“`html
What Are Ganglions?
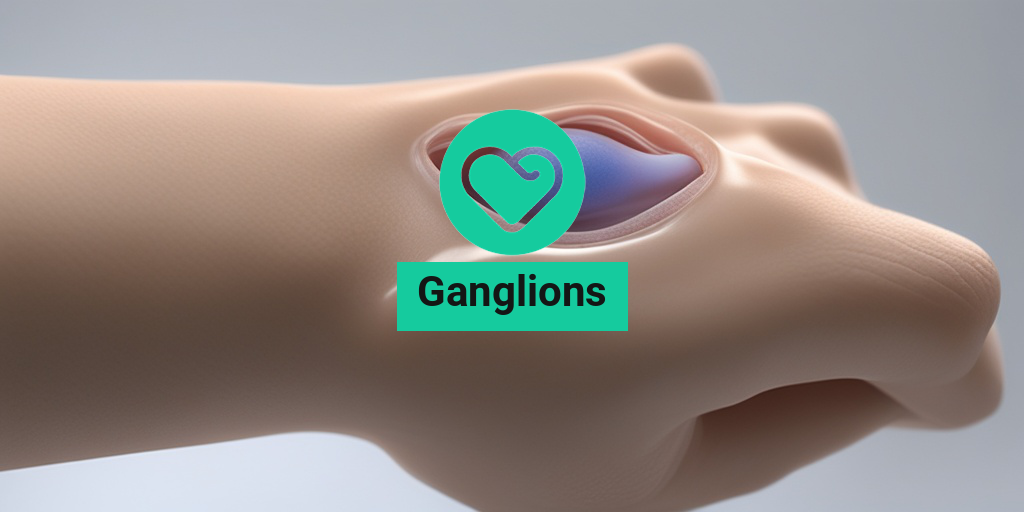
Ganglions are small, fluid-filled sacs that can develop in various parts of the body, most commonly around joints and tendons. They are often referred to as ganglion cysts when they occur in the wrist or hand, but they can also appear on the foot and other areas. These cysts are typically benign, meaning they are not cancerous, and they can vary in size from a pea to a golf ball.
Understanding Ganglions in the Body
Ganglions are formed when the synovial fluid, which lubricates joints and tendons, leaks out and collects in a sac-like structure. This can happen due to repetitive movements, injury, or even without any clear cause. While ganglions can occur anywhere in the body, they are most commonly found in:
- Wrist and Hand: The most frequent location for ganglion cysts.
- Foot and Ankle: Often found on the top of the foot or near the ankle joint.
- Knee: Ganglions can develop behind the knee, known as Baker’s cysts.
- Neck and Spine: Less common but can occur in these areas as well.
Ganglions Lymphatiques
It’s important to differentiate between ganglion cysts and ganglions lymphatiques (lymph nodes). Lymph nodes are part of the lymphatic system and play a crucial role in the immune response. When lymph nodes become swollen, it can indicate an infection or other health issues. In contrast, ganglion cysts are not related to the lymphatic system and are generally harmless.
Ganglion Cyst Symptoms
While many ganglion cysts are asymptomatic and may not require treatment, some individuals may experience symptoms that can affect their daily lives. Here are some common symptoms associated with ganglion cysts:
Visible Swelling
The most noticeable symptom of a ganglion cyst is a visible lump or swelling in the affected area. This lump may fluctuate in size and can sometimes become more prominent with activity.
Pain or Discomfort
Some people may experience pain or discomfort, especially if the cyst is pressing on nearby nerves or tissues. This pain can range from mild to severe and may worsen with movement or pressure.
Restricted Movement
If a ganglion cyst is located near a joint, it may limit the range of motion. For example, a cyst on the wrist can make it difficult to flex or extend the hand fully.
Other Symptoms
In rare cases, ganglion cysts can cause tingling or numbness in the fingers or toes if they are pressing on a nerve. If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice a lump that is painful, growing, or affecting your mobility, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can perform a physical examination and may recommend imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, to determine the nature of the lump.
For more information on ganglions and their management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. 🩺
In conclusion, while ganglions are generally harmless, understanding their symptoms and when to seek help can lead to better management and relief. If you have any concerns about ganglion cysts or related symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance.
“`

“`html
Ganglion Causes and Risk Factors
Ganglions, often referred to as ganglion cysts, are fluid-filled sacs that commonly develop near joints and tendons, particularly in the hands and feet. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with ganglions can help in prevention and early detection.
What Causes Ganglions?
The exact cause of ganglions remains somewhat unclear, but several factors may contribute to their formation:
- Joint or Tendon Irritation: Repeated stress or irritation to a joint or tendon can lead to the development of ganglions. This is particularly common in individuals who engage in repetitive motions, such as athletes or those in certain occupations.
- Trauma: A previous injury to a joint or tendon may increase the likelihood of a ganglion forming. Even minor injuries can trigger the development of these cysts.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic tendency to develop ganglions, suggesting that family history can play a role.
