What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects both the skin and joints. It typically occurs in individuals who have psoriasis, a skin disorder characterized by red, scaly patches. However, not everyone with psoriasis will develop psoriatic arthritis, and some people may experience joint symptoms without any visible skin lesions.
This condition is marked by inflammation in the joints, which can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling. The exact cause of psoriatic arthritis is still not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Understanding psoriatic arthritis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Types of Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis can manifest in several forms, each with its own set of characteristics:
- Symmetric Psoriatic Arthritis: Affects the same joints on both sides of the body.
- Asymmetric Psoriatic Arthritis: Affects different joints on each side, often with fewer joints involved.
- Distal Interphalangeal Predominant: Primarily affects the joints closest to the nails.
- Spondylitis: Involves inflammation of the spine and can lead to stiffness and pain in the back.
- Arthritis Mutilans: A rare but severe form that can cause significant joint damage and deformity.
Each type can vary in severity and may require different treatment approaches. If you suspect you have psoriatic arthritis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Psoriatic Arthritis Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis is vital for early intervention and management. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals, but some common signs include:
Joint Symptoms
- Joint Pain: Persistent pain in the joints, particularly in the knees, fingers, and lower back.
- Swelling: Inflammation can cause noticeable swelling in the affected joints.
- Stiffness: Many individuals experience stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the affected joints freely.
Skin Symptoms
- Psoriasis: Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Nail Changes: Pitting, discoloration, or separation of the nail from the nail bed.
Other Symptoms
In addition to joint and skin symptoms, psoriatic arthritis can also lead to:
- Fatigue: A common complaint among those with chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Eye Inflammation: Conditions like uveitis can occur, leading to redness and discomfort in the eyes.
It’s important to note that symptoms can fluctuate, with periods of flare-ups followed by remission. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have a history of psoriasis, it’s crucial to seek medical advice.
For those looking for more information on psoriatic arthritis, including treatment options and management strategies, Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) offers a wealth of evidence-based resources to help you navigate your health journey.
In conclusion, understanding psoriatic arthritis and its symptoms is the first step towards effective management. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life, allowing individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives. 🌟
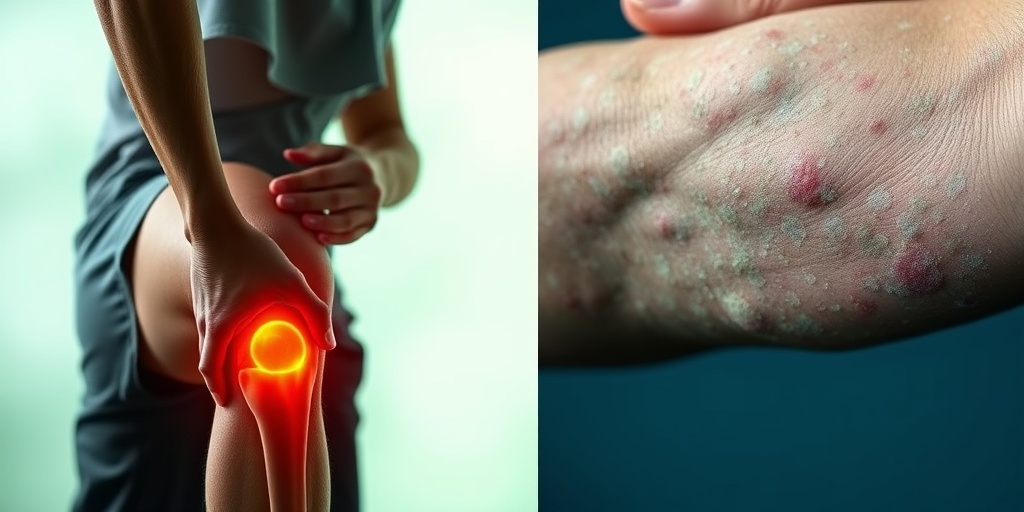
Causes of Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects both the skin and joints. Understanding the causes of psoriatic arthritis is crucial for effective management and treatment. While the exact cause remains unclear, several factors contribute to its development.
Genetic Predisposition
One of the primary factors linked to psoriatic arthritis is genetics. If you have a family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, your risk of developing the condition increases significantly. Studies suggest that certain genes may play a role in the immune system’s response, leading to inflammation and joint damage.
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system is designed to protect the body from infections and diseases. However, in psoriatic arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, particularly in the skin and joints. This autoimmune response leads to the characteristic symptoms of the disease, including joint pain and skin lesions.
Environmental Triggers
Various environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate psoriatic arthritis in individuals predisposed to the condition. Some common triggers include:
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, can trigger the onset of psoriasis and, subsequently, psoriatic arthritis.
