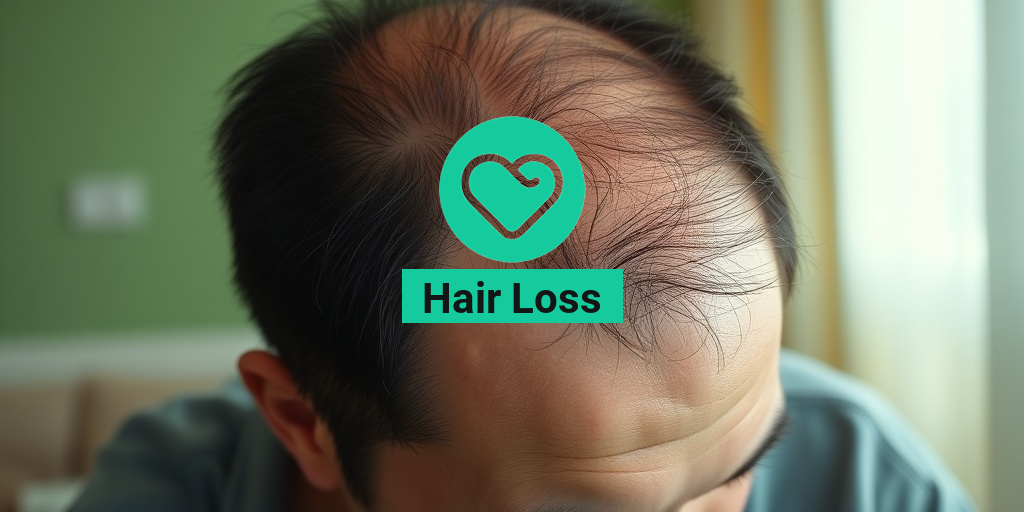
What Is Hair Loss?
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, refers to the condition where an individual experiences a significant reduction in hair density or complete loss of hair from the scalp or other parts of the body. This condition can affect both men and women, and it can occur at any age. While it is often perceived as a cosmetic issue, hair loss can have profound psychological effects, impacting self-esteem and overall quality of life.
There are various factors that contribute to hair loss, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and environmental influences. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and management. For instance, conditions like androgenetic alopecia (commonly known as male or female pattern baldness) are hereditary and can lead to progressive hair thinning.
In recent years, advancements in hair loss treatments have emerged, including topical solutions like minoxidil and oral medications such as finasteride. These treatments aim to stimulate hair growth and slow down the progression of hair loss. If you’re experiencing hair loss, consulting with a healthcare professional can help you identify the best course of action tailored to your needs.
Types of Hair Loss
Understanding the different types of hair loss is essential for determining the most effective treatment options. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia
This is the most prevalent form of hair loss, affecting both men and women. In men, it typically presents as a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while women usually experience overall thinning without a receding hairline. This condition is linked to genetic factors and the influence of hormones like DHT (dihydrotestosterone).
2. Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss that occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle. This can be triggered by stress, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause), or medical conditions. Fortunately, hair often regrows once the underlying cause is addressed.
3. Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden hair loss in patches. This type of hair loss can affect any hair-bearing area and may resolve on its own, although some individuals may require treatment to promote regrowth.
4. Traction Alopecia
This type of hair loss is caused by prolonged tension on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, or extensions. It is essential to recognize this condition early, as continued tension can lead to permanent hair loss.
5. Postpartum Hair Loss
Many women experience hair loss after childbirth due to hormonal fluctuations. This condition, known as postpartum hair loss, typically occurs around three to six months after delivery and is usually temporary. Most women notice their hair returning to its normal fullness within a year.
6. Scarring Alopecia
Scarring alopecia, or cicatricial alopecia, is a rare type of hair loss that results from inflammation damaging hair follicles and leading to scar tissue formation. This condition can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune diseases, or skin disorders. Treatment often focuses on managing inflammation and preventing further hair loss.
Regardless of the type of hair loss you may be experiencing, there are various hair loss treatments available, including specialized shampoos for hair loss, supplements, and medications. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable options for your specific situation.
For more information on hair loss and effective treatments, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. 🌟

Hair Loss Symptoms
Hair loss can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms early can help you seek appropriate treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for:
Thinning Hair
One of the most noticeable symptoms of hair loss is thinning hair. This can occur gradually and may be more apparent on the crown of the head or along the hairline. If you notice that your hair is becoming less dense, it might be time to consider a hair loss treatment.
Excessive Shedding
It’s normal to lose some hair daily, but if you find that you’re shedding more than usual, it could be a sign of a problem. Pay attention to your hairbrush or shower drain; if you see a significant amount of hair, it may indicate a need for intervention.
Bald Spots
Some individuals experience bald spots or patches of hair loss. This can occur suddenly and may be associated with conditions like alopecia areata. If you notice any bald patches, consult a healthcare professional for advice.
