What Is ACC?
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands, although it can also occur in other areas such as the breast, skin, and respiratory tract. This malignancy is characterized by its slow growth and tendency to invade surrounding tissues, making it a unique challenge for both patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding the Nature of ACC
ACC is classified as a type of salivary gland cancer, but its origins can be traced back to the epithelial cells that line various glands in the body. The cancer is known for its distinctive histological features, which include a cribriform pattern and a mix of solid and tubular structures. These characteristics can make diagnosis tricky, often requiring a biopsy for confirmation.
One of the most concerning aspects of ACC is its propensity for local recurrence and distant metastasis, particularly to the lungs and bones. Despite its slow growth, ACC can be aggressive, necessitating a comprehensive treatment approach that may include surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
Who Is at Risk?
While the exact cause of ACC remains unclear, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this cancer:
- Age: ACC is more commonly diagnosed in adults, particularly those aged 40 to 60.
- Gender: There is a slight female predominance in cases of ACC.
- Exposure to Radiation: Previous radiation therapy to the head and neck region may elevate the risk.
Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and management of the disease. For more detailed information on ACC and its implications, you can visit Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
ACC Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. However, the symptoms can vary significantly depending on the tumor’s location and size.
Common Symptoms of ACC
Some of the most frequently reported symptoms include:
- Pain or Discomfort: Patients may experience persistent pain in the affected area, especially if the tumor is pressing against nearby nerves.
- Swelling: A noticeable lump or swelling may develop in the neck or mouth, often mistaken for a benign condition.
- Changes in Saliva Production: Individuals may notice changes in saliva consistency or an increase in dry mouth.
- Difficulty Swallowing: As the tumor grows, it may obstruct the throat, leading to swallowing difficulties.
- Facial Nerve Weakness: In some cases, ACC can affect facial nerves, resulting in weakness or paralysis on one side of the face.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for those diagnosed with ACC.
In conclusion, understanding Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and its symptoms is vital for early detection and effective treatment. If you or someone you know is facing this diagnosis, consider reaching out to healthcare providers for personalized advice and support. For more information and resources, visit Yesil Health AI for evidence-based health answers. 🌟
ACC Causes and Risk Factors
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands, but it can also occur in other areas such as the breast, skin, and respiratory tract. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with ACC is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
What Causes ACC?
The exact cause of ACC remains largely unknown. However, researchers have identified several factors that may contribute to its development:
- Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations, particularly in the MYB gene, have been linked to ACC. These mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, a hallmark of cancer.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to specific environmental toxins, such as those found in industrial settings, may increase the risk of developing ACC. However, more research is needed to establish a direct link.
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions that cause chronic inflammation in the salivary glands may also play a role in the development of ACC. Inflammation can lead to cellular changes that predispose individuals to cancer.
Identifying Risk Factors
While anyone can develop ACC, certain risk factors may increase an individual’s likelihood of being diagnosed with this cancer:
- Age: ACC is more commonly diagnosed in adults, particularly those aged 40 to 60 years.
- Gender: Studies suggest that ACC may be slightly more prevalent in women than in men.
- Occupation: Individuals working in industries with high exposure to chemicals, such as the rubber and plastics industries, may have a higher risk of developing ACC.
- Previous Cancer History: Those with a history of other cancers may be at an increased risk for ACC, particularly if they have undergone radiation therapy.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and seek medical advice if they notice any concerning symptoms. Early detection is key in managing ACC effectively. 🩺
ACC Diagnosis
Diagnosing Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma can be challenging due to its rarity and the subtlety of its symptoms. However, a thorough diagnostic process is essential for effective treatment. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis of ACC.
Initial Evaluation
The diagnostic process often begins with a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. During this stage, doctors will:
- Assess Symptoms: Patients may report symptoms such as swelling in the affected area, pain, or changes in sensation. These symptoms can often be mistaken for less serious conditions.