- Injury: Physical trauma to the skin or joints can initiate the inflammatory process.
- Stress: High levels of stress can weaken the immune system and trigger flare-ups.
- Weather Changes: Cold and damp weather may worsen symptoms for some individuals.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty or pregnancy, can also influence the onset of psoriatic arthritis. Women may experience changes in their symptoms during these times, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors for Psoriatic Arthritis
Identifying the risk factors for psoriatic arthritis can help in early detection and management of the condition. While anyone can develop psoriatic arthritis, certain factors increase the likelihood of its occurrence.
Age
Psoriatic arthritis can develop at any age, but it most commonly appears between the ages of 30 and 50. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent joint damage and improve quality of life.
Obesity
Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for psoriatic arthritis. Excess weight can put additional stress on the joints and may exacerbate inflammation. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of psoriatic arthritis. Smoking can impair the immune system, while alcohol may trigger flare-ups in individuals with psoriasis. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can be beneficial for overall health and may reduce the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis.
Other Autoimmune Diseases
Individuals with other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, are at a higher risk of developing psoriatic arthritis. The presence of one autoimmune condition can increase the likelihood of others due to shared genetic and environmental factors.
Family History
A family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis significantly increases the risk of developing the condition. If you have relatives with these conditions, it’s essential to be vigilant about any symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for early evaluation.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with psoriatic arthritis can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. If you suspect you may be at risk, consider discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options. 🌟

Diagnosing Psoriatic Arthritis
Diagnosing psoriatic arthritis can be a complex process, as it often shares symptoms with other forms of arthritis and skin conditions. Understanding the signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here’s what you need to know about the diagnostic process.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Before a diagnosis can be made, it’s essential to recognize the common symptoms associated with psoriatic arthritis. These may include:
- Joint Pain: Pain and stiffness in the joints, particularly in the fingers, toes, and spine.
- Swelling: Swelling in the joints and surrounding tissues.
- Skin Changes: Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales, known as psoriasis.
- Nail Changes: Pitting, abnormal nail growth, or separation from the nail bed.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness and lack of energy.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing psoriatic arthritis typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your healthcare provider will ask about:
- Your symptoms and their duration.
- Any family history of arthritis or psoriasis.
- Previous skin conditions or joint issues.
During the physical examination, the doctor will check for swelling, tenderness, and range of motion in your joints. They may also look for signs of psoriasis on your skin and nails.
Diagnostic Tests
If your doctor suspects psoriatic arthritis, they may recommend several diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- X-rays: These can help identify joint damage and changes associated with arthritis.
- Blood Tests: While there’s no specific blood test for psoriatic arthritis, tests can rule out other types of arthritis and check for inflammation markers.
- MRI or Ultrasound: These imaging tests can provide detailed images of your joints and help assess inflammation.
It’s important to note that diagnosing psoriatic arthritis can take time, and it may require consultations with specialists, such as rheumatologists or dermatologists, to reach a conclusive diagnosis.
Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, managing psoriatic arthritis effectively is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. Treatment options vary based on the severity of the condition and individual patient needs. Here’s a breakdown of the most common treatment strategies.
Medications
Medications play a vital role in managing psoriatic arthritis. They can help reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow disease progression. Common categories of medications include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): Medications such as methotrexate can slow the progression of the disease and prevent joint damage.
- Biologics: These are advanced medications that target specific parts of the immune system. They are often prescribed for moderate to severe cases of psoriatic arthritis.
- Topical Treatments: For skin symptoms, topical treatments like corticosteroids or vitamin D analogs can be effective.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medications, certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of psoriatic arthritis:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help maintain joint function and reduce stiffness.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the joints and improve symptoms.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be beneficial for individuals with psoriatic arthritis. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to improve flexibility, strength, and overall joint function. This can help alleviate pain and enhance mobility.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies, such as:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help relieve muscle tension and improve circulation.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices like yoga and meditation can help manage stress, which may exacerbate symptoms.
In conclusion, while psoriatic arthritis can be challenging to manage, a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies can lead to improved outcomes and a better quality of life. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan tailored to your needs. 🌟
Managing Psoriatic Arthritis at Home
Living with psoriatic arthritis can be challenging, but there are several effective strategies you can implement at home to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. This condition, which combines the symptoms of arthritis with the skin condition psoriasis, requires a multifaceted approach to treatment and self-care. Here are some practical tips to help you manage psoriatic arthritis effectively.
