What Is Idiopathic Edema?
Idiopathic edema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling, particularly in the extremities, face, and abdomen. The term “idiopathic” indicates that the exact cause of this edema is unknown, making it a bit of a medical mystery. While edema can often be attributed to specific health issues, such as heart or kidney problems, idiopathic edema does not have a clear underlying cause.
This condition is more commonly observed in women, especially those who are premenopausal or postmenopausal. It can be quite distressing, as the swelling can fluctuate and may worsen at certain times, such as during the menstrual cycle. Understanding idiopathic edema is crucial for those affected, as it can significantly impact quality of life.
How Does Idiopathic Edema Develop?
The development of idiopathic edema is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its occurrence:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly estrogen, can influence fluid retention.
- Dietary Factors: High sodium intake may exacerbate fluid retention.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can lead to edema.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of movement can hinder proper circulation and fluid drainage.
While these factors may play a role, the absence of a definitive cause makes idiopathic edema a challenging condition to manage.
Symptoms of Idiopathic Edema
The symptoms of idiopathic edema can vary widely among individuals, but they typically include:
- Swelling: The most prominent symptom is swelling in various parts of the body, particularly the legs, feet, and face. This swelling can be more pronounced at the end of the day or after prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
- Weight Fluctuations: Individuals may notice sudden changes in weight due to fluid retention, which can be alarming.
- Discomfort: The swelling can lead to feelings of heaviness or discomfort in the affected areas.
- Skin Changes: In some cases, the skin over the swollen areas may appear stretched or shiny.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While idiopathic edema is generally not life-threatening, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience significant swelling or if the swelling is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Severe headache
- Changes in vision
These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires immediate attention.
Managing Idiopathic Edema
Although there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for idiopathic edema, several strategies may help manage the symptoms:
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium-rich foods can help balance fluid levels.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity can improve circulation and reduce fluid retention.
- Compression Garments: Wearing compression stockings can help minimize swelling in the legs.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can actually help reduce fluid retention.
For personalized advice and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for understanding various health conditions, including idiopathic edema.
In conclusion, idiopathic edema can be a perplexing condition, but understanding its symptoms and potential management strategies can empower those affected to seek appropriate care and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you have idiopathic edema, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for guidance. 🌟
Causes of Idiopathic Edema
Idiopathic edema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling. The term “idiopathic” means that the exact cause of the edema is unknown. However, several factors may contribute to its development. Understanding these causes can help in managing the condition effectively.
Hormonal Fluctuations
One of the primary causes of idiopathic edema, especially in females, is hormonal fluctuations. Changes in hormone levels, particularly during the menstrual cycle, can lead to fluid retention. This is often observed in women who experience significant swelling before their periods, a condition sometimes referred to as premenstrual syndrome (PMS). 🌸
Dietary Factors
Certain dietary choices can also play a role in the development of idiopathic edema. High sodium intake is known to cause the body to retain water, leading to swelling. Additionally, a diet low in protein can affect the body’s ability to maintain fluid balance, contributing to edema. It’s essential to monitor your diet and make adjustments if you notice symptoms of swelling.
Medications
Some medications can cause fluid retention as a side effect. Common culprits include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Hormonal therapies
If you suspect that your medication may be contributing to idiopathic edema, consult your healthcare provider for alternatives or adjustments. 💊
Underlying Health Conditions
While idiopathic edema is characterized by an unknown cause, it can sometimes be associated with underlying health conditions. These may include:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disorders
- Liver disease
It’s crucial to rule out these conditions through proper medical evaluation if you experience persistent swelling.
Physical Inactivity
Lack of physical activity can also contribute to fluid retention. When the body is inactive for extended periods, especially while sitting or standing, it can lead to poor circulation and swelling in the legs and feet. Regular exercise can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of edema. 🏃♀️
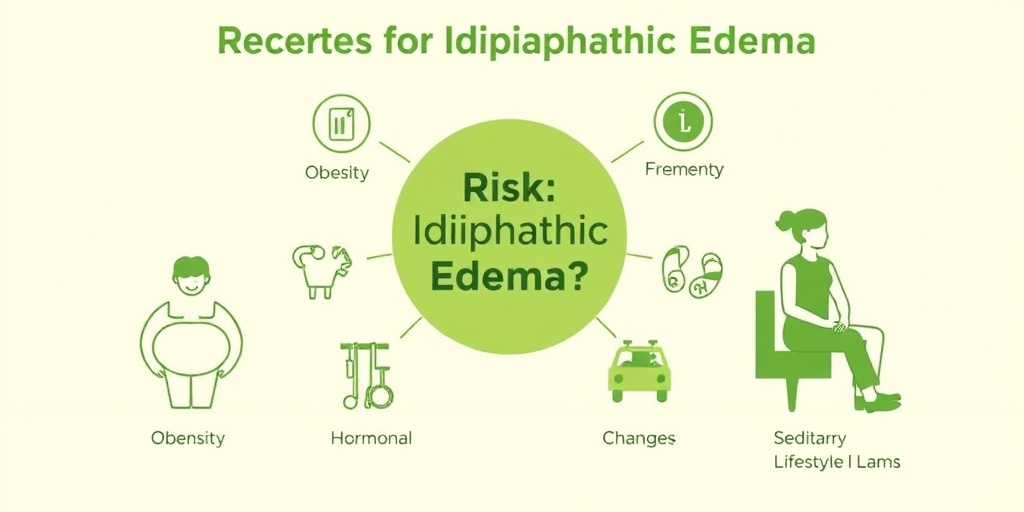
Risk Factors for Idiopathic Edema
Identifying the risk factors associated with idiopathic edema can help individuals take preventive measures. While anyone can develop this condition, certain groups may be more susceptible.
