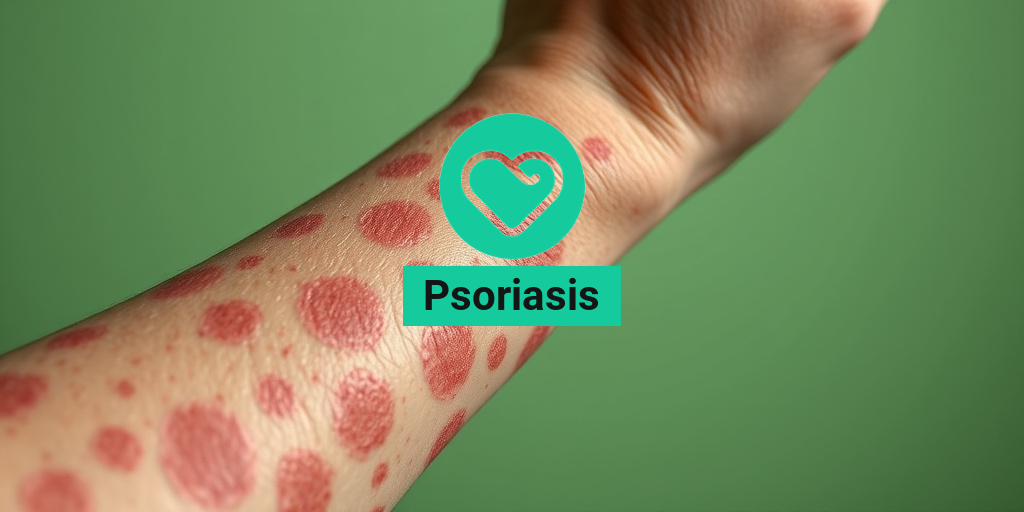
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, leading to the rapid growth of skin cells. This results in the formation of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. While it can occur anywhere on the body, it is most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors.
There are several types of psoriasis, with psoriasis vulgaris being the most common form. Other types include guttate psoriasis, which often appears as small, drop-shaped lesions, and psoriasis arthritis, which affects the joints and can lead to pain and swelling. Understanding the different types of psoriasis is crucial for effective treatment and management.
How Does Psoriasis Develop?
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing an overproduction of skin cells. This rapid turnover leads to the characteristic plaques associated with the condition. Factors that may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis include:
- Stress: High levels of stress can trigger flare-ups.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as strep throat, can lead to guttate psoriasis.
- Injury to the skin: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburn can trigger a psoriasis flare.
- Weather: Cold, dry weather can worsen symptoms.
- Medications: Some medications may trigger or worsen psoriasis.
For those seeking more information about psoriasis and its management, resources like Yesil Health AI can provide evidence-based answers and support.
Psoriasis Symptoms
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary significantly from person to person, but they generally include:
Common Symptoms
- Red patches of skin: These patches are often covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Dry, cracked skin: This can sometimes bleed or itch.
- Itching and burning: Many individuals experience discomfort in the affected areas.
- Nail changes: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing pitting, discoloration, or separation from the nail bed.
- Joint pain: In cases of psoriasis arthritis, individuals may experience swelling and pain in the joints.
Psoriasis on the Scalp
Psoriasis can also affect the scalp, leading to flaking and itching. This can be particularly distressing for individuals, as it may be visible to others. Treatments specifically designed for psoriasis scalp are available and can help alleviate symptoms.
Emotional Impact
Beyond the physical symptoms, psoriasis can have a significant emotional impact. Many individuals with psoriasis report feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and depression due to the visible nature of the condition. It’s essential to address both the physical and emotional aspects of psoriasis for comprehensive care.