- Age: Ganglions are most commonly found in individuals aged 15 to 40, although they can occur at any age.
Risk Factors for Developing Ganglions
While anyone can develop ganglions, certain factors may increase the risk:
- Occupation: Jobs that require repetitive wrist or hand movements, such as typing or assembly line work, can elevate the risk of ganglion formation.
- Sports Activities: Athletes, particularly those involved in sports that stress the hands and wrists (like gymnastics or tennis), are more susceptible to ganglions.
- Existing Joint Conditions: Individuals with conditions like arthritis may be at a higher risk for developing ganglions due to joint inflammation.
Being aware of these causes and risk factors can empower individuals to take proactive measures in managing their joint health. If you notice any unusual lumps or swelling, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Ganglion Diagnosis
Diagnosing ganglions typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging techniques. Understanding the diagnostic process can help alleviate concerns and ensure appropriate treatment.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing a ganglion is a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. During this examination, the doctor will:
- Assess the Lump: The doctor will examine the size, shape, and location of the lump. Ganglions are usually round or oval and can vary in size.
- Evaluate Symptoms: The healthcare provider will inquire about any pain, discomfort, or limitations in movement associated with the ganglion.
Imaging Tests
If the physical examination suggests a ganglion, the doctor may recommend imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- X-rays: While X-rays cannot directly visualize ganglions, they can help rule out other conditions, such as bone tumors or fractures.
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses sound waves to create images of the soft tissues, allowing the doctor to see the cyst and assess its characteristics.
- MRI: In some cases, an MRI may be ordered for a more detailed view of the ganglion and surrounding structures, especially if surgery is being considered.
Other Diagnostic Considerations
In rare cases, a healthcare provider may perform a needle aspiration to extract fluid from the ganglion. This procedure can help confirm the diagnosis and relieve pressure if the cyst is causing discomfort.
Understanding the diagnostic process for ganglions can help patients feel more informed and prepared. If you suspect you have a ganglion or are experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis can lead to effective management and treatment options. 🩺
“`

“`html
Ganglion Treatment Options
Ganglions, often referred to as ganglion cysts, are fluid-filled sacs that typically develop near joints or tendons, most commonly in the hands and feet. While they are generally harmless, they can cause discomfort or pain, leading many to seek treatment. Here, we explore various treatment options available for ganglions.
1. Observation and Monitoring
In many cases, ganglions do not require immediate treatment. If the cyst is not causing pain or discomfort, your healthcare provider may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular monitoring can help determine if the ganglion changes in size or symptoms develop.
2. Aspiration
For ganglions that cause discomfort, aspiration is a common treatment option. This procedure involves using a needle to draw out the fluid from the cyst. While this can provide immediate relief, it’s important to note that ganglions can recur after aspiration.
3. Corticosteroid Injections
Another option is the injection of corticosteroids into the ganglion. This can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. However, like aspiration, this treatment may not permanently eliminate the cyst.
4. Surgical Removal
If the ganglion is persistent, painful, or affecting your daily activities, surgical removal may be necessary. This procedure involves excising the cyst and the stalk that connects it to the joint or tendon. Surgical intervention typically has a higher success rate in preventing recurrence compared to other treatments.
5. Physical Therapy
In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve joint function. This can be particularly beneficial if the ganglion is affecting mobility or causing discomfort during movement.
6. Stellate Ganglion Block
For individuals experiencing chronic pain associated with ganglions, a stellate ganglion block may be considered. This procedure involves injecting anesthetic into the stellate ganglion, a collection of nerves located in the neck. It can provide significant pain relief for certain conditions, including complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS).
Ganglion Home Remedies
While medical treatments are effective, some individuals prefer to explore home remedies for managing ganglion symptoms. Here are a few options that may help alleviate discomfort:
1. Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling. The heat promotes blood circulation and may encourage the cyst to shrink. Simply soak a cloth in warm water, wring it out, and apply it to the ganglion for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
2. Ice Packs
Conversely, using ice packs can help numb the area and reduce inflammation. Wrap ice in a cloth and apply it to the ganglion for 10-15 minutes at a time. This can be particularly useful after activities that aggravate the cyst.
3. Epsom Salt Soaks
Soaking the affected area in warm water mixed with Epsom salt can provide relief. Epsom salt contains magnesium, which may help reduce swelling and discomfort. Aim for a soak of about 15-30 minutes, a few times a week.
4. Herbal Remedies
Some people find relief using herbal remedies such as turmeric or ginger, known for their anti-inflammatory properties. You can consume these in food or as supplements, but always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
5. Rest and Elevation
Resting the affected area and keeping it elevated can help reduce swelling and discomfort. Avoid activities that put strain on the joint or tendon where the ganglion is located.
6. Gentle Massage
Gently massaging the area around the ganglion may help improve circulation and reduce tension. Be cautious not to apply too much pressure directly on the cyst, as this could exacerbate pain.
