“`html
What Are COVID-19 Complications?
The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has affected millions of lives worldwide, leading to a wide range of health issues. While many individuals experience mild symptoms or remain asymptomatic, others may face serious complications that can significantly impact their health. Understanding these complications is crucial for both prevention and management.
COVID-19 complications refer to the severe health problems that can arise as a result of the virus. These complications can occur during the acute phase of the infection or even after recovery, a phenomenon often referred to as “long COVID.” The severity and type of complications can vary widely among individuals, influenced by factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the presence of other risk factors.
Why Do Complications Occur?
Complications from COVID-19 arise due to the virus’s ability to affect multiple organ systems. The virus primarily targets the respiratory system, but it can also impact the cardiovascular, neurological, and gastrointestinal systems. The body’s immune response to the virus can lead to inflammation and damage to these organs, resulting in various complications.
Who Is at Risk?
While anyone can experience complications from COVID-19, certain groups are at higher risk. These include:
- Older adults, particularly those over 65
- Individuals with pre-existing health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or chronic respiratory issues
- People with weakened immune systems
- Obese individuals
Understanding your risk factors is essential for taking preventive measures and seeking timely medical attention if needed.
Common COVID-19 Complications
COVID-19 can lead to a variety of complications, some of which may require hospitalization or long-term care. Here are some of the most common complications associated with the virus:
1. Respiratory Issues
One of the most significant complications of COVID-19 is respiratory distress. This can manifest as:
- Pneumonia: Inflammation of the lungs can lead to severe breathing difficulties.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A life-threatening condition where fluid builds up in the lungs, making it hard to breathe.
2. Cardiovascular Complications
COVID-19 can also affect the heart and blood vessels, leading to complications such as:
- Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle, which can affect its ability to pump blood.
- Blood Clots: Increased risk of clotting can lead to strokes or pulmonary embolism.
3. Neurological Issues
Some individuals may experience neurological complications, including:
- Headaches: Persistent headaches can occur during and after infection.
- Loss of Taste or Smell: A common symptom that can linger long after recovery.
- Confusion or Delirium: Particularly in older adults, COVID-19 can lead to cognitive issues.
4. Gastrointestinal Problems
COVID-19 can also affect the digestive system, leading to symptoms such as:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some patients report gastrointestinal symptoms as initial signs of infection.
- Diarrhea: This can occur alongside respiratory symptoms or independently.
5. Long COVID
Many individuals experience lingering symptoms long after the acute phase of the illness, a condition known as long COVID. Symptoms can include fatigue, joint pain, and cognitive difficulties, significantly impacting quality of life.
For those seeking more information on COVID-19 and its complications, Yesil Health AI offers evidence-based health answers and resources to help you navigate your health concerns.
In conclusion, understanding the potential complications of COVID-19 is vital for effective management and prevention. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly. Stay informed, stay safe, and take care of your health! 🌟
“`
“`html
Long-Term Effects of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted global health, and while many individuals recover from the virus, a significant number experience lingering effects. These long-term effects, often referred to as “long COVID,” can vary widely in severity and duration.
Understanding Long COVID
Long COVID is a term used to describe a range of symptoms that persist for weeks or even months after the initial infection has resolved. Research indicates that approximately 10-30% of individuals who recover from COVID-19 may experience these prolonged symptoms. The most common long-term effects include:
- Fatigue: Many survivors report extreme tiredness that interferes with daily activities.
- Respiratory Issues: Some individuals experience ongoing shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Cognitive Impairment: Often referred to as “brain fog,” this can include memory issues, difficulty concentrating, and confusion.
- Joint and Muscle Pain: Persistent aches and pains can affect mobility and overall quality of life.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia and other sleep-related issues are common among long COVID patients.
Who is Affected?
While anyone can develop long COVID, certain factors may increase the risk. These include:
- Severity of Initial Infection: Those who experienced severe symptoms during their COVID-19 illness are more likely to have long-term effects.
- Pre-existing Health Conditions: Individuals with chronic illnesses, such as diabetes or heart disease, may face a higher risk.
- Age: Older adults are generally more susceptible to long COVID.
- Gender: Some studies suggest that women may be more likely to experience long-term symptoms.
Managing Long-Term Effects
For those dealing with long COVID, it’s essential to seek medical advice and support. Treatment plans may include:
- Physical Rehabilitation: Tailored exercise programs can help improve strength and endurance.
- Cognitive Therapy: Strategies to enhance memory and concentration can be beneficial.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support.
As research continues, understanding the long-term effects of COVID-19 will be crucial in providing effective care and support for those affected. 🩺
COVID-19 Complications in Vulnerable Groups
Certain populations are at a higher risk of experiencing severe complications from COVID-19. Understanding these vulnerabilities is essential for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Identifying Vulnerable Groups
Vulnerable groups include individuals who may face increased risks due to various factors, such as age, underlying health conditions, and socioeconomic status. Key vulnerable populations include:
- Older Adults: Individuals aged 65 and older are at a significantly higher risk of severe illness and complications.
- People with Chronic Conditions: Those with conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory illnesses are more likely to experience severe outcomes.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: People with weakened immune systems due to conditions like cancer or organ transplants face heightened risks.
- Pregnant Women: Research indicates that pregnant individuals may have an increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Common Complications in Vulnerable Groups
For those in vulnerable groups, COVID-19 can lead to serious complications, including:
- Pneumonia: A severe lung infection that can be life-threatening.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A severe condition that causes fluid buildup in the lungs.
- Cardiovascular Issues: COVID-19 can lead to heart inflammation and other cardiovascular complications.
- Kidney Damage: Severe cases may result in acute kidney injury.
Preventive Measures for Vulnerable Groups
To protect vulnerable populations, it’s crucial to implement effective preventive measures:
- Vaccination: Ensuring that vulnerable individuals receive COVID-19 vaccines can significantly reduce the risk of severe illness.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance from others can help minimize exposure.
- Mask-Wearing: Wearing masks in crowded or indoor settings can provide additional protection.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Monitoring health conditions and seeking timely medical advice can help manage risks.
By understanding the complications associated with COVID-19 in vulnerable groups, we can better protect those at risk and promote healthier communities. 🌍
“`

“`html
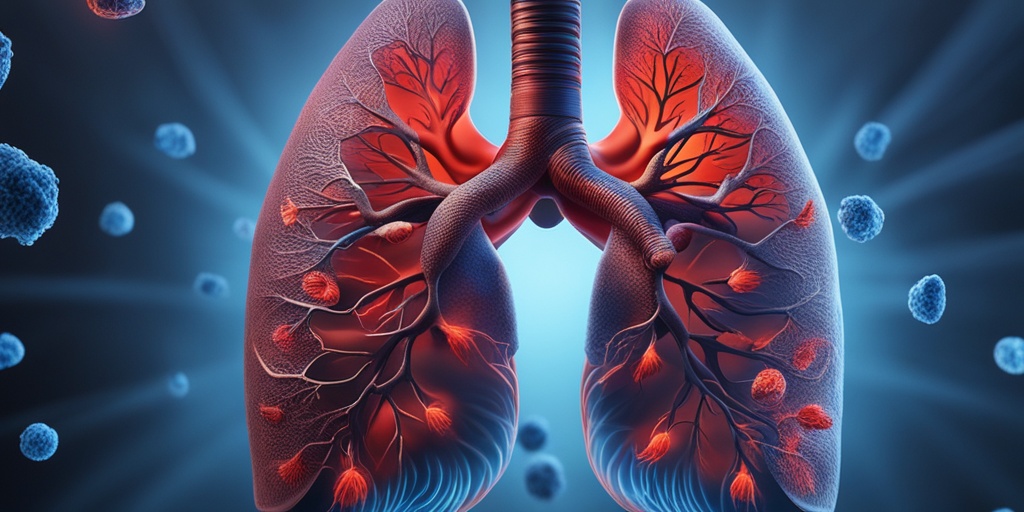
How COVID-19 Affects the Respiratory System
The respiratory system is one of the primary targets of the Coronavirus (COVID-19). Understanding how this virus impacts our lungs and airways is crucial for grasping the severity of the disease and its potential complications.
