What Is Goiter?
Goiter is a condition characterized by an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is located at the base of your neck. This gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, energy levels, and overall hormonal balance. When the thyroid becomes enlarged, it can lead to noticeable swelling in the neck, often referred to as a “goiter neck.” But what causes this condition, and how can it be treated? Let’s dive deeper into the world of goiter.
Understanding the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland produces hormones that are essential for maintaining your body’s metabolism. These hormones include thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). When the thyroid is functioning properly, it helps regulate your heart rate, body temperature, and even your weight. However, when there is an imbalance—whether due to insufficient iodine, autoimmune diseases, or other factors—the thyroid can become enlarged, resulting in a goiter.
Types of Goiter
Goiters can be classified into several types, including:
- Simple Goiter: This is the most common type, often caused by iodine deficiency.
- Multinodular Goiter: This type features multiple nodules within the thyroid gland.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune disorder that can lead to goiter due to inflammation.
- Toxic Goiter: This type is associated with hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid produces excess hormones.
Understanding the type of goiter is essential for determining the appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Goiter Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of goiter is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. While some individuals may not experience any symptoms, others may notice several signs that indicate the presence of a goiter.
Common Symptoms of Goiter
Here are some of the most common symptoms associated with goiter:
- Swelling in the Neck: The most visible sign of goiter is swelling at the base of the neck, which can vary in size.
- Difficulty Swallowing: An enlarged thyroid can press against the esophagus, making it hard to swallow.
- Difficulty Breathing: In severe cases, the goiter may compress the windpipe, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Coughing or Hoarseness: The pressure from the goiter can irritate the throat, causing a persistent cough or changes in voice.
- Changes in Hormonal Levels: Depending on the underlying cause, individuals may experience symptoms of hyperthyroidism (such as weight loss, increased heart rate, and anxiety) or hypothyroidism (such as weight gain, fatigue, and depression).
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any swelling in your neck or experience difficulty swallowing or breathing, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment options and prevent complications. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, blood tests, or imaging studies to determine the cause of the goiter and recommend appropriate treatment.
For more detailed information on goiter and its management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
Conclusion
Goiter is a condition that can significantly impact your health and well-being. By understanding what goiter is and recognizing its symptoms, you can take proactive steps toward seeking treatment. Whether it’s through dietary changes, medication, or surgery, addressing goiter early can lead to better health outcomes. Remember, your thyroid health is vital, so don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you have concerns! 🌟
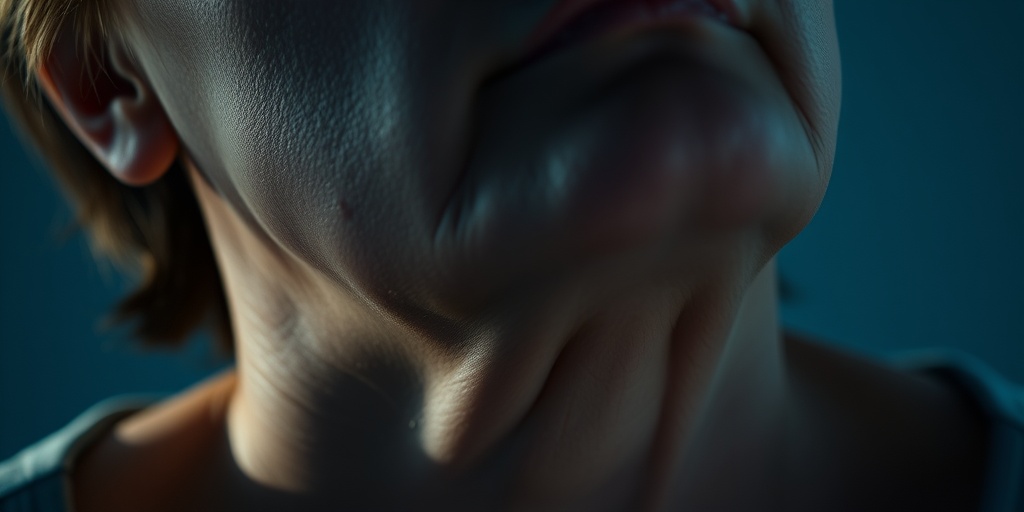

Goiter Causes
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is located at the base of your neck. This condition can occur for various reasons, and understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here are some of the primary causes of goiter:
Iodine Deficiency
One of the most common causes of goiter worldwide is a deficiency in iodine. Iodine is an essential nutrient that the body needs to produce thyroid hormones. When there is insufficient iodine in the diet, the thyroid gland enlarges in an attempt to capture more iodine from the bloodstream. This can lead to a noticeable swelling in the neck.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune conditions, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, can also lead to goiter formation. In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing inflammation and enlargement. Conversely, Graves’ disease results in an overproduction of thyroid hormones, which can also cause the gland to swell.