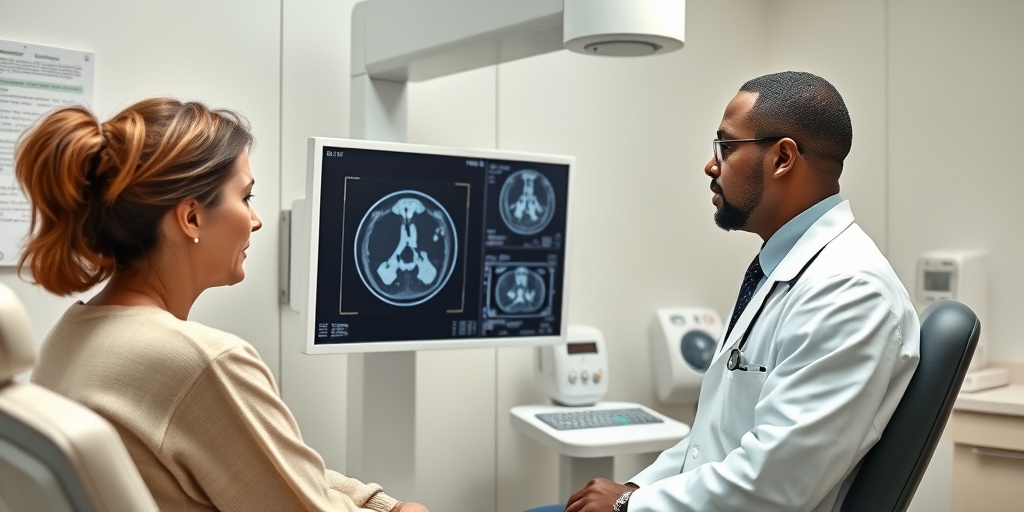
- Conduct Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds are commonly used to visualize the tumor and assess its size and location.
Biopsy for Confirmation
Once a suspicious mass is identified, a biopsy is typically performed to confirm the diagnosis. This involves:
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): A thin needle is used to extract a small sample of tissue from the tumor. This sample is then examined under a microscope for cancerous cells.
- Excisional Biopsy: In some cases, a larger portion of the tumor may be removed for analysis, providing more comprehensive information about the cancer.
Pathological Examination
After the biopsy, a pathologist will analyze the tissue sample to determine if it is indeed ACC. This examination includes:
- Histological Analysis: The pathologist looks for specific cellular characteristics that are indicative of ACC.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic tests may be conducted to identify mutations associated with ACC, which can help guide treatment options.
Diagnosing ACC requires a multi-faceted approach, combining clinical evaluation, imaging, and laboratory tests. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms that could indicate ACC, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life. 🌟
ACC Treatment Options
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands, but can also occur in other areas such as the breast, skin, and respiratory tract. Understanding the treatment options available for ACC is crucial for patients and their families. Here, we will explore the various treatment modalities that can be employed to manage this condition.
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for ACC. The goal is to remove the tumor completely while preserving as much surrounding healthy tissue as possible. Depending on the tumor’s location and size, the surgical approach may vary:
- Wide Local Excision: This involves removing the tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue.
- Salivary Gland Removal: In cases where the tumor is located in the salivary glands, the affected gland may need to be removed.
- Reconstructive Surgery: If significant tissue is removed, reconstructive surgery may be necessary to restore function and appearance.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is often used in conjunction with surgery, especially if there is a risk of residual cancer cells. It can also be an option for patients who are not surgical candidates. The types of radiation therapy include:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common form, where high-energy beams are directed at the tumor site.
- Brachytherapy: This involves placing radioactive material directly inside or near the tumor.
Radiation therapy can help reduce the risk of recurrence and manage symptoms, particularly in advanced cases of ACC. However, it may come with side effects such as fatigue and skin irritation. 🌟
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is not typically the first choice for treating ACC, as this cancer tends to be less responsive to traditional chemotherapy agents. However, it may be considered in advanced cases or when the cancer has metastasized. Newer targeted therapies and clinical trials are also being explored to improve outcomes for patients with ACC.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Recent advancements in cancer treatment have led to the development of targeted therapies and immunotherapies that may be effective for ACC. These treatments focus on specific genetic mutations or pathways involved in cancer growth. Some promising options include:
- Targeted Agents: These drugs target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth and survival.
- Immunotherapy: This approach helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the efficacy of these treatments for ACC, providing hope for improved outcomes in the future. 🌈
ACC Prognosis
The prognosis for patients with Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma can vary significantly based on several factors, including the tumor’s location, size, and stage at diagnosis. Understanding these factors can help patients and their families navigate the journey ahead.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several key factors can influence the prognosis of ACC:
- Location of the Tumor: Tumors located in the salivary glands may have different outcomes compared to those in other areas.
- Stage at Diagnosis: Early-stage ACC generally has a better prognosis than advanced-stage disease.
- Histological Features: The microscopic characteristics of the tumor can provide insights into its aggressiveness.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for ACC can be challenging to determine due to its rarity and variability. However, studies suggest that the 5-year survival rate for localized ACC can be around 70-90%, while the rate drops significantly for metastatic cases. It’s important to note that many patients with ACC can live for years with the disease, often experiencing long periods of remission.
