What Is a Hip Fracture?
A hip fracture is a serious injury that occurs when there is a break in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone) near the hip joint. This type of fracture is particularly common among older adults, especially those with osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and makes them more susceptible to breaks. Hip fractures can significantly impact mobility and quality of life, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
There are several types of hip fractures, including:
- Intracapsular Fractures: These occur within the hip joint capsule and can affect blood supply to the femoral head.
- Extracapsular Fractures: These occur outside the hip joint capsule and are generally more stable.
- Subcapital Fractures: These are located just below the head of the femur.
Understanding the nature of a hip fracture is essential for effective treatment and recovery. If you suspect a hip fracture, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and a quicker return to daily activities.
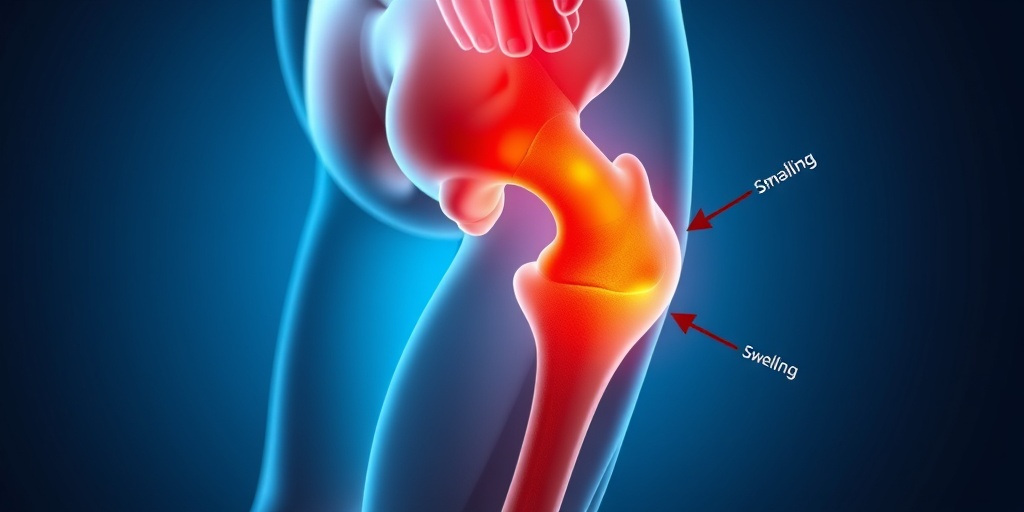
Hip Fracture Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of a hip fracture is vital for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Severe pain in the hip or groin area is often the first sign. This pain may worsen with movement.
- Inability to Move: Individuals may find it difficult or impossible to stand or walk after the injury.
- Swelling and Bruising: The area around the hip may become swollen and bruised.
- Deformity: The leg on the injured side may appear shorter or turned outward.
In elderly patients, symptoms may sometimes be less obvious, and they might attribute their discomfort to aging or arthritis. However, if any of the above symptoms are present, especially after a fall, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
At Yesil Health AI, you can find more information about hip fractures and their management. Understanding the symptoms and seeking timely medical advice can make a significant difference in recovery outcomes.
In conclusion, a hip fracture is a serious condition that requires immediate attention. By being aware of the symptoms and types of fractures, you can take proactive steps towards recovery and regain your mobility. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful recovery! 🦴✨
Causes of Hip Fractures
Hip fractures are serious injuries that can significantly impact a person’s mobility and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes of hip fractures is crucial for prevention and timely treatment. Here are some of the primary causes:
1. Falls
The most common cause of hip fractures, especially in the elderly, is falls. A simple slip or trip can lead to a fracture, particularly if the individual has weakened bones. Factors contributing to falls include:
- Environmental hazards: Clutter, poor lighting, and slippery surfaces can increase the risk of falling.
- Physical limitations: Weakness, balance issues, or impaired vision can make falls more likely.
2. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. As people age, bone density naturally decreases, which can lead to hip fractures even with minimal trauma. Regular screening and preventive measures are essential for those at risk.
3. High-impact activities
While falls are the leading cause, high-impact activities can also result in hip fractures. Athletes or individuals engaged in contact sports may experience fractures due to sudden impacts or awkward falls. It’s important for active individuals to maintain strength and flexibility to reduce the risk.
4. Medical conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the likelihood of hip fractures. These include:
- Neurological disorders: Conditions like Parkinson’s disease can affect balance and coordination.
- Chronic illnesses: Diseases such as diabetes or heart disease can contribute to overall frailty.