Changes in Hair Texture
Hair that becomes brittle, dry, or changes in texture can also be a symptom of hair loss. If your hair feels different than usual, it might be worth exploring hair loss treatments or consulting a dermatologist.
Itchy or Flaky Scalp
Sometimes, an itchy or flaky scalp can accompany hair loss. Conditions like dandruff or scalp psoriasis can contribute to hair shedding. Addressing the underlying scalp issue may help improve hair health.
Causes of Hair Loss
Understanding the causes of hair loss is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some of the most common factors that contribute to this condition:
Genetics
One of the leading causes of hair loss is genetics. Conditions like androgenetic alopecia (commonly known as male or female pattern baldness) can be inherited from either parent. If you have a family history of hair loss, you may be more susceptible.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can significantly impact hair health. For women, events such as pregnancy, menopause, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to female hair loss. Postpartum hair loss is also a common experience for new mothers, often resolving on its own.
Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can lead to hair loss, including:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder that causes sudden hair loss.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can affect hair growth.
- Iron Deficiency: Low iron levels can lead to hair shedding.
Medications
Certain medications can have side effects that include hair loss. Common culprits include:
- Antidepressants
- Blood Thinners
- Chemotherapy Drugs
If you suspect your medication is causing hair loss, consult your doctor for alternatives.
Stress
High levels of stress can lead to a type of hair loss known as telogen effluvium, where hair follicles enter a resting phase and shed more than usual. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or therapy can help mitigate this effect.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can also contribute to hair loss. Key vitamins and minerals that support hair health include:
- Biotin
- Vitamin D
- Iron
- Zinc
Incorporating a balanced diet or considering hair loss vitamins may help improve your hair’s condition.
By understanding the symptoms and causes of hair loss, you can take proactive steps toward finding the right hair loss treatment for your needs. Whether it’s through lifestyle changes, medications like minoxidil or finasteride, or specialized hair loss shampoos, there are options available to help you regain your confidence and promote healthy hair growth. 🌱

Risk Factors for Hair Loss
Understanding the risk factors for hair loss is crucial for both prevention and treatment. Hair loss can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing it. Here are some of the most common risk factors:
Genetics
One of the primary causes of hair loss is genetics. Conditions like androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, are hereditary. If your family has a history of hair loss, you may be more susceptible to it as well.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can significantly impact hair health. For women, events such as pregnancy, menopause, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hair thinning or loss. Postpartum hair loss is also a common issue that many new mothers face due to hormonal shifts.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can contribute to hair loss, including:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder that causes patchy hair loss.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can lead to hair thinning.
- Scalp Infections: Fungal infections like ringworm can damage hair follicles.
Medications
Certain medications can have side effects that include hair loss. Common culprits include:
- Antidepressants
- Blood thinners
- Chemotherapy drugs
If you suspect your medication is affecting your hair, consult your healthcare provider for alternatives.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
High levels of stress can lead to a type of hair loss known as telogen effluvium, where hair follicles enter a resting phase and fall out. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking can also contribute to hair loss. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in hair loss vitamins and supplements can help mitigate these effects.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to harsh chemicals, pollution, and even excessive heat from styling tools can damage hair and lead to loss. Using a shampoo for hair loss that is gentle and free from sulfates can help protect your hair.
Hair Loss Diagnosis
Diagnosing hair loss involves a comprehensive approach to identify the underlying causes. If you’re experiencing hair thinning or bald patches, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Here’s what you can expect during the diagnosis process:
Medical History Review
Your doctor will start by taking a detailed medical history. This includes:
- Family history of hair loss
- Any recent illnesses or surgeries
- Current medications and supplements
- Dietary habits and lifestyle factors
Physical Examination
A physical examination of your scalp and hair will help the doctor assess the extent of hair loss. They will look for patterns of hair loss, the condition of your scalp, and any signs of inflammation or infection.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to check for underlying health issues that could be contributing to hair loss. Common tests include:
- Thyroid function tests
- Hormone levels
- Iron levels
Scalp Biopsy
In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be necessary. This involves taking a small sample of the scalp to examine the hair follicles under a microscope. This can help diagnose conditions like alopecia areata or scarring alopecia.
Pull Test
A pull test may be performed to determine how many hairs come out when gently tugged. This can help assess the stage of hair loss and whether it is temporary or chronic.
Understanding the risk factors for hair loss and the diagnosis process can empower you to take proactive steps in managing your hair health. Whether it’s through lifestyle changes, medications like minoxidil or finasteride, or specialized hair loss treatments, there are options available to help you maintain a healthy head of hair. 🌟

Hair Loss Treatment Options
Experiencing hair loss can be distressing, but the good news is that there are numerous treatment options available. Whether you’re dealing with male or female hair loss, understanding the various treatments can help you make informed decisions. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most effective hair loss treatments currently available.
Medications
Two of the most commonly prescribed medications for hair loss are minoxidil and finasteride. Both have been clinically proven to help with hair regrowth and are widely used.