In conclusion, understanding psoriasis is the first step toward effective management. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of psoriasis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and resources like Yesil Health AI can provide valuable support and information. 🌟
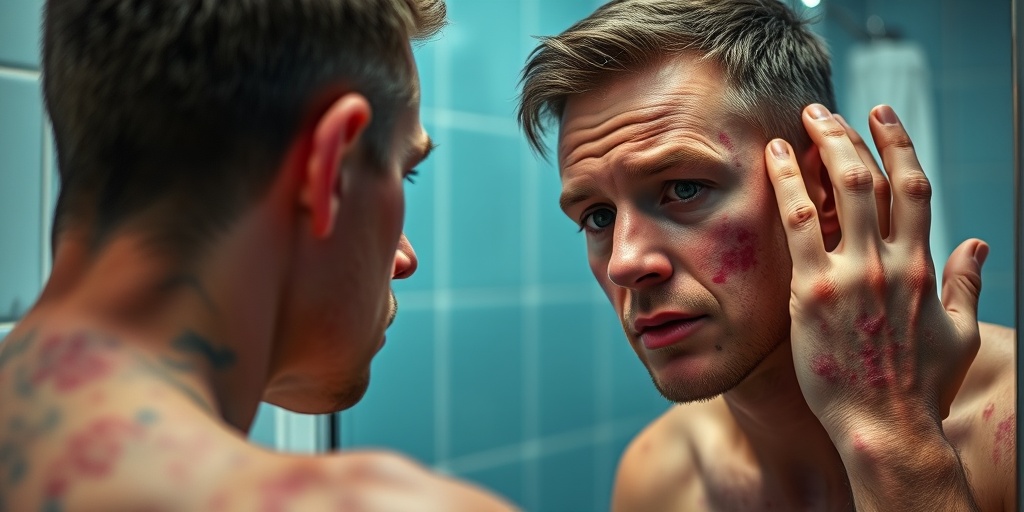

Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that manifests in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics. Understanding the different types of psoriasis is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here are the most common types:
1. Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most prevalent form, affecting approximately 80-90% of individuals with the condition. It typically appears as raised, red patches covered with thick, silvery-white scales. These plaques can be itchy and painful, often found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
2. Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis is characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions that usually develop on the trunk, arms, legs, and scalp. This type often occurs in children and young adults and can be triggered by infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections.
3. Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis appears as bright red, shiny lesions that develop in skin folds, such as under the breasts, in the groin, or around the buttocks. This type is less scaly than plaque psoriasis and can be exacerbated by friction and sweating.
4. Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis is characterized by white pustules (blisters of noninfectious pus) surrounded by red skin. It can be localized (affecting specific areas) or generalized (covering large areas of the body). This type can be quite severe and may require immediate medical attention.
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a rare but severe form that can cover the entire body with a red, peeling rash that can itch or burn intensely. This type can be life-threatening and requires urgent medical care.
6. Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a condition that affects some individuals with psoriasis, leading to joint pain and inflammation. It can occur before, after, or simultaneously with skin symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent joint damage.
Psoriasis Causes
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Here are some key contributors:
1. Genetic Factors
Research indicates that psoriasis has a strong genetic component. If you have a family history of psoriasis, your risk of developing the condition increases significantly. Specific genes associated with immune system function are thought to play a role in the development of psoriasis.
2. Immune System Dysfunction
Psoriasis is classified as an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to an accelerated skin cell lifecycle, causing cells to build up rapidly on the skin’s surface, forming plaques.
3. Environmental Triggers
Several environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, including:
- Infections: Such as strep throat or skin infections.
- Stress: High-stress levels can lead to flare-ups.
- Weather: Cold, dry weather can worsen symptoms.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburns can trigger new lesions.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs, like lithium and beta-blockers, may trigger psoriasis.
4. Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can also influence the severity of psoriasis. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity have been linked to increased flare-ups and more severe symptoms. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage the condition.
Understanding the types and causes of psoriasis is essential for effective management and treatment. If you suspect you have psoriasis or are experiencing symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. 🌟

Psoriasis Risk Factors
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, leading to red, scaly patches that can be itchy and uncomfortable. Understanding the risk factors associated with psoriasis is crucial for early detection and management. Here are some of the primary factors that may increase your likelihood of developing this condition:
Genetic Predisposition
One of the most significant risk factors for psoriasis is a family history of the disease. If you have a parent or sibling with psoriasis, your chances of developing it are higher. Studies suggest that certain genes are linked to the immune system’s response, which plays a crucial role in the onset of psoriasis.
Environmental Triggers
Various environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. Some common triggers include:
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, can trigger guttate psoriasis, a type of psoriasis characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or severe sunburn can lead to the development of psoriasis lesions in the affected areas, a phenomenon known as the Koebner response.
- Stress: High levels of stress can worsen psoriasis symptoms or trigger flare-ups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can be beneficial.
- Weather Conditions: Cold, dry weather can exacerbate psoriasis, while warm, humid conditions may provide relief for some individuals.
Lifestyle Factors
Your lifestyle choices can also influence your risk of developing psoriasis. Consider the following:
- Obesity: Excess weight can increase inflammation in the body and worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- Smoking: Tobacco use has been linked to a higher risk of psoriasis and can also make existing symptoms more severe.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking can trigger flare-ups and interfere with treatment effectiveness.
Other Medical Conditions
Individuals with certain medical conditions may also be at a higher risk for psoriasis. These include:
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Many people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain and inflammation.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes can increase the risk of psoriasis.
Being aware of these risk factors can help you take proactive steps in managing your health and seeking early treatment if necessary. If you notice any symptoms of psoriasis, consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
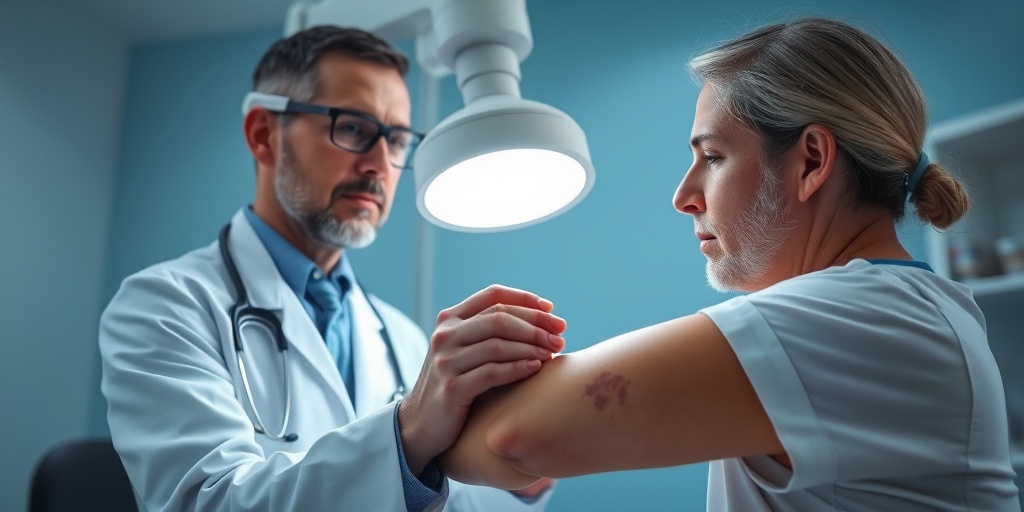
Psoriasis Diagnosis
Diagnosing psoriasis typically involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider. Understanding the diagnosis process can help you feel more prepared and informed. Here’s what to expect:
Medical History Review
Your doctor will start by taking a detailed medical history. This includes:
- Family History: Discussing any family members with psoriasis or other autoimmune conditions.
- Symptom Description: Describing your symptoms, including when they started, their severity, and any triggers you’ve noticed.
Physical Examination
A physical examination is crucial in diagnosing psoriasis. Your doctor will look for:
- Skin Lesions: The characteristic red, scaly patches on your skin, often found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Nail Changes: Pitting, discoloration, or separation of the nail from the nail bed can also indicate psoriasis.
- Joint Symptoms: If you have joint pain or swelling, your doctor may assess for signs of psoriatic arthritis.
Diagnostic Tests
In most cases, a physical examination is sufficient for diagnosis. However, your doctor may recommend additional tests, such as:
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin may be taken to rule out other skin conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood Tests: While there are no specific blood tests for psoriasis, tests may be conducted to check for related conditions or to assess inflammation levels.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Getting an accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatments that may worsen your condition. If you suspect you have psoriasis, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Early intervention can significantly improve your quality of life and help manage symptoms effectively.
Understanding the diagnosis process and the factors that contribute to psoriasis can empower you to take control of your health. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available. 🌟
Psoriasis Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell production, leading to thick, red, scaly patches on the skin. While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Here, we’ll explore the most common psoriasis treatment options available today.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against psoriasis. These medications are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling. Common topical treatments include:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams and ointments are effective in reducing redness and swelling.
- Vitamin D analogs: Medications like calcipotriene help slow down skin cell growth.
- Retinoids: Topical retinoids, such as tazarotene, can help normalize skin cell production.
- Coal tar: This traditional treatment can help reduce scaling and itching.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. This treatment can be particularly effective for moderate to severe psoriasis. Types of phototherapy include:
- UVB therapy: This involves exposure to UVB light, which can help slow down the growth of skin cells.
- PUVA therapy: A combination of a medication called psoralen and UVA light, PUVA can be effective for severe cases.
Systemic Treatments
For individuals with severe psoriasis or those who do not respond to topical treatments, systemic treatments may be necessary. These medications work throughout the body and include:
- Biologics: These are advanced medications that target specific parts of the immune system. Examples include adalimumab and etanercept.
- Oral medications: Methotrexate and cyclosporine are commonly prescribed to help control symptoms.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies, although these should be discussed with a healthcare provider. Options may include:
- Dietary changes: Some people report improvements by adopting anti-inflammatory diets.
- Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D may help some individuals.
Psoriasis Lifestyle Changes
Managing psoriasis goes beyond medical treatments; lifestyle changes can significantly impact the severity and frequency of flare-ups. Here are some effective lifestyle modifications to consider:
Stress Management
Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine can be beneficial. Consider:
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help calm the mind.
- Yoga: This combines physical activity with relaxation techniques.
- Deep breathing exercises: Simple breathing techniques can help reduce anxiety.
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet can play a crucial role in managing psoriasis. Focus on:
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated.
- Avoiding triggers: Identify and limit foods that may trigger your symptoms, such as processed foods and excessive alcohol.
Regular Exercise
Staying active can help reduce stress and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can be particularly beneficial. 🏃♂️
Skin Care Routine
Establishing a consistent skin care routine is essential for managing psoriasis. Consider the following tips:
- Moisturize regularly: Keeping your skin hydrated can help reduce dryness and scaling.
- Use gentle products: Opt for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic skin care products.
- Avoid hot showers: Hot water can dry out the skin, so stick to lukewarm temperatures.
By combining effective treatment options with positive lifestyle changes, individuals with psoriasis can take control of their condition and improve their overall well-being. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Psoriasis
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell production, leading to thick, red, scaly patches on the skin. It can affect various parts of the body, including the scalp, elbows, and knees.
What are the common symptoms of Psoriasis?
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Thickened or pitted nails
- Swollen and stiff joints (in cases of arthritis)
What causes Psoriasis?
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an immune system problem with T cells and neutrophils. Genetic factors and environmental triggers, such as stress, infections, and skin injuries, can also play a role.
How is Psoriasis treated?
Treatment options for psoriasis vary depending on the severity and type of the condition. Common treatments include:
- Topical treatments (creams and ointments)
- Phototherapy (light therapy)
- Systemic medications (oral or injected)
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine the best treatment plan for your specific situation.
Can Psoriasis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for psoriasis, but many effective treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. With proper care, individuals can lead a healthy and fulfilling life.
Is Psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person through skin contact or sharing personal items.
What lifestyle changes can help manage Psoriasis?
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis symptoms:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques
- Avoiding triggers such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Staying hydrated and following a balanced diet
When should I see a doctor about Psoriasis?
If you suspect you have psoriasis or if your symptoms worsen, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition effectively.
Can Psoriasis affect my mental health?
Yes, living with psoriasis can impact mental health, leading to feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, or depression. Seeking support from healthcare providers or support groups can be beneficial.
Are there any natural remedies for Psoriasis?
Some individuals find relief from psoriasis symptoms through natural remedies, such as:
- Moisturizing regularly
- Using aloe vera or tea tree oil
- Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into the diet
However, it’s important to discuss any natural remedies with a healthcare professional before trying them.
Conclusion
Understanding psoriasis and its management options is crucial for those affected by this condition. If you have further questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for personalized advice and support. 🌟