1. Stay Active with Gentle Exercise
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining joint function and reducing stiffness. However, it’s important to choose low-impact exercises that won’t exacerbate your symptoms. Consider activities such as:
- Walking 🚶♂️
- Swimming 🏊♀️
- Yoga 🧘♀️
- Cycling 🚴♂️
These exercises can help improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce inflammation. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Your diet plays a significant role in managing psoriatic arthritis. Certain foods can help reduce inflammation and improve your overall health. Consider incorporating the following into your meals:
- Fruits and Vegetables 🍏🥦
- Whole Grains 🍞
- Healthy Fats (like olive oil and avocados) 🥑
- Lean Proteins (such as fish and poultry) 🍗
Additionally, try to limit processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats, as these can trigger inflammation and worsen symptoms.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis, making it essential to find effective ways to manage it. Here are some techniques you might find helpful:
- Meditation 🧘♂️
- Deep Breathing Exercises 🌬️
- Mindfulness Practices 🧠
- Engaging in Hobbies 🎨
Finding time for relaxation and self-care can significantly improve your mental well-being and help you cope with the physical challenges of psoriatic arthritis.
4. Use Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to affected joints can provide relief from pain and stiffness. Here’s how to use these therapies effectively:
- Heat Therapy: Use warm towels, heating pads, or warm baths to relax muscles and improve circulation.
- Cold Therapy: Apply ice packs wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling and numb sharp pain.
Experiment with both methods to see which one works best for you, and consider alternating between them for optimal relief.
5. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health and can help reduce inflammation. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water a day, and consider herbal teas as a hydrating option. Staying hydrated can also help keep your skin healthy, which is particularly important for those with psoriasis.
Living with Psoriatic Arthritis
Living with psoriatic arthritis means adapting to a new normal while finding ways to thrive despite the challenges. Here are some insights and tips to help you navigate daily life with this condition.
1. Understand Your Condition
Knowledge is power. Understanding the nature of psoriatic arthritis, including its symptoms and potential complications, can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Familiarize yourself with common symptoms such as:
- Joint Pain 🤕
- Swelling in joints
- Stiffness, especially in the morning
- Skin Lesions associated with psoriasis
Being aware of these symptoms can help you recognize flare-ups early and take appropriate action.
2. Build a Support Network
Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly beneficial. Consider joining support groups, either in-person or online, where you can share experiences, tips, and encouragement. Having a support network can help you feel less isolated and more empowered in managing your condition.
3. Communicate with Your Healthcare Provider
Regular communication with your healthcare provider is essential for managing psoriatic arthritis effectively. Be open about your symptoms, treatment side effects, and any concerns you may have. This collaboration can lead to better treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
4. Prioritize Self-Care
Make self-care a priority in your daily routine. This can include:
- Setting aside time for relaxation 🛀
- Engaging in enjoyable activities 🎶
- Practicing good sleep hygiene 💤
Taking care of your mental and emotional health is just as important as managing physical symptoms.
5. Stay Informed About Treatment Options
There are various treatment options available for psoriatic arthritis, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Stay informed about new treatments and discuss them with your healthcare provider to find the best approach for your situation. This proactive attitude can help you manage your condition more effectively.
By implementing these strategies and maintaining a positive outlook, you can lead a fulfilling life while managing psoriatic arthritis. Remember, you are not alone in this journey! 🌈

Frequently Asked Questions about Psoriatic Arthritis
What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects both the skin and joints. It typically occurs in individuals who have psoriasis, a skin disorder characterized by red, scaly patches. This type of arthritis can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
What are the symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis?
The symptoms of psoriatic arthritis can vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness, especially in the morning
- Fatigue
- Changes in nails, such as pitting or separation from the nail bed
- Skin lesions associated with psoriasis
How is Psoriatic Arthritis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and imaging tests. Doctors may also perform blood tests to rule out other types of arthritis.
What treatments are available for Psoriatic Arthritis?
Treatment options for psoriatic arthritis may include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs)
- Biologic medications
- Physical therapy
- Topical treatments for skin symptoms
Can lifestyle changes help manage Psoriatic Arthritis?
Yes! Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. These may include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise to improve joint function
- Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
Is Psoriatic Arthritis hereditary?
There is evidence to suggest that psoriatic arthritis can run in families, indicating a genetic component. However, environmental factors also play a significant role in its development.
What is the ICD-10 code for Psoriatic Arthritis?
The ICD-10 code for psoriatic arthritis is M07.0. This code is used for medical billing and documentation purposes.
Are there any specific nail symptoms associated with Psoriatic Arthritis?
Yes, individuals with psoriatic arthritis may experience nail changes such as:
- Pitting (small dents in the nails)
- Thickening of the nails
- Separation of the nail from the nail bed
Where can I find more information about Psoriatic Arthritis?
For more detailed information, consider visiting reputable health websites, consulting with healthcare professionals, or joining support groups focused on psoriatic arthritis.




