What Is Calcaneal Valgus?
Calcaneal valgus is a foot deformity characterized by an abnormal positioning of the heel bone (calcaneus) that tilts outward. This condition can lead to various complications if left untreated, affecting not only the foot but also the overall alignment of the lower extremities. Understanding calcaneal valgus is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Understanding the Anatomy
To grasp the concept of calcaneal valgus, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of the foot. The calcaneus is the largest bone in the foot, forming the heel. In a normal foot, the calcaneus aligns vertically with the tibia (shin bone). However, in calcaneal valgus, the calcaneus tilts laterally, causing the foot to roll inward. This misalignment can lead to a range of issues, including pain and instability.
Causes of Calcaneal Valgus
Calcaneal valgus can arise from various factors, including:
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may inherit a tendency toward this deformity.
- Neuromuscular disorders: Conditions that affect muscle control can lead to abnormal foot positioning.
- Injury or trauma: Previous injuries to the foot or ankle can contribute to the development of calcaneal valgus.
- Improper footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support can exacerbate the condition.
Calcaneal Valgus Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of calcaneal valgus is vital for timely intervention. Individuals with this condition may experience a variety of signs, which can vary in severity.
Common Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms associated with calcaneal valgus include:
- Pain in the heel or arch: Discomfort may arise due to the abnormal positioning of the foot.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the heel and ankle can occur, leading to visible swelling.
- Difficulty walking: The misalignment can affect gait, making walking uncomfortable or challenging.
- Foot fatigue: Individuals may experience increased fatigue in the feet after standing or walking for extended periods.
Associated Conditions
Calcaneal valgus can also be associated with other foot deformities, such as:
- Flatfoot: A condition where the arch of the foot collapses, often seen in conjunction with calcaneal valgus.
- Overpronation: Excessive inward rolling of the foot during walking or running, which can lead to further complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of calcaneal valgus, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment options, potentially preventing further complications. A healthcare provider may recommend imaging studies, such as X-rays, to assess the severity of the deformity.
For comprehensive information and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI. They provide valuable resources that can help you understand calcaneal valgus and its implications better.
In conclusion, calcaneal valgus is a significant foot deformity that can impact daily activities and overall quality of life. By recognizing the symptoms and understanding the condition, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their foot health. 🦶✨
Causes of Calcaneal Valgus
Calcaneal valgus, often referred to as a calcaneal valgus deformity, is a condition characterized by an abnormal positioning of the heel bone (calcaneus) that tilts outward. Understanding the causes of this condition is crucial for effective treatment and management. Here are some of the primary causes:
1. Genetic Factors
Genetics can play a significant role in the development of calcaneal valgus. If there is a family history of foot deformities, individuals may be more predisposed to this condition. Genetic predisposition can influence the structure and alignment of the bones and joints in the foot.
2. Developmental Issues
Calcaneal valgus can arise from developmental issues during childhood. As children grow, their bones and joints undergo significant changes. If these changes do not occur properly, it can lead to misalignments such as calcaneal valgus. This is particularly common in children with conditions like cerebral palsy or other neuromuscular disorders.
3. Trauma or Injury
Injuries to the foot or ankle can also lead to calcaneal valgus. A fracture or severe sprain can disrupt the normal alignment of the bones, resulting in a valgus position. This is especially true if the injury affects the ligaments or tendons that support the foot’s structure.
4. Muscle Imbalances
Muscle imbalances around the foot and ankle can contribute to calcaneal valgus. If certain muscles are stronger or tighter than others, they can pull the foot into an abnormal position. For instance, tightness in the calf muscles can lead to an outward tilt of the heel.
5. Flat Feet
Individuals with flat feet (pes planus) are at a higher risk of developing calcaneal valgus. The lack of a proper arch can lead to overpronation, where the foot rolls inward excessively. This misalignment can cause the heel to tilt outward, resulting in calcaneal valgus.
Risk Factors for Calcaneal Valgus
Identifying the risk factors associated with calcaneal valgus is essential for prevention and early intervention. Here are some key risk factors to consider:
1. Age
Calcaneal valgus is more commonly observed in children, particularly during their growth spurts. However, it can also occur in adults, especially if there are underlying conditions or previous injuries. Monitoring foot development in children is crucial to catch any abnormalities early.
2. Obesity
Excess body weight can place additional stress on the feet and ankles, increasing the risk of developing calcaneal valgus. The added pressure can exacerbate existing structural issues, leading to misalignment and deformities.
3. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity can contribute to muscle weakness and imbalances in the foot and ankle. Regular exercise helps maintain muscle strength and flexibility, which are vital for proper foot alignment. Engaging in activities that promote foot health can reduce the risk of calcaneal valgus.