5. Medications
Some medications can affect bone health or increase the risk of falls. For example, certain sedatives, antidepressants, and blood pressure medications may lead to dizziness or impaired coordination. Always consult with a healthcare provider about the potential side effects of medications.
Risk Factors for Hip Fractures
Identifying risk factors for hip fractures is essential for prevention, especially in vulnerable populations. Here are some key risk factors to consider:
1. Age
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for hip fractures. As individuals age, their bones naturally become weaker, and the likelihood of falls increases. Women, in particular, are at higher risk post-menopause due to decreased estrogen levels, which can accelerate bone loss.
2. Gender
Women are more likely than men to suffer from hip fractures, primarily due to the effects of menopause on bone density. However, men are not immune, especially if they have risk factors such as low testosterone levels or a history of smoking.
3. Family history
A family history of osteoporosis or hip fractures can increase an individual’s risk. Genetic factors play a role in bone density and strength, making it essential to be aware of family medical history.
4. Lifestyle choices
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can contribute to the risk of hip fractures. Factors include:
- Smoking: Smoking can weaken bones and reduce overall health.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: High alcohol intake can impair balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls.
- Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weakened muscles and bones, making falls more likely.
5. Nutritional deficiencies
A diet lacking in essential nutrients, particularly calcium and vitamin D, can lead to weakened bones. Ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients is vital for maintaining bone health and preventing fractures.
6. Chronic health conditions
Chronic health conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, kidney disease, or hyperthyroidism can affect bone health and increase the risk of fractures. Regular check-ups and management of these conditions are crucial for reducing risk.
By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with hip fractures, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their bone health and reduce the likelihood of injury. 🦴💪
Diagnosing a Hip Fracture
Diagnosing a hip fracture is a crucial step in ensuring proper treatment and recovery. This injury is particularly common among the elderly, but it can occur in individuals of all ages due to falls, accidents, or sports injuries. Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic methods can help in seeking timely medical attention.
Common Symptoms of a Hip Fracture
Recognizing the symptoms of a hip fracture is essential for prompt diagnosis. Here are some common signs to look out for:
- Pain in the hip or groin: This is often the most immediate and noticeable symptom.
- Inability to bear weight: Many individuals find it difficult or impossible to put weight on the affected leg.
- Swelling and bruising: The area around the hip may become swollen and bruised.
- Deformity: The leg may appear shorter or turned outward compared to the other leg.
Diagnostic Procedures
If a hip fracture is suspected, a healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination followed by imaging tests. Here are the common diagnostic procedures:
- X-rays: This is the most common imaging test used to confirm a hip fracture. It can reveal the location and type of fracture.
- CT scans: In some cases, a CT scan may be ordered for a more detailed view of the hip joint.
- MRIs: An MRI can be useful for detecting hairline fractures that may not be visible on X-rays.
Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment and recovery. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a hip fracture, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. 🏥
Hip Fracture Treatment Options
Treating a hip fracture effectively is vital for restoring mobility and reducing the risk of complications. Treatment options can vary based on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health. Here’s a closer look at the available treatment options:
Non-Surgical Treatments
In some cases, particularly with less severe fractures, non-surgical treatments may be sufficient. These options include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Limiting weight-bearing activities can help the fracture heal.
- Physical Therapy: Once the initial pain subsides, physical therapy can aid in regaining strength and mobility.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can help manage discomfort.
Surgical Treatments
For many patients, especially those with more severe fractures, surgery is often necessary. The most common surgical options include:
- Internal Fixation: This involves using screws, plates, or rods to stabilize the fracture.
- Hip Replacement: In cases where the fracture is severe, a partial or total hip replacement may be recommended.
Both surgical options aim to restore function and alleviate pain, allowing patients to return to their daily activities. 🦴
Post-Treatment Recovery
Recovery from a hip fracture can take time and varies from person to person. Here are some key aspects of the recovery process:
- Rehabilitation: Engaging in a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for regaining strength and mobility.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers ensure that the healing process is on track.
- Home Modifications: Making adjustments at home, such as removing tripping hazards, can help prevent future falls.
Understanding the treatment options available for a hip fracture can empower patients and their families to make informed decisions about care. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action tailored to individual needs. 💪

Rehabilitation After a Hip Fracture
Recovering from a hip fracture can be a challenging journey, especially for the elderly, who are more susceptible to such injuries. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring mobility, strength, and independence. Here’s what you need to know about the rehabilitation process after a hip fracture.