Gender and Age
Idiopathic edema is more commonly observed in females, particularly those in their reproductive years. Hormonal changes during this time can significantly influence fluid retention. Additionally, older adults may be at a higher risk due to age-related changes in body composition and circulation.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese can increase the likelihood of developing idiopathic edema. Excess body weight can put additional pressure on the circulatory system, leading to fluid retention. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can be beneficial in managing this risk factor. ⚖️
Genetic Predisposition
There may be a genetic component to idiopathic edema, as some individuals may have a family history of the condition. If you have relatives who have experienced similar symptoms, it may be worth discussing with your healthcare provider.
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may contribute to fluid retention. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or therapy, can be helpful in reducing the impact of stress on your body. 🧘♂️
Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle is a significant risk factor for many health issues, including idiopathic edema. Lack of movement can lead to poor circulation and fluid buildup. Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can help mitigate this risk.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors of idiopathic edema is crucial for effective management. By recognizing these elements, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health. 🌟
Diagnosing Idiopathic Edema
Diagnosing idiopathic edema can be a complex process, as it often requires a thorough evaluation to rule out other potential causes of swelling. This condition is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, leading to noticeable swelling, particularly in the legs, arms, and sometimes the face. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis:
Medical History Review
The first step in diagnosing idiopathic edema involves a detailed medical history. Your doctor will ask about:
- Your symptoms: When did the swelling start? Is it constant or does it fluctuate?
- Any previous medical conditions: Have you experienced similar symptoms in the past?
- Medications: Are you taking any medications that could contribute to fluid retention?
- Lifestyle factors: Do you have a sedentary lifestyle, or are you exposed to high temperatures frequently?
Physical Examination
After reviewing your medical history, your doctor will conduct a physical examination. This may include:
- Assessing the areas of swelling: Your doctor will check for pitting edema, where pressing on the swollen area leaves an indentation.
- Checking for signs of other conditions: This may involve looking for signs of heart, kidney, or liver issues.
Diagnostic Tests
If idiopathic edema is suspected, your doctor may recommend several tests to rule out other conditions:
- Blood tests: These can help assess kidney and liver function, as well as check for electrolyte imbalances.
- Urinalysis: This test can help determine if there are any underlying kidney issues.
- Imaging studies: Ultrasounds or CT scans may be used to visualize the affected areas and check for abnormalities.
It’s important to note that idiopathic edema is often diagnosed by exclusion, meaning that other potential causes of edema must be ruled out before a definitive diagnosis can be made. This can sometimes lead to frustration for patients, as the process may take time. However, understanding the diagnostic steps can help ease concerns and clarify what to expect during the evaluation.
Treatment Options for Idiopathic Edema
Treating idiopathic edema can be challenging, as the exact cause of the condition is often unknown. However, there are several treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here’s a look at some of the most common approaches:
Dietary Changes
One of the first steps in managing idiopathic edema is often through dietary modifications. Consider the following:
- Reduce sodium intake: High sodium levels can lead to fluid retention. Aim to limit processed foods and opt for fresh ingredients.
- Increase potassium-rich foods: Foods like bananas, oranges, and spinach can help balance sodium levels and reduce swelling.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms:
- Diuretics: These medications help the body eliminate excess fluid through urine. However, they should be used cautiously and under a doctor’s supervision.
- Hormonal treatments: For some women, hormonal fluctuations can contribute to idiopathic edema. Hormonal therapies may be considered in these cases.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating certain lifestyle changes can also be beneficial:
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity can help improve circulation and reduce fluid retention.
- Elevation of limbs: Elevating swollen limbs can help reduce swelling, especially after long periods of sitting or standing.
- Compression garments: Wearing compression stockings can provide support and help manage swelling in the legs.
Natural Remedies
Some individuals may find relief through natural treatments. While scientific evidence may be limited, the following options are often discussed:
- Herbal supplements: Certain herbs, like dandelion and ginger, are believed to have diuretic properties.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can help the body maintain a proper fluid balance.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment or remedy, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. With the right approach, many individuals with idiopathic edema can find effective ways to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. 🌿💧

Home Remedies for Idiopathic Edema
Idiopathic edema is a condition characterized by swelling, often in the legs, feet, and sometimes the face, without a clear underlying cause. While medical treatment is essential, many individuals seek natural remedies to alleviate symptoms. Here are some effective home remedies that may help manage idiopathic edema:
1. Stay Hydrated 💧
It may seem counterintuitive, but drinking plenty of water can actually help reduce edema. When your body is dehydrated, it tends to retain more fluid. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water a day to keep your body well-hydrated.
2. Elevate Your Legs
Elevating your legs can help reduce swelling. Try to keep your legs elevated above the level of your heart for 20-30 minutes a few times a day. This can promote better circulation and help fluid drain away from the affected areas.
3. Compression Garments
Wearing compression stockings or sleeves can provide support and help reduce swelling. These garments apply pressure to the legs, which can improve blood flow and decrease fluid accumulation.
4. Dietary Adjustments 🍏
Making changes to your diet can also play a significant role in managing idiopathic edema. Consider the following:
- Reduce Sodium Intake: High sodium levels can lead to fluid retention. Aim to limit processed foods and opt for fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Increase Potassium-Rich Foods: Foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach can help balance sodium levels and reduce swelling.
- Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
5. Herbal Remedies 🌿
Several herbs are known for their diuretic properties, which can help reduce fluid retention. Some popular options include:
- Dandelion: This herb is often used as a natural diuretic and may help reduce swelling.
- Green Tea: Known for its antioxidant properties, green tea can also promote fluid balance in the body.
- Ginger: This spice has anti-inflammatory properties and can aid digestion, potentially reducing swelling.
6. Regular Exercise 🏃♀️
Engaging in regular physical activity can improve circulation and help prevent fluid buildup. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can be particularly beneficial.
7. Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate many health conditions, including edema. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Living with Idiopathic Edema
Living with idiopathic edema can be challenging, but understanding the condition and implementing effective management strategies can significantly improve your quality of life. Here are some tips for navigating daily life with idiopathic edema:
1. Monitor Your Symptoms
Keeping a journal of your symptoms can help you identify triggers and patterns. Note when swelling occurs, its severity, and any activities or foods that may contribute to it. This information can be valuable for discussions with your healthcare provider.
2. Communicate with Your Healthcare Provider
Regular check-ins with your doctor are crucial. Discuss any changes in your symptoms or new treatments you may want to try. Your healthcare provider can help tailor a management plan that suits your needs.
3. Educate Yourself
Understanding idiopathic edema, including its causes and potential treatments, empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. Research reputable sources and consider joining support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges.
4. Create a Supportive Environment
Surround yourself with supportive friends and family who understand your condition. They can provide emotional support and help you stick to your management plan.
5. Focus on Self-Care 🧘♂️
Prioritize self-care activities that promote relaxation and well-being. Whether it’s taking a warm bath, practicing mindfulness, or enjoying a hobby, self-care can help reduce stress and improve your overall health.
6. Stay Informed About Treatment Options
While home remedies can be effective, it’s essential to stay informed about medical treatments for idiopathic edema. Discuss options such as medications or therapies with your healthcare provider to find the best approach for your situation.
Living with idiopathic edema requires a proactive approach, but with the right strategies and support, you can manage your symptoms effectively and lead a fulfilling life. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Edema, Idiopathic
What is Edema, Idiopathic?
Edema, idiopathic refers to swelling caused by an accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues without a known underlying cause. This condition can affect various parts of the body, including the legs, arms, and face.
What are the common causes of Idiopathic Edema?
The exact causes of idiopathic edema are often unclear. However, some potential factors may include:
- Hormonal changes, particularly in females
- Dietary factors, such as high salt intake
- Medications that may cause fluid retention
- Underlying health conditions that are not easily identifiable
How is Idiopathic Edema diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and possibly additional tests to rule out other conditions. Doctors may use imaging studies or blood tests to assist in the diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for Idiopathic Edema?
Treatment for idiopathic edema may vary based on the severity and individual circumstances. Common approaches include:
- Dietary modifications, such as reducing salt intake
- Diuretics to help eliminate excess fluid
- Compression garments to reduce swelling
- Natural treatments, such as herbal remedies
Is Idiopathic Edema more common in females?
Yes, idiopathic edema is often reported more frequently in females, particularly during hormonal fluctuations such as menstruation or pregnancy.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Idiopathic Edema?
Absolutely! Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly help manage idiopathic edema. These may include:
- Staying hydrated
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing
- Maintaining a balanced diet
What is the ICD-10 code for Idiopathic Edema?
The ICD-10 code for idiopathic edema is I89.0, which is used for billing and coding purposes in healthcare settings.
Are there any natural treatments for Idiopathic Edema?
Yes, some individuals explore natural treatments for idiopathic edema, such as:
- Herbal supplements like dandelion or ginger
- Increased potassium intake through foods like bananas
- Staying active with yoga or gentle exercises
Where can I find support for Idiopathic Edema?
Online communities, such as forums on Reddit, can provide support and shared experiences from others dealing with idiopathic edema. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals can offer personalized guidance.
Is there a link between Idiopathic Edema and other health conditions?
While idiopathic edema is often considered a standalone condition, it can sometimes be associated with other health issues, such as heart or kidney problems. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation.