Initial Infection and Symptoms
When a person contracts COVID-19, the virus primarily enters through the respiratory tract. The initial symptoms often include:
- Cough – A persistent dry cough is common.
- Shortness of breath – Difficulty breathing can occur, especially in severe cases.
- Chest pain – Some individuals report discomfort or tightness in the chest.
These symptoms arise as the virus infects the cells lining the respiratory tract, leading to inflammation and irritation. This inflammatory response can cause significant damage to lung tissue, resulting in complications.
Severe Respiratory Complications
In more severe cases, COVID-19 can lead to serious respiratory complications, including:
- Pneumonia – This is a common complication where the lungs become inflamed and filled with fluid, making it difficult to breathe.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) – A life-threatening condition characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs.
- Respiratory failure – In severe cases, the lungs may fail to provide enough oxygen to the body, necessitating mechanical ventilation.
These complications can lead to long-term health issues, even after recovery from the virus. Studies have shown that some individuals experience lingering respiratory problems, often referred to as “long COVID.” 🌬️
Preventive Measures for Respiratory Health
To protect your respiratory system from COVID-19, consider the following preventive measures:
- Vaccination – Getting vaccinated significantly reduces the risk of severe illness.
- Wearing masks – Especially in crowded or indoor settings, masks can help prevent the spread of the virus.
- Practicing good hygiene – Regular handwashing and sanitizing surfaces can reduce transmission.
By taking these precautions, you can help safeguard your respiratory health and reduce the risk of complications associated with COVID-19. 🛡️
Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19
The impact of COVID-19 extends beyond the respiratory system, significantly affecting cardiovascular health. Understanding these complications is vital for those recovering from the virus.
How COVID-19 Affects the Heart
Research indicates that COVID-19 can lead to various cardiovascular issues, including:
- Myocarditis – Inflammation of the heart muscle, which can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood.
- Arrhythmias – Irregular heartbeats that can lead to serious complications.
- Heart attacks – COVID-19 can increase the risk of heart attacks due to inflammation and blood clotting.
These complications can occur even in individuals who had mild or asymptomatic cases of COVID-19, highlighting the virus’s unpredictable nature. ❤️
Long-term Cardiovascular Effects
Many survivors of COVID-19 report ongoing cardiovascular issues, which may include:
- Fatigue – Persistent tiredness can affect daily activities.
- Chest pain – Some individuals experience ongoing discomfort in the chest.
- Shortness of breath – Difficulty breathing can persist long after the initial infection.
These symptoms can be part of a broader condition known as “long COVID,” which affects many individuals post-recovery. It’s essential for those experiencing these symptoms to seek medical advice. 🩺
Protecting Your Heart Health
To mitigate the risk of cardiovascular complications from COVID-19, consider the following strategies:
- Regular check-ups – Stay in touch with your healthcare provider to monitor heart health.
- Healthy lifestyle choices – A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can strengthen heart health.
- Stress management – Techniques such as meditation and yoga can help reduce stress, benefiting overall cardiovascular health.
By prioritizing heart health, you can reduce the risk of complications associated with COVID-19 and improve your overall well-being. 💖
“`
“`html
Neurological Effects of COVID-19
The impact of Coronavirus (COVID-19) extends beyond respiratory symptoms, with emerging evidence highlighting significant neurological effects. As the pandemic continues to evolve, understanding these complications is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Common Neurological Symptoms
Patients recovering from COVID-19 have reported a range of neurological symptoms, which can vary in severity. Some of the most common include:
- Headaches: Many individuals experience persistent headaches, which can be debilitating.
- Loss of Taste and Smell: Anosmia (loss of smell) and ageusia (loss of taste) are frequently reported, often lingering long after other symptoms have resolved.