4. Footwear Choices
Wearing improper footwear can significantly impact foot health. Shoes that lack support or do not fit properly can lead to misalignments and deformities. High heels, for example, can alter the natural position of the foot and contribute to conditions like calcaneal valgus.
5. Previous Foot Conditions
Individuals with a history of foot conditions, such as bunions or plantar fasciitis, may be at a higher risk for developing calcaneal valgus. These conditions can alter the mechanics of the foot, leading to misalignments over time.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of calcaneal valgus is essential for effective management and treatment. By addressing these issues early, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their foot health and prevent further complications. 🦶✨

Diagnosis of Calcaneal Valgus
Calcaneal valgus, often referred to as a calcaneal valgus deformity, is a condition characterized by an abnormal positioning of the heel bone (calcaneus) that tilts outward. Diagnosing this condition involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Here’s a closer look at how healthcare professionals diagnose calcaneal valgus.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing calcaneal valgus is a thorough clinical evaluation. During this assessment, a healthcare provider will:
- Review Medical History: Understanding the patient’s medical history, including any previous foot or ankle injuries, is crucial.
- Conduct a Physical Examination: The doctor will examine the foot and ankle for signs of deformity, misalignment, or discomfort.
- Assess Gait: Observing how the patient walks can provide insights into the severity of the condition and its impact on mobility.
Imaging Studies
In many cases, imaging studies are necessary to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the deformity. Common imaging techniques include:
- X-rays: These are typically the first imaging tests performed. X-rays can reveal the angle of the calcaneus and help differentiate between calcaneal valgus vs varus conditions.
- CT Scans: In more complex cases, a CT scan may be used to provide a detailed view of the bone structure.
- MRI: This imaging technique can help assess soft tissue involvement, such as ligaments and tendons, which may be affected by the deformity.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the healthcare provider can discuss appropriate treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs. 🩺
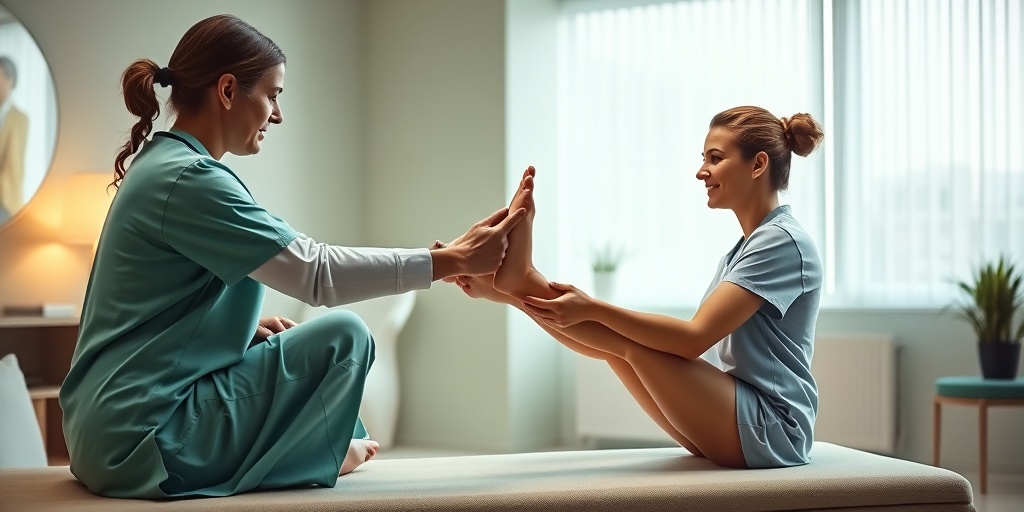
Treatment Options for Calcaneal Valgus
Treating calcaneal valgus involves a multifaceted approach that aims to alleviate symptoms, correct the deformity, and improve overall foot function. The treatment plan may vary based on the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, and their activity level. Here are some common treatment options:
Conservative Treatments
For many patients, especially those with mild to moderate calcaneal valgus, conservative treatments can be effective:
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the foot and ankle, improve flexibility, and enhance overall stability.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotics can help redistribute pressure on the foot and provide better arch support, which may alleviate discomfort associated with calcaneal valgus.
- Footwear Modifications: Wearing shoes with proper arch support and cushioning can significantly improve comfort and function.
- Activity Modification: Reducing high-impact activities that exacerbate symptoms can be beneficial during the healing process.
Surgical Options
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if the deformity is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include:
- Osteotomy: This procedure involves cutting and realigning the bones of the foot to correct the deformity.
- Arthrodesis: In some cases, fusing certain joints in the foot may be recommended to stabilize the structure and reduce pain.
- Soft Tissue Procedures: These may involve repairing or lengthening tendons and ligaments to improve alignment and function.