- Minoxidil: Available over-the-counter, minoxidil is a topical solution that stimulates hair follicles. It’s suitable for both men and women and is often found in various hair loss shampoos and treatments. Regular application can lead to noticeable results within a few months.
- Finasteride: This prescription medication is primarily for men and works by inhibiting the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting finasteride, as it may have side effects.
Hair Loss Shampoos
Choosing the right shampoo for hair loss can make a significant difference. Look for products that contain ingredients like ketoconazole, saw palmetto, or biotin, which are known to promote hair health. Some of the best hair loss shampoos also include natural extracts that nourish the scalp and strengthen hair follicles.
Hair Transplant Surgery
For those seeking a more permanent solution, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor site to areas experiencing thinning or baldness. While it can be costly, many find it to be a worthwhile investment for restoring their hairline.
Hair Loss Supplements and Vitamins
Incorporating hair loss vitamins and supplements into your routine can support overall hair health. Look for products that contain:
- Biotin: Essential for keratin production, biotin can help strengthen hair.
- Vitamin D: Deficiency in vitamin D has been linked to hair loss, so ensuring adequate levels can be beneficial.
- Iron: Low iron levels can lead to hair thinning, especially in women.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it’s appropriate for your needs.
Preventing Hair Loss
While some factors contributing to hair loss are beyond our control, there are several proactive steps you can take to minimize the risk. Here are some effective strategies for preventing hair loss:
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Your diet plays a crucial role in hair health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help strengthen your hair. Focus on including:
- Protein: Hair is primarily made of protein, so ensure you’re getting enough from sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these healthy fats can promote scalp health.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants, they help combat oxidative stress that can lead to hair loss.
Reduce Stress
High-stress levels can contribute to hair loss, particularly in women. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise can help maintain your hair’s health. Consider incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine to promote overall well-being.
Avoid Harsh Hair Treatments
Frequent use of harsh chemicals, heat styling tools, and tight hairstyles can damage hair and lead to breakage. To protect your hair:
- Limit the use of heat styling tools.
- Choose gentle, sulfate-free shampoos.
- Opt for loose hairstyles to reduce tension on the hair follicles.
Regular Scalp Care
Taking care of your scalp is essential for preventing hair loss. Regularly massage your scalp to improve blood circulation and promote hair growth. Additionally, consider using essential oils like rosemary or peppermint, which are known for their hair growth properties.
By understanding the various hair loss treatment options and implementing preventive measures, you can take control of your hair health and work towards maintaining a full, vibrant head of hair. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Hair Loss
What are the common causes of hair loss?
Hair loss can be attributed to various factors, including:
- Genetics: A family history of hair loss can increase your risk.
- Hormonal changes: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid issues can lead to hair loss.
- Medical conditions: Diseases such as alopecia areata and scalp infections can cause hair loss.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including those for cancer, arthritis, and depression, may result in hair loss.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger temporary hair loss.
What treatments are available for hair loss?
There are several effective treatments for hair loss, including:
- Minoxidil: An over-the-counter topical treatment that promotes hair growth.
- Finasteride: A prescription medication that helps reduce hair loss in men.
- Hair transplant: A surgical option that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body to another.
- Hair loss shampoos: Specialized shampoos designed to strengthen hair and reduce shedding.
- Supplements: Vitamins and minerals that support hair health, such as biotin and zinc.
Are there specific hair loss treatments for women?
Yes, women can experience hair loss due to various reasons, and there are treatments tailored for them, including:
- Minoxidil for women: A lower concentration of minoxidil is often recommended for female hair loss.
- Hormonal therapies: Treatments that address hormonal imbalances can be effective.
- Hair loss vitamins: Supplements specifically formulated for women’s hair health.
How can I prevent hair loss?
To help prevent hair loss, consider the following tips:
- Maintain a healthy diet: Ensure you are getting enough vitamins and minerals.
- Manage stress: Engage in relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
- Avoid harsh treatments: Limit the use of heat styling tools and chemical treatments.
- Be gentle with your hair: Use a wide-toothed comb and avoid tight hairstyles.
What is postpartum hair loss?
Postpartum hair loss is a common condition that affects many women after childbirth. It is typically caused by hormonal changes and usually resolves on its own within a few months. If you are experiencing significant hair loss after giving birth, consult your healthcare provider for advice.
What are the best hair loss shampoos?
The best hair loss shampoos often contain ingredients like:
- Biotin: Supports hair strength and growth.
- Caffeine: Stimulates hair follicles.
- Ketoconazole: Helps with dandruff and scalp health.
Look for products that are specifically formulated for hair loss to maximize effectiveness.
Can supplements help with hair loss?
Yes, certain supplements can support hair health. Look for those containing:
- Biotin: Known for promoting hair growth.
- Vitamin D: Plays a role in hair follicle cycling.
- Zinc: Essential for hair tissue growth and repair.
When should I see a doctor about hair loss?
If you notice sudden or patchy hair loss, or if hair loss is accompanied by other symptoms like itching or redness, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatments.