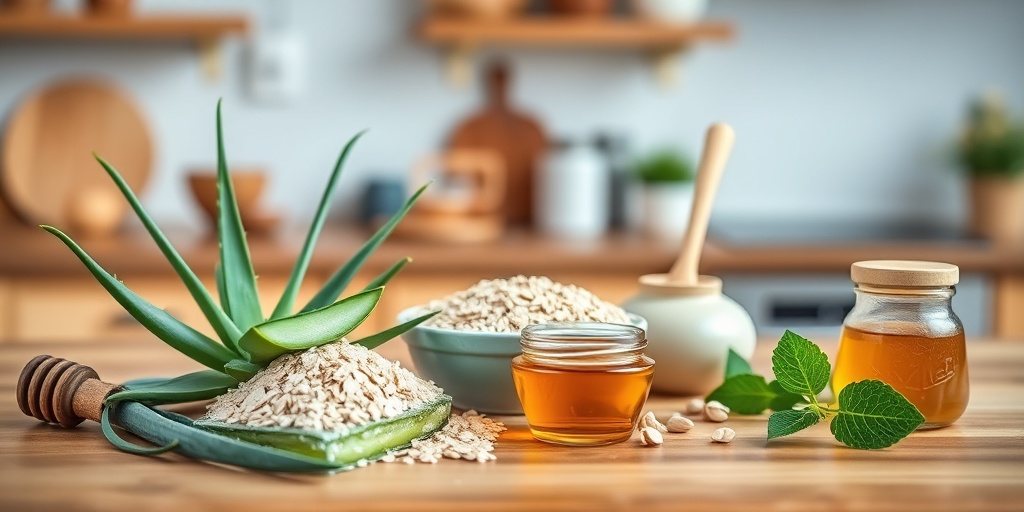
Hives Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can help soothe the discomfort associated with hives. These natural approaches can be effective in providing relief and are often easy to implement. Here are some popular home remedies:
1. Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the affected areas can help reduce swelling and itching. Simply wrap ice in a cloth or use a cold pack and apply it to the hives for 10-15 minutes. This method can provide immediate relief and is especially helpful during flare-ups. ❄️
2. Oatmeal Baths
Taking an oatmeal bath can be soothing for itchy skin. Colloidal oatmeal is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and can help calm irritated skin. Add a cup of colloidal oatmeal to your bathwater and soak for 15-20 minutes. This remedy is particularly beneficial for children experiencing hives. 🛁
3. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is renowned for its soothing properties. Applying fresh aloe vera gel directly to the hives can help reduce inflammation and provide relief from itching. Its cooling effect can be particularly comforting during flare-ups. 🌿
4. Baking Soda Paste
Creating a paste with baking soda and water can also help alleviate itching. Mix equal parts baking soda and water to form a paste, then apply it to the hives. Leave it on for about 10-15 minutes before rinsing off. This remedy can help neutralize the skin’s pH and reduce irritation.
5. Herbal Remedies
Some herbal remedies, such as chamomile and green tea, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help soothe hives. Drinking these teas or using chamomile tea bags as a compress can provide additional relief. 🍵
While these home remedies can be effective, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional if your hives persist or worsen. Understanding the underlying cause of your hives is crucial for effective management and treatment.

Hives Prevention Tips
Hives, also known as urticaria, can be an uncomfortable and frustrating condition. They appear as raised, itchy welts on the skin and can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, stress, and certain medications. While it may not be possible to prevent hives entirely, there are several effective strategies you can adopt to minimize your risk of outbreaks. Here are some hives prevention tips to keep in mind:
1. Identify and Avoid Triggers
The first step in preventing hives is to identify what triggers your outbreaks. Common triggers include:
- Food Allergies: Common culprits include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy.
- Environmental Factors: Pollen, pet dander, and dust mites can provoke hives.
- Medications: Some people may develop hives from antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Stress: Emotional stress can lead to hives in some individuals.
Keeping a hives diary can help you track your outbreaks and identify patterns related to specific triggers. Once you know what to avoid, you can take proactive measures to reduce your exposure.
2. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Living a healthy lifestyle can bolster your immune system and reduce the likelihood of hives. Here are some tips:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps maintain skin health and can reduce irritation.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your immune system.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Since stress is a known trigger for hives, finding effective ways to manage it is crucial. Consider incorporating relaxation techniques into your routine, such as:
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help calm your mind and reduce stress levels.
- Yoga: This combines physical activity with relaxation, making it an excellent stress reliever.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing techniques can help you relax during stressful situations.
4. Use Hypoallergenic Products
When it comes to skincare and household products, opting for hypoallergenic options can help prevent hives. Look for:
- Fragrance-Free Soaps and Lotions: These are less likely to irritate sensitive skin.
- Non-Irritating Laundry Detergents: Choose products that are free from dyes and harsh chemicals.
- Natural Cleaning Supplies: Consider using vinegar or baking soda as alternatives to chemical cleaners.
5. Consult with a Healthcare Professional
If you have a history of hives or are at risk, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and may recommend:
- Allergy Testing: Identifying specific allergens can help you avoid triggers.
- Preventive Medications: Antihistamines or other medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms.
Hives: When to See a Doctor
While many cases of hives are mild and resolve on their own, there are instances when medical attention is necessary. Knowing when to seek help can prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Here are some guidelines on when to see a doctor for hives:
1. Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If your hives last longer than six weeks or continue to worsen despite home treatment, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. Chronic hives can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires further investigation.
2. Difficulty Breathing or Swelling
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Shortness of Breath: This could indicate a severe allergic reaction.
- Swelling of the Face, Lips, or Tongue: This may also signal anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition.
3. Accompanying Symptoms
If your hives are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as:
- Fever: This may indicate an infection.
- Joint Pain: This could suggest an autoimmune disorder.
In such cases, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly.
4. History of Severe Allergic Reactions
If you have a history of severe allergic reactions, it’s crucial to consult with a doctor whenever you experience hives. They can help you develop a management plan and provide guidance on using an epinephrine auto-injector if necessary.
5. Concerns About Medication Side Effects
If you suspect that your hives are a side effect of a medication you’re taking, contact your healthcare provider. They can assess your situation and may suggest alternative treatments.
In summary, while hives can be bothersome, understanding how to prevent them and knowing when to seek medical help can significantly improve your quality of life. Stay informed and proactive about your health! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Hives
What are hives?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. They can appear anywhere on the body and are often a reaction to allergens, stress, or other triggers.
What causes hives?
There are numerous potential causes of hives, including:
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or insect stings
- Environmental factors such as pollen or pet dander
- Physical triggers like heat, cold, or pressure
- Stress and anxiety
- Infections or illnesses
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious. They are a skin reaction and cannot be spread from person to person.
How can I treat hives at home?
For mild cases of hives, you can try the following home remedies:
- Apply a cool compress to the affected area
- Take over-the-counter antihistamines to relieve itching
- Avoid known triggers, such as certain foods or stressors
- Wear loose-fitting clothing to minimize irritation
When should I see a doctor for hives?
If you experience severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or if your hives persist for more than a few days, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Can hives occur in babies?
Yes, hives can occur in babies and young children. If you notice welts or rashes on your child’s skin, consult a pediatrician for proper evaluation and treatment.
What is the difference between hives and a rash?
While both hives and rashes can cause skin irritation, hives are typically raised, itchy welts that can come and go quickly, whereas rashes are often more persistent and can cover larger areas of the skin.
Can stress cause hives?
Yes, stress is a known trigger for hives. Emotional or physical stress can lead to the release of histamines in the body, resulting in skin reactions.
Are there any long-term effects of hives?
In most cases, hives are temporary and resolve without long-term effects. However, chronic hives may require ongoing management and can impact quality of life.
How can I prevent hives?
To help prevent hives, consider the following tips:
- Identify and avoid known allergens
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise
Is there a connection between hives and food allergies?
Yes, certain food allergies can trigger hives. Common allergens include nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy. If you suspect a food allergy, consult with a healthcare professional for testing and guidance.