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps that can develop within the thyroid gland. While many nodules are benign, some can lead to an enlarged thyroid, resulting in a goiter. These nodules may produce excess thyroid hormones, contributing to the enlargement.
Medications and Treatments
Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can affect thyroid function and potentially lead to goiter development. Additionally, treatments for hyperthyroidism, such as radioactive iodine therapy, can sometimes result in an enlarged thyroid gland.
Other Factors
Other factors that may contribute to goiter formation include:
- Genetics: A family history of thyroid disease can increase the risk.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those found in pesticides, may play a role.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy and menopause can influence thyroid size and function.
Goiter Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors associated with goiter can help in early detection and prevention. Here are some key risk factors to consider:
Iodine Intake
As mentioned earlier, a diet low in iodine significantly increases the risk of developing a goiter. Populations in regions where iodine is not naturally present in the soil or water are particularly vulnerable. Incorporating iodine-rich foods, such as fish, dairy products, and iodized salt, can help mitigate this risk.
Gender and Age
Women are more likely than men to develop goiter, particularly during periods of hormonal change, such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Additionally, older adults are at a higher risk due to the natural decline in thyroid function that can occur with age.
Family History
A family history of thyroid disease can increase your risk of developing a goiter. If you have relatives with thyroid conditions, it’s essential to monitor your thyroid health regularly.
Existing Thyroid Conditions
If you have a history of thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, you may be at a higher risk for developing a goiter. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help manage these conditions effectively.
Environmental Exposures
Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as radiation or chemicals, can increase the risk of goiter. For instance, individuals living near nuclear power plants or those who have undergone radiation therapy for head and neck cancers may be at a higher risk.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors associated with goiter is essential for prevention and early intervention. If you notice any swelling in your neck or experience symptoms related to thyroid dysfunction, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance. 🩺
Goiter Diagnosis
Diagnosing a goiter involves a comprehensive approach that includes a physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests. A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which can occur due to several factors, including iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases, or nodules. Understanding how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition is crucial for effective management.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing a goiter typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. During this examination, the doctor will:
- Inspect the neck for any visible swelling or enlargement.
- Palpate the thyroid gland to assess its size, texture, and any nodules.
- Check for signs of thyroid dysfunction, such as changes in heart rate or skin texture.
Medical History
Alongside the physical examination, the doctor will take a detailed medical history. This may include:
- Family history of thyroid disease.
- Previous thyroid issues or surgeries.
- Symptoms such as weight changes, fatigue, or temperature sensitivity.
Diagnostic Tests
If a goiter is suspected, several diagnostic tests may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause:
- Blood Tests: These tests measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) to assess thyroid function.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound can provide images of the thyroid gland, helping to identify nodules or structural abnormalities.
- Thyroid Scan: This imaging test uses radioactive iodine to evaluate the function of the thyroid gland and detect any overactive or underactive areas.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy: If nodules are present, a biopsy may be performed to rule out cancer.
By combining these methods, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose a goiter and tailor a treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of the patient. 🩺
Goiter Treatment Options
Treating a goiter depends on its size, symptoms, and underlying cause. Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available, ranging from observation to medication and surgery. Understanding these options can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health.
Observation
In cases where the goiter is small and asymptomatic, a “watchful waiting” approach may be recommended. This involves regular monitoring of the goiter’s size and thyroid function without immediate intervention. Regular check-ups can help ensure that any changes are promptly addressed. 👀
Medications
If the goiter is caused by an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed. This typically involves:
- Levothyroxine: A synthetic thyroid hormone that helps normalize hormone levels and reduce the size of the goiter.
For goiters caused by hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), antithyroid medications may be used to reduce hormone production. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and shrink the goiter over time.
Iodine Supplementation
In regions where iodine deficiency is common, iodine supplementation may be recommended. This can help prevent further enlargement of the thyroid gland and improve overall thyroid function. Foods rich in iodine, such as iodized salt, seafood, and dairy products, can also be beneficial. 🧂
Surgery
In cases where the goiter is large, causing difficulty in breathing or swallowing, or if there is a suspicion of cancer, surgical intervention may be necessary. The surgical options include:
- Thyroidectomy: Partial or total removal of the thyroid gland, depending on the size and nature of the goiter.
Surgery is typically considered a last resort when other treatment options have failed or are not appropriate.
In conclusion, the treatment of a goiter is highly individualized, and it is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of action based on their specific circumstances. 💊

Goiter Home Remedies
Goiter, an enlargement of the thyroid gland, can be a source of concern for many individuals. While medical treatment is essential in some cases, there are several home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms and support thyroid health. Here are some effective options to consider:
1. Iodine-Rich Foods
Iodine is crucial for thyroid function, and a deficiency can lead to goiter. Incorporating iodine-rich foods into your diet can be beneficial. Some excellent sources include:
- Seaweed: Varieties like nori, kelp, and dulse are packed with iodine.
- Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon and tuna are not only delicious but also rich in iodine.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese can provide a good amount of iodine.
2. Herbal Remedies
Several herbs are believed to support thyroid health and may help manage goiter symptoms:
- Bladderwrack: This seaweed is often used in herbal medicine for its high iodine content.
- Ashwagandha: Known for its adaptogenic properties, it may help balance thyroid hormones.
- Guggul: This resin from the Commiphora mukul tree is thought to support thyroid function.
3. Essential Oils
Some essential oils may help promote thyroid health. Consider using:
- Frankincense Oil: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it may support overall thyroid function.
- Lavender Oil: This calming oil can help reduce stress, which is beneficial for thyroid health.
Always dilute essential oils with a carrier oil before applying them to the skin.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can also aid in managing goiter:
- Stress Management: High stress can negatively impact thyroid health. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can be helpful.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity can improve overall health and support thyroid function.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining bodily functions, including thyroid health.
Goiter Prevention Tips
Preventing goiter involves maintaining a healthy thyroid and ensuring adequate iodine intake. Here are some practical tips to help you keep your thyroid gland healthy:
1. Ensure Adequate Iodine Intake
As mentioned earlier, iodine is vital for thyroid health. To prevent goiter, consider the following:
- Use Iodized Salt: This is an easy way to ensure you’re getting enough iodine in your diet.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include a variety of foods rich in vitamins and minerals that support thyroid health.
2. Regular Health Check-ups
Routine check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor your thyroid function. If you have a family history of thyroid issues, discuss this with your doctor to determine if you need regular screenings.
3. Limit Goitrogenic Foods
Some foods can interfere with thyroid function, especially when consumed in large amounts. These include:
- Cruciferous Vegetables: While healthy, foods like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale can be goitrogenic. Cooking them can reduce their goitrogenic properties.
- Soy Products: Excessive consumption of soy can affect thyroid function, so moderation is key.
4. Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may affect thyroid health. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as:
- Mindfulness Meditation: This practice can help calm the mind and reduce stress.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can boost your mood and lower stress levels.
5. Stay Informed
Educate yourself about thyroid health and stay updated on any new research or recommendations. Knowledge is a powerful tool in preventing health issues.
By following these goiter prevention tips and considering home remedies, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy thyroid and overall well-being. 🌱

Frequently Asked Questions
What is a goiter?
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. This condition can occur due to various factors, including iodine deficiency, autoimmune diseases, or nodules in the thyroid. It may not always indicate a serious health issue, but it can lead to noticeable swelling in the neck.
What are the common symptoms of a goiter?
- Swelling at the base of the neck
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Coughing or hoarseness
- Changes in thyroid hormone levels, leading to symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
What causes a goiter?
Several factors can contribute to the development of a goiter, including:
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease can affect thyroid function.
- Nodules: Benign or malignant growths in the thyroid can lead to enlargement.
How is a goiter diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests to check thyroid hormone levels, and imaging tests such as ultrasound to assess the size and structure of the thyroid gland.
What are the treatment options for a goiter?
Treatment for a goiter depends on its cause and symptoms. Options may include:
- Medication: Hormone replacement therapy or anti-thyroid medications.
- Surgery: In cases of large goiters or those causing breathing or swallowing difficulties.
- Iodine supplementation: If iodine deficiency is the cause.
Can a goiter be prevented?
While not all cases can be prevented, ensuring adequate iodine intake through diet or supplements can help reduce the risk of developing a goiter. Foods rich in iodine include fish, dairy products, and iodized salt.
Is a goiter serious?
In many cases, a goiter is not serious and may not require treatment. However, if it causes significant symptoms or is associated with thyroid dysfunction, it is important to seek medical advice.
How can I manage my goiter symptoms at home?
For mild cases, managing symptoms may include:
- Staying hydrated
- Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients
- Monitoring any changes in symptoms and consulting a healthcare provider as needed
When should I see a doctor?
If you notice swelling in your neck, experience difficulty breathing or swallowing, or have other concerning symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and potential treatment of a goiter.