It’s essential for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgical options with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision. 🦶
Overall, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of calcaneal valgus can lead to improved outcomes and a better quality of life. Whether through conservative measures or surgical intervention, addressing this condition is crucial for maintaining foot health and mobility.

Home Remedies for Calcaneal Valgus
Calcaneal valgus, a condition characterized by an outward angling of the heel bone, can lead to discomfort and mobility issues. While medical intervention is often necessary, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms and improve foot alignment. Here are some effective strategies you can try:
1. Foot Exercises
Engaging in specific foot exercises can strengthen the muscles around the ankle and improve alignment. Consider incorporating the following exercises into your routine:
- Toe Raises: Stand with your feet flat on the ground. Slowly raise your heels while keeping your toes on the floor. Hold for a few seconds and lower back down.
- Arch Lifts: While seated, place your feet flat on the floor. Try to lift the arch of your foot while keeping your toes and heel on the ground.
- Calf Stretches: Stand facing a wall, place your hands on it, and step one foot back. Keep the back leg straight and bend the front knee to stretch the calf muscle.
2. Proper Footwear
Wearing the right shoes is crucial for managing calcaneal valgus. Look for footwear that provides:
- Arch Support: Shoes with good arch support can help maintain proper foot alignment.
- Cushioning: Adequate cushioning can reduce impact and provide comfort during walking.
- Wide Toe Box: A wider toe box allows your toes to spread naturally, reducing pressure on the foot.
3. Ice Therapy
If you’re experiencing pain or swelling, applying ice can be beneficial. Wrap ice in a cloth and apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes. This can help reduce inflammation and provide relief.
4. Epsom Salt Soaks
Soaking your feet in warm water mixed with Epsom salt can help relax muscles and reduce discomfort. The magnesium in Epsom salt may also aid in reducing inflammation. Aim for a soak of about 15-20 minutes.
5. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce stress on your feet. If you’re overweight, consider adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise routine to help manage your weight effectively.
Long-Term Outlook for Calcaneal Valgus
The long-term outlook for individuals with calcaneal valgus varies based on several factors, including the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. Understanding what to expect can help you manage the condition better.
1. Severity of the Deformity
Calcaneal valgus can range from mild to severe. In mild cases, individuals may experience minimal discomfort and can often manage symptoms with home remedies and lifestyle changes. However, severe cases may require more intensive treatment, including physical therapy or surgery.
2. Treatment Options
For many, a combination of home remedies and professional treatment can lead to significant improvement. Options include:
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the foot and improve alignment.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotic devices can provide additional support and help correct foot positioning.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the bones and restore proper function.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Making lifestyle adjustments can also play a crucial role in the long-term management of calcaneal valgus. This includes:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can help maintain fitness without putting excessive strain on the feet.
- Foot Care: Regularly inspecting your feet for any signs of discomfort or changes can help catch issues early.
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals: Regular check-ups with a podiatrist can ensure that your condition is monitored and managed effectively.
In conclusion, while calcaneal valgus can present challenges, understanding home remedies and the long-term outlook can empower individuals to take control of their foot health. With the right approach, many can lead active, fulfilling lives despite this condition. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Calcaneal Valgus
What is Calcaneal Valgus?
Calcaneal Valgus is a foot deformity characterized by an outward angulation of the heel bone (calcaneus). This condition can lead to various complications, including altered gait and discomfort.
What causes Calcaneal Valgus?
Calcaneal Valgus can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Genetic predisposition
- Neuromuscular disorders
- Injury or trauma to the foot
- Improper footwear
How is Calcaneal Valgus diagnosed?
A healthcare professional typically diagnoses Calcaneal Valgus through a physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays. These assessments help determine the severity of the deformity and any associated conditions.
What are the treatment options for Calcaneal Valgus?
Treatment for Calcaneal Valgus may include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen foot muscles
- Orthotic devices to improve foot alignment
- Medication for pain relief
- Surgery in severe cases to correct the deformity
Is Calcaneal Valgus common in adults?
While Calcaneal Valgus is often diagnosed in children, it can also occur in adults. Factors such as age, lifestyle, and previous injuries can contribute to the development of this condition later in life.
How does Calcaneal Valgus differ from Calcaneal Varus?
Calcaneal Valgus involves an outward angulation of the heel, while Calcaneal Varus refers to an inward angulation. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is crucial for appropriate treatment.
What is the ICD-10 code for Calcaneal Valgus?
The ICD-10 code for Calcaneal Valgus is typically classified under foot deformities. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider for the specific code relevant to individual cases.
Can Calcaneal Valgus be prevented?
While not all cases of Calcaneal Valgus can be prevented, wearing supportive footwear and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Where can I find more information about Calcaneal Valgus?
For more detailed information, consider consulting medical resources or speaking with a healthcare professional who specializes in foot and ankle conditions.




