What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a term that’s often thrown around, but what does it really mean? Simply put, arthritis is a condition that affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. It’s not just a single disease, but rather an umbrella term that encompasses over 100 different conditions, each with its unique set of symptoms and characteristics.
At its core, arthritis is a result of the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation and damage. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, making everyday activities a struggle.
According to the Arthritis Foundation, more than 54 million adults in the United States have been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, making it one of the most common chronic conditions in the country. And, it’s not just limited to older adults – people of all ages, including children and young adults, can develop arthritis.
Types of Arthritis
As mentioned earlier, there are over 100 different types of arthritis, each with its unique characteristics and symptoms. Here are some of the most common types:
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, affecting over 30 million people in the United States alone. It’s a degenerative condition that occurs when the cartilage in the joints wears down, causing bone-on-bone friction and pain. OA typically affects the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes the immune system to attack the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. It can affect any joint, but typically starts in the hands and feet. RA can also cause fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that affects people with psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. PsA causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can affect any joint, but typically starts in the fingers and toes.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread muscle pain, fatigue, and tender points. While it’s not traditionally considered a type of arthritis, it’s often associated with joint pain and stiffness.
These are just a few examples of the many types of arthritis that exist. Each type has its unique set of symptoms and characteristics, and understanding the differences is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
If you’re struggling with arthritis symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. And, for evidence-based health answers, consider checking out Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for reliable health information.
Stay tuned for more articles on arthritis, where we’ll dive deeper into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this complex condition 🏥.
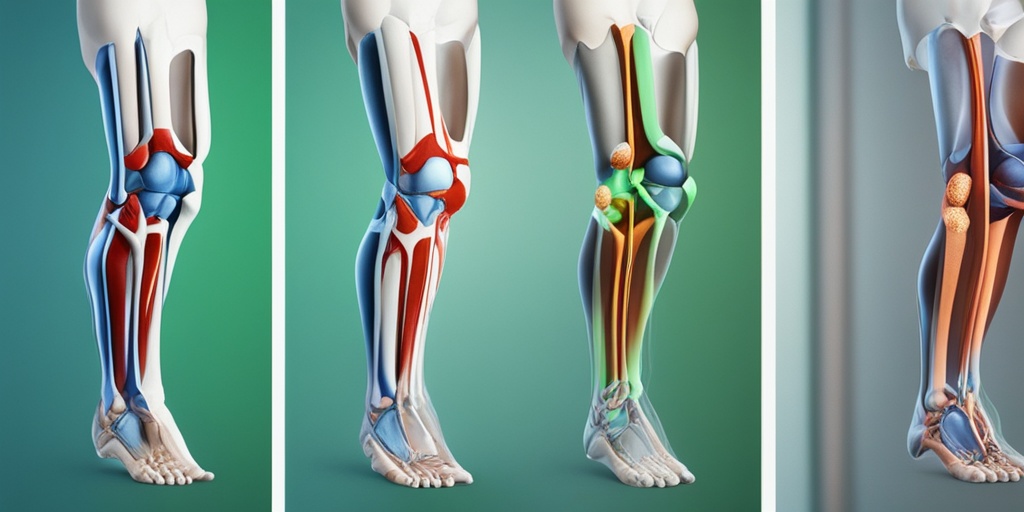
Arthritis Symptoms
Are you experiencing persistent joint pain, stiffness, or swelling? You might be wondering if you have arthritis. With over 100 different types of arthritis, it’s essential to recognize the common symptoms to seek proper diagnosis and treatment. 🤕
Common Arthritis Symptoms:
While arthritis symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity, here are some common signs to look out for:
- Joint Pain: Pain, aching, or stiffness in one or multiple joints, especially in the hands, feet, knees, hips, or spine.
- Swollen Joints: Visible swelling or redness around the affected joint.
- Stiffness: Morning stiffness that lasts for more than 30 minutes, or stiffness after periods of inactivity.
- Reduced Mobility: Difficulty moving the affected joint or performing daily activities.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or exhausted, even after resting.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased appetite or weight loss due to chronic pain and discomfort.
Other Possible Symptoms:
In addition to the common symptoms, some people with arthritis may experience:
- Fever: Recurring or persistent fever, especially in cases of infectious arthritis.
- Rash: Skin rashes or lesions, often seen in psoriatic arthritis or lupus.
- Numbness or Tingling: Numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the hands or feet.