Long-Term Outlook
ACC is known for its slow growth and tendency to recur, which means that long-term follow-up is essential. Regular check-ups and imaging studies can help detect any recurrence early, allowing for timely intervention. Patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support their overall well-being during and after treatment. 🌱
In conclusion, while the journey with ACC can be challenging, advancements in treatment options and a better understanding of prognosis are paving the way for improved outcomes. Staying informed and connected with healthcare providers is key to navigating this rare cancer effectively.
ACC Living with the Condition
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands, though it can also occur in other areas such as the breast, skin, and respiratory tract. Living with ACC can be a challenging journey, but understanding the condition and its implications can empower patients and their families. 🌟
Understanding ACC: What You Need to Know
ACC is characterized by slow growth and a tendency to recur after treatment. It is often diagnosed in adults, typically between the ages of 40 and 60. The symptoms can vary depending on the tumor’s location, but common signs include:
- Pain or swelling in the affected area
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Changes in voice or speech
- Persistent lumps that do not go away
Due to its slow-growing nature, many patients may not experience symptoms until the disease has progressed. Regular check-ups and awareness of any changes in your body are crucial for early detection. 🩺
Managing Symptoms and Treatment Options
Living with ACC often involves a multi-faceted approach to treatment. The primary treatment options include:
- Surgery: The most common treatment, aiming to remove the tumor completely.
- Radiation therapy: Often used post-surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: May be considered in advanced cases or when surgery is not an option.
Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual, taking into account the tumor’s location, size, and the patient’s overall health. It’s essential to have open discussions with your healthcare team about the best options for you. 💬
Emotional and Psychological Support
Beyond physical treatment, living with ACC can take an emotional toll. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, or fear of recurrence. Here are some strategies to help manage these feelings:
- Join support groups: Connecting with others who understand your journey can provide comfort and insight.
- Seek professional help: Therapists or counselors can offer coping strategies and emotional support.
- Practice mindfulness: Techniques such as meditation and yoga can help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
Remember, it’s okay to ask for help and lean on your support system. You are not alone in this journey. 🤝
ACC Research and Future Directions
Research into Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma is ongoing, with scientists and medical professionals striving to improve treatment outcomes and enhance the quality of life for patients. The future looks promising as new discoveries and technologies emerge. 🔬
Current Research Trends
Recent studies have focused on understanding the genetic and molecular characteristics of ACC. This research aims to:
- Identify biomarkers: These can help predict how aggressive the cancer may be and guide treatment decisions.
- Explore targeted therapies: These treatments aim to attack specific cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
- Investigate immunotherapy: This approach harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer more effectively.
Such advancements could lead to more personalized treatment plans, improving outcomes for patients diagnosed with ACC. 📈
Clinical Trials and Patient Involvement
Clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing ACC research. Patients are encouraged to consider participating in these trials, as they can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the broader understanding of the disease. Here’s how to get involved:
- Consult your oncologist: They can provide information on available trials and whether you qualify.
- Visit clinical trial registries: Websites like ClinicalTrials.gov list ongoing studies related to ACC.
- Stay informed: Follow ACC research organizations and advocacy groups for updates on new trials and findings.
Participating in research not only benefits the individual but also helps pave the way for future patients. Together, we can work towards better treatments and outcomes for those affected by ACC. 🌍

Frequently Asked Questions about Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC)
What is Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma?
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the salivary glands, but it can also occur in other areas such as the breast, skin, and respiratory tract. It is characterized by slow growth and a tendency to invade surrounding tissues.
What are the symptoms of ACC?
Common symptoms of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma may include:
- Swelling or a lump in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort
- Changes in voice or difficulty speaking
- Difficulty swallowing
- Numbness or weakness in the face
How is ACC diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma typically involves:
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs
- Biopsy to analyze tissue samples
What are the treatment options for ACC?
Treatment for Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma may include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy in some cases
It is essential to discuss the best treatment plan with a healthcare provider.
What is the prognosis for patients with ACC?
The prognosis for individuals diagnosed with Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma can vary based on factors such as the tumor’s location, size, and whether it has spread to other areas. Generally, ACC has a relatively good prognosis, but it can be challenging to treat due to its tendency to recur.
Are there any support resources available for ACC patients?
Yes! There are various support resources available for patients with Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Organizations and support groups can provide information, emotional support, and connect patients with others facing similar challenges. 🌟
Can lifestyle changes help in managing ACC?
While lifestyle changes alone cannot cure Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall well-being. This includes:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Staying physically active
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption
Where can I find more information about ACC?
For more information about Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, consider visiting reputable medical websites, cancer organizations, or consulting with healthcare professionals who specialize in oncology.