- Cognitive Impairment: Some patients describe “brain fog,” characterized by difficulty concentrating, memory issues, and confusion.
- Neuropathic Pain: This includes sensations of tingling, burning, or numbness, often affecting the extremities.
- Seizures: In rare cases, COVID-19 has been linked to seizures, particularly in patients with pre-existing neurological conditions.
Long-Term Effects on Mental Health
The psychological toll of COVID-19 cannot be overlooked. Many survivors report increased levels of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The stress of illness, isolation, and uncertainty during the pandemic can exacerbate these conditions.
Additionally, studies suggest that the virus may directly affect brain function, potentially leading to long-term cognitive decline. Ongoing research is essential to fully understand these implications and develop effective treatment strategies.
Mechanisms Behind Neurological Complications
Researchers are investigating several mechanisms that may explain the neurological effects of COVID-19:
- Direct Viral Infection: The virus may invade the central nervous system, leading to inflammation and damage.
- Immune Response: The body’s immune response to the virus can inadvertently harm brain tissue, resulting in neurological symptoms.
- Vascular Issues: COVID-19 can cause blood clotting and vascular inflammation, potentially leading to strokes or other neurological complications.
Preventing COVID-19 Complications
Preventing complications from Coronavirus (COVID-19) is essential for safeguarding both individual and public health. Here are some effective strategies to minimize risks:
Vaccination
Getting vaccinated is one of the most effective ways to prevent severe illness and complications from COVID-19. Vaccines have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and long-term effects significantly. Stay updated on booster shots as recommended by health authorities. 💉
Practicing Good Hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene practices can help reduce the spread of the virus:
- Handwashing: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in public places.
- Mask-Wearing: Wear masks in crowded or enclosed spaces to protect yourself and others.
- Social Distancing: Keep a safe distance from others, particularly in high-risk areas.
Monitoring Health
Stay vigilant about your health and seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of COVID-19. Early intervention can help prevent complications. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing health conditions should consult their healthcare providers for tailored advice on managing their risks.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can bolster your immune system and overall well-being:
- Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve cardiovascular health and boost immunity.
- Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep to support your body’s recovery and immune function.
By taking proactive steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with COVID-19. Remember, staying informed and prepared is key to navigating this ongoing health crisis. 🌟
“`

“`html
Frequently Asked Questions about Coronavirus (COVID-19) Complications
What are the common complications associated with COVID-19?
COVID-19 can lead to several complications, particularly in severe cases. Some of the most common complications include:
- Pneumonia: A serious lung infection that can be life-threatening.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A severe condition that causes fluid to build up in the lungs.
- Blood Clots: Increased risk of clotting can lead to strokes or heart attacks.
- Organ Failure: In severe cases, organs such as the kidneys or liver may fail.
- Long COVID: Persistent symptoms that can last for weeks or months after recovery.
Who is at higher risk for complications from COVID-19?
Individuals at higher risk for complications include:
- Older adults (65 years and older)
- People with underlying health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or respiratory issues
- Individuals with weakened immune systems
- Pregnant women
How can I recognize complications from COVID-19?
Recognizing complications early is crucial. Look for symptoms such as:
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless.
- Chest pain: Persistent pain or pressure in the chest.
- Confusion: Sudden changes in mental status or confusion.
- High fever: A fever that does not respond to medication.
What should I do if I experience complications?
If you experience any severe symptoms or complications, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room. 🚑
Can complications from COVID-19 be treated?
Yes, many complications can be treated effectively with timely medical intervention. Treatment may include:
- Oxygen therapy: To help with breathing difficulties.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent or treat blood clots.
- Ventilator support: For severe respiratory distress.
- Rehabilitation: For recovery from long COVID symptoms.
Is vaccination effective in preventing complications from COVID-19?
Yes, vaccination significantly reduces the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and complications associated with COVID-19. It is recommended to stay updated with booster shots as advised by health authorities. 💉
Where can I find more information about COVID-19 complications?
For more information, you can visit reputable health organization websites such as:
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Your local health department
“`