Understanding the Rehabilitation Process
The rehabilitation process typically begins shortly after surgery or treatment for a hip fracture. The main goals are to:
- Restore mobility
- Improve strength
- Enhance balance
- Reduce pain
Physical therapy is often a key component of rehabilitation. A physical therapist will design a personalized program that may include:
- Range of motion exercises
- Strength training
- Balance exercises
- Walking and mobility training
Timeline for Recovery
The timeline for recovery can vary significantly based on factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of the fracture. Generally, patients can expect:
- First few days: Focus on pain management and initial mobility exercises.
- Weeks 1-2: Gradual increase in physical activity, often with the aid of a walker or crutches.
- Weeks 3-6: More intensive physical therapy sessions to improve strength and balance.
- 6 weeks and beyond: Continued rehabilitation with a focus on returning to daily activities.
Tips for Successful Rehabilitation
To maximize recovery after a hip fracture, consider the following tips:
- Stay Consistent: Attend all scheduled therapy sessions and follow your therapist’s recommendations.
- Set Realistic Goals: Understand that recovery takes time and set achievable milestones.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Proper nutrition can aid in healing and recovery.
- Stay Positive: A positive mindset can significantly impact your recovery journey.
Preventing Hip Fractures
Preventing a hip fracture is crucial, especially for older adults who are at higher risk. Here are some effective strategies to help reduce the likelihood of experiencing a hip fracture.
Strengthening Bones and Muscles
Maintaining strong bones and muscles is essential for preventing fractures. Consider the following:
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D to support bone health. Foods rich in these nutrients include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, dancing, or resistance training, to strengthen bones and improve muscle tone.
Home Safety Modifications
Making your home safer can significantly reduce the risk of falls, which often lead to hip fractures. Here are some modifications to consider:
- Remove Clutter: Keep floors clear of obstacles that could cause tripping.
- Install Grab Bars: Place grab bars in bathrooms and near stairs for added support.
- Improve Lighting: Ensure all areas of your home are well-lit to prevent falls.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help identify risk factors for hip fractures. Discuss any concerns regarding bone health, medication side effects, or balance issues. Your doctor may recommend:
- Bone Density Tests: To assess bone health and risk of osteoporosis.
- Medication Review: To evaluate any medications that may affect balance or bone density.
By taking proactive steps to strengthen bones, modify your living environment, and stay on top of your health, you can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing a hip fracture. 🦴✨

Frequently Asked Questions about Hip Fracture
What is a hip fracture?
A hip fracture is a break in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone) that occurs near the hip joint. It is a serious injury, particularly common in older adults, often resulting from falls or accidents.
What are the symptoms of a hip fracture?
Common hip fracture symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the hip or groin
- Inability to put weight on the affected leg
- Swelling and bruising around the hip area
- Shortening of the leg on the side of the fracture
- Outward rotation of the leg
How is a hip fracture diagnosed?
A hip fracture is typically diagnosed through a combination of a physical examination and imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, to confirm the presence and type of fracture.
What types of hip fractures are there?
There are several hip fracture types, including:
- Intracapsular fractures – occur within the hip joint capsule.
- Extracapsular fractures – occur outside the hip joint capsule.
- Femoral neck fractures – occur just below the ball of the hip joint.
- Intertrochanteric fractures – occur between the greater and lesser trochanters of the femur.
What treatments are available for a hip fracture?
Treatment options for a hip fracture may include:
- Surgery – to repair the fracture, which may involve inserting screws, plates, or hip replacement.
- Physical therapy – to aid recovery and regain strength and mobility.
- Medication – for pain management and to prevent complications.
What is the recovery process like after hip fracture surgery?
The hip fracture recovery process varies by individual but generally includes:
- Initial rest and limited weight-bearing on the affected leg.
- Gradual increase in mobility through physical therapy.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor healing.
Most individuals can expect to return to normal activities within a few months, depending on their overall health and adherence to rehabilitation.
Who is at risk for hip fractures?
Hip fractures in the elderly are particularly common due to factors such as decreased bone density, balance issues, and a higher likelihood of falls. Other risk factors include:
- Age
- Gender (women are at higher risk)
- Chronic health conditions
- Medications that affect balance or bone health
What is the ICD-10 code for a hip fracture?
The hip fracture ICD 10 code varies based on the specific type of fracture, but common codes include:
- S72.0 – Femoral neck fracture
- S72.1 – Intertrochanteric fracture
- S72.2 – Subtrochanteric fracture
Can hip fractures be prevented?
While not all hip fractures can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk, such as:
- Regular exercise to improve strength and balance
- Home modifications to reduce fall hazards
- Regular vision checks
- Ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake
When should I seek medical attention for a suspected hip fracture?
If you or someone else experiences severe hip pain, inability to move the leg, or any of the symptoms mentioned above after a fall or injury, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. 🚑