- Eye Problems: Dry eyes, blurred vision, or eye pain, commonly seen in rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact causes of arthritis are still not fully understood, research has identified several factors that contribute to the development of this condition. 🧬
Genetics:
Having a family history of arthritis, especially rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, can increase your risk of developing the condition. Genetic factors can affect the production of collagen, cartilage, or other joint tissues, making you more susceptible to arthritis.
Aging:
As we age, our joints naturally degenerate, leading to wear and tear on the cartilage and bones. This can cause osteoarthritis, especially in weight-bearing joints like the hips, knees, and spine.
Injury or Trauma:
A previous injury or trauma to a joint can increase the risk of developing arthritis in that joint. This is especially true for post-traumatic arthritis, which can occur after a sports injury, car accident, or other traumatic event.
Obesity:
Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on your joints, particularly in the hips, knees, and spine. This can lead to osteoarthritis and other types of arthritis.
Infections:
Certain infections, such as Lyme disease or viral hepatitis, can trigger arthritis in some people. In rare cases, infections can cause infectious arthritis, which requires prompt medical attention.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of arthritis can help you take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking early diagnosis, you can work with your healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan and improve your quality of life. 💪

Arthritis Diagnosis
Receiving an arthritis diagnosis can be a life-changing moment. It’s essential to understand the diagnosis process, as it can help you better manage your condition and improve your quality of life. In this section, we’ll delve into the world of arthritis diagnosis, exploring the common signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and what to expect during the diagnosis process.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Arthritis
If you’re experiencing persistent joint pain, stiffness, or swelling, you may be wondering if you have arthritis. While these symptoms can be indicative of arthritis, they can also be caused by other conditions. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Some common signs and symptoms of arthritis include:
- Joint pain or stiffness that lasts for more than two weeks
- Swollen or inflamed joints
- Redness or warmth around the affected joint
- Difficulty moving the affected joint
- Fatigue or fever
Diagnostic Tests for Arthritis
To diagnose arthritis, your healthcare professional may perform a combination of physical exams, medical history reviews, and diagnostic tests. These tests can help identify the type of arthritis you have and rule out other conditions. Some common diagnostic tests include:
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) test: This blood test checks for the presence of RF, an antibody that’s often present in people with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Anti-citrullinated protein antibody (anti-CCP) test: This blood test is used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis and can help predict the severity of the condition.
- X-rays: These imaging tests can help identify bone damage, joint space narrowing, and bone spurs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This imaging test can help identify inflammation and damage in the soft tissues surrounding the joints.
- Joint fluid analysis: This test involves analyzing the fluid within the affected joint to check for inflammation, infection, or bleeding.
- Your symptoms, including when they started, how long they last, and how severe they are
- Your medical history, including any previous injuries or conditions
- Your family medical history, as some types of arthritis can be hereditary
- Your lifestyle, including your diet, exercise habits, and occupation
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These medications, such as methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine, can help slow down the progression of arthritis.
- Corticosteroids: These medications, such as prednisone, can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Biologics: These medications, such as adalimumab and etanercept, can help reduce inflammation and slow down the progression of arthritis.
- Physical therapy: This type of therapy can help improve joint mobility, strength, and flexibility.
- Occupational therapy: This type of therapy can help you learn new ways to perform daily tasks and activities.
- Massage therapy: This type of therapy can help reduce pain and improve joint mobility.
What to Expect During the Diagnosis Process
During the diagnosis process, your healthcare professional will likely ask you a series of questions about your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. Be prepared to discuss:
Remember, an accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Be open and honest with your healthcare professional, and don’t hesitate to ask questions or seek a second opinion if needed.
Arthritis Treatment Options
While there’s no cure for arthritis, there are various treatment options available to help manage the condition and improve your quality of life. In this section, we’ll explore the different types of arthritis treatment options, from medication and therapy to lifestyle changes and alternative remedies.
Medication for Arthritis
Medications can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow down the progression of arthritis. Some common medications used to treat arthritis include:
Therapy for Arthritis
Therapy can help improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall function. Some common types of therapy for arthritis include:
Remember, it’s essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits your unique needs and goals. By combining medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage your arthritis and improve your quality of life. 💊🏥

Medications for Arthritis
When it comes to managing arthritis, medications play a crucial role in reducing symptoms, slowing down disease progression, and improving quality of life. With numerous options available, it’s essential to understand the different types of medications, their benefits, and potential side effects.