While these home remedies can provide relief, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Remember, ganglions can vary in size and symptoms, so what works for one person may not work for another. 🩺
“`

“`html
Ganglion Complications
Ganglions, often referred to as ganglion cysts, are fluid-filled sacs that typically develop near joints or tendons, particularly in the hands, wrists, and feet. While many ganglions are harmless and may not require treatment, they can sometimes lead to complications that warrant attention. Understanding these complications is crucial for anyone experiencing symptoms related to ganglions.
Common Complications Associated with Ganglions
Although ganglions are generally benign, they can cause several complications, including:
- Pain and Discomfort: Ganglions can exert pressure on surrounding nerves, leading to pain, tingling, or numbness, especially if located near a joint.
- Limited Range of Motion: If a ganglion is situated near a joint, it may restrict movement, making daily activities challenging.
- Infection: In rare cases, a ganglion can become infected, leading to swelling, redness, and increased pain. This situation requires immediate medical attention.
- Recurrence: Even after treatment, ganglions can recur, particularly if the underlying cause is not addressed.
Specific Areas of Concern
Ganglions can form in various parts of the body, and complications may vary based on their location:
- Ganglions on the Foot: These can cause significant discomfort while walking or standing, potentially leading to altered gait and further complications.
- Ganglions in the Head and Neck: While less common, ganglions in these areas can lead to headaches or neck pain, affecting overall quality of life.
- Ganglions in the Wrist: Wrist ganglions are particularly notorious for causing pain and limiting wrist mobility, impacting activities like typing or sports.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any of the following symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional:
- Persistent pain that does not improve with rest
- Swelling or redness around the ganglion
- Signs of infection, such as fever or increased warmth
- Difficulty moving the affected joint
Early intervention can help prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment. Remember, while ganglions are often harmless, being proactive about your health is always a wise choice! 🩺
Ganglion Prevention Tips
Preventing ganglions involves understanding their causes and taking proactive measures to minimize risk factors. Here are some effective tips to help you avoid developing ganglions:
1. Maintain Joint Health
Keeping your joints healthy is crucial in preventing ganglions. Here are some ways to do this:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to strengthen muscles around your joints without putting excessive strain on them.
- Stretching: Incorporate stretching into your routine to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
2. Protect Your Joints
Taking precautions during activities that put stress on your joints can help prevent ganglions:
- Use Protective Gear: If you participate in sports or activities that may lead to joint injuries, wear appropriate protective gear.
- Avoid Repetitive Motions: If your job involves repetitive hand or wrist movements, take regular breaks to reduce strain.
3. Manage Underlying Conditions
Conditions such as arthritis can increase the risk of developing ganglions. Managing these conditions effectively can help:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Regular check-ups and following treatment plans can help keep underlying conditions in check.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support joint health and overall well-being.
4. Stay Informed
Understanding ganglions and their potential complications can empower you to take action:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about the symptoms and risk factors associated with ganglions to recognize any changes in your body early.
- Regular Self-Examinations: Check your joints and tendons regularly for any unusual lumps or changes.
By following these prevention tips, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing ganglions and maintain better joint health. Remember, a proactive approach is key! 💪
“`

“`html
Frequently Asked Questions about Ganglions
What are ganglions?
Ganglions are clusters of nerve cell bodies located in the peripheral nervous system. They play a crucial role in transmitting signals throughout the body.
What is a ganglion cyst?
A ganglion cyst is a noncancerous lump that typically forms near joints or tendons, often in the hands or feet. These cysts are filled with a jelly-like fluid and can vary in size.
What are swollen lymph nodes (ganglions lymphatiques enflés)?
Swollen lymph nodes, or ganglions lymphatiques enflés, occur when the lymphatic system responds to infection or illness. They can be tender and may indicate an underlying health issue.
How do ganglions affect the body?
Ganglions are essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. They help relay signals between the brain and various parts of the body, influencing movement and sensation.
Can ganglions be found in the head and neck?
Yes, ganglions in the head and neck are common. They can be involved in various functions, including sensory perception and motor control.
What does “ganglions in English” refer to?
The term “ganglions in English” refers to the translation and understanding of the term “ganglions” in the English language, encompassing both nerve clusters and ganglion cysts.
Are there treatments for ganglion cysts?
Treatments for ganglion cysts may include observation, aspiration (draining the cyst), or surgical removal if the cyst causes pain or discomfort.
What is a stellate ganglion block?
A stellate ganglion block is a medical procedure used to relieve pain by injecting anesthetic into the stellate ganglion, a group of nerves located in the neck. This procedure can be beneficial for various conditions, including chronic pain syndromes.
How can I prevent ganglion cysts?
- Maintain proper joint health through regular exercise.
- Avoid repetitive movements that strain the joints.
- Use protective gear during sports or activities that may cause injury.
When should I see a doctor about ganglions?
If you notice persistent swelling, pain, or changes in the size of a ganglion or cyst, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and potential treatment.
“`