Analgesics and Pain Relievers
These medications are designed to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with arthritis. Over-the-counter (OTC) options like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) are commonly used. However, it’s essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult with your doctor before taking any medication, especially if you have a history of stomach problems or kidney disease.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
DMARDs are a class of medications that slow down the progression of arthritis by reducing inflammation and preventing joint damage. Examples of DMARDs include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine. These medications can be taken orally or injected, and they often take several weeks or months to show their full effects.
Biologics
Biologics are a type of DMARD that targets specific proteins involved in the inflammatory process. They are usually prescribed for moderate to severe arthritis and can be administered through injections or infusions. Examples of biologics include adalimumab (Humira), etanercept (Enbrel), and infliximab (Remicade).
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint. They are often used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain during acute flares. However, long-term use can lead to side effects like weight gain, mood changes, and osteoporosis.
Topical Creams and Ointments
Topical creams and ointments, such as capsaicin cream or diclofenac gel, can be applied directly to the affected joint to reduce pain and inflammation. These medications are often used in combination with other treatments and can provide quick relief.
Lifestyle Changes for Arthritis Management
While medications can help alleviate symptoms, making lifestyle changes can significantly improve your overall health and well-being. By incorporating these changes into your daily routine, you can better manage your arthritis and reduce your reliance on medications.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts additional strain on your joints, especially in the hips, knees, and ankles. Losing weight can reduce pressure on these joints and alleviate pain. Aim for a healthy body mass index (BMI) through a combination of diet and exercise.
Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise can help improve joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen surrounding muscles. Low-impact activities like yoga, swimming, and cycling are ideal for people with arthritis. Consult with your doctor or a physical therapist to create a personalized exercise plan.
Eat an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Certain foods can trigger inflammation, while others can help reduce it. Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Include anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, turmeric, and ginger in your meals.
Get Enough Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, and it can also help reduce arthritis symptoms. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and establish a relaxing bedtime routine to improve sleep quality.
Manage Stress
Stress can exacerbate arthritis symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to help manage stress and anxiety.
Remember, managing arthritis requires a comprehensive approach that combines medications, lifestyle changes, and self-care. By working closely with your healthcare provider and making informed decisions, you can take control of your arthritis and improve your quality of life. 💊🏥

Frequently Asked Questions about Arthritis
What are the common symptoms of arthritis?
Arthritis symptoms can vary depending on the type, but common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, redness, and warmth around the affected joint. Some people may also experience fatigue, fever, or loss of appetite.
What are the different types of arthritis?
There are over 100 types of arthritis, but some of the most common include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout. Each type has its own unique causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is the best treatment for arthritis?
Treatment for arthritis usually involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies. Medications can help reduce pain and inflammation, while lifestyle changes such as exercise, weight loss, and stress management can help manage symptoms. Alternative therapies like physical therapy, acupuncture, and massage can also provide relief.
Can arthritis be cured?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for arthritis, but with proper treatment and management, symptoms can be significantly reduced, and quality of life can be improved. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to slowing down the progression of the disease.
How can I manage arthritis pain?
There are several ways to manage arthritis pain, including over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, topical creams, and alternative therapies like heat and cold therapy, exercise, and relaxation techniques. It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to find the best pain management plan for your specific needs.
Can I exercise with arthritis?
Yes, exercise is an essential part of managing arthritis! Gentle exercises like yoga, swimming, and cycling can help improve joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen surrounding muscles. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to develop an exercise plan that’s safe and suitable for your specific condition.
What are some natural remedies for arthritis?
Some natural remedies that may help alleviate arthritis symptoms include turmeric, ginger, omega-3 fatty acids, and glucosamine. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your regimen, as they may interact with medications or have side effects.
Can I prevent arthritis?
While there is no surefire way to prevent arthritis, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding joint injuries can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. Additionally, eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may also help.
What is the prognosis for arthritis?
The prognosis for arthritis varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. With proper treatment and management, many people with arthritis can lead active, fulfilling lives. However, some types of arthritis can lead to joint deformity, disability, or other complications if left untreated or poorly managed.
Where can I find more information about arthritis?
There are many resources available for people with arthritis, including the Arthritis Foundation, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). You can also consult with a healthcare provider or a rheumatologist for personalized information and guidance.




