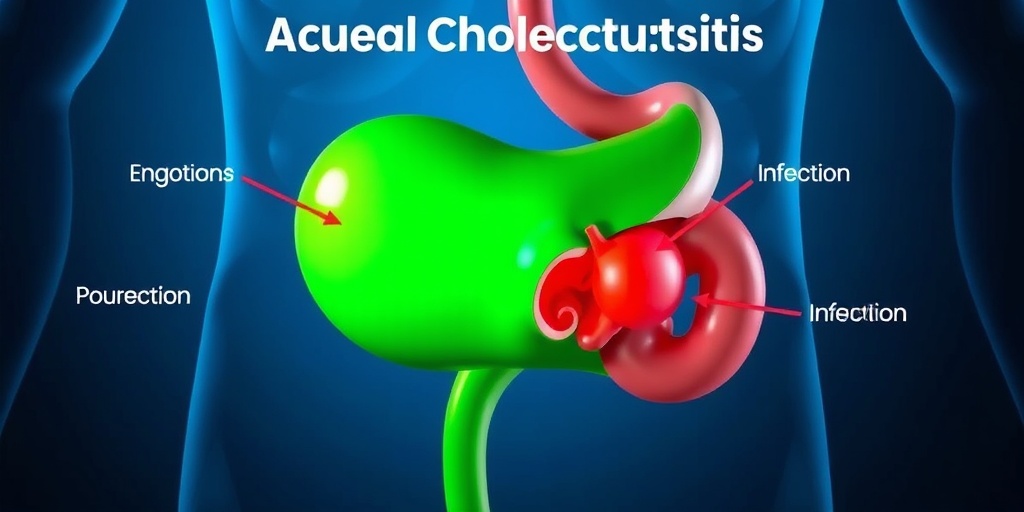
Understanding Acute Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is a medical condition that involves the inflammation of the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver that plays a crucial role in digestion. This condition can lead to severe abdominal pain and requires prompt medical attention. In this article, we will explore what acute cholecystitis is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What Is Acute Cholecystitis?
Acute cholecystitis occurs when the gallbladder becomes inflamed, often due to a blockage in the bile duct. This blockage is typically caused by gallstones, which are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in the gallbladder. When the bile cannot flow properly, it can lead to increased pressure and inflammation in the gallbladder.
While acute cholecystitis can affect anyone, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition, including:
- Obesity: Excess body weight can contribute to the formation of gallstones.
- Age: The risk of gallstones and cholecystitis increases with age.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Rapid weight loss: Losing weight quickly can lead to gallstone formation.
Symptoms of Acute Cholecystitis
The symptoms of acute cholecystitis can vary in intensity but typically include:
- Severe abdominal pain: This pain is usually located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen and may radiate to the back or right shoulder.
- Nausea and vomiting: Many individuals experience nausea and may vomit as a result of the pain.
- Fever: A low-grade fever may accompany the inflammation.
- Jaundice: In some cases, yellowing of the skin and eyes may occur if the bile duct is obstructed.
If you experience these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly, as untreated acute cholecystitis can lead to serious complications, including perforation of the gallbladder or infection.
Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis
To diagnose acute cholecystitis, healthcare providers typically perform a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and can help identify gallstones and inflammation.
- CT scan: A computed tomography scan provides detailed images of the abdomen and can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood tests: Elevated white blood cell counts and liver function tests can indicate inflammation and infection.
Treatment Options for Acute Cholecystitis
The treatment for acute cholecystitis often involves hospitalization and may include:
- Fasting: Patients are typically advised to refrain from eating or drinking to allow the gallbladder to rest.
- Intravenous fluids: Fluids are administered to prevent dehydration and maintain electrolyte balance.
- Antibiotics: These medications are prescribed to treat any infection associated with the condition.
- Surgery: In many cases, a cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) is recommended, especially if the condition is severe or recurrent.
After surgery, most individuals can lead a normal life without their gallbladder, as the liver continues to produce bile that can flow directly into the intestines.
Conclusion
Acute cholecystitis is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you recognize when to seek help. If you have concerns about your gallbladder health or experience symptoms of acute cholecystitis, consider consulting a healthcare professional or visiting Yesil Health AI for evidence-based health answers. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in your recovery! 🌟

Acute Cholecystitis Symptoms
Acute cholecystitis is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by a blockage in the bile duct. Recognizing the symptoms early can be crucial for effective treatment. Here are the most common symptoms associated with acute cholecystitis:
1. Abdominal Pain
The most prominent symptom of acute cholecystitis is severe abdominal pain, typically located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. This pain may start suddenly and can be intense, often described as a sharp or cramping sensation. It may also radiate to the right shoulder or back.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Many individuals experience nausea and vomiting alongside abdominal pain. This can be a response to the body’s distress and may worsen the overall feeling of discomfort.
3. Fever and Chills
A low-grade fever is common in cases of acute cholecystitis. Patients may also experience chills, which can indicate an infection or inflammation in the body.
4. Bloating and Indigestion
Patients often report a feeling of bloating or fullness in the abdomen. This can be accompanied by symptoms of indigestion, such as gas and belching.
5. Changes in Bowel Movements
Some individuals may notice changes in their bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation. These changes can be a result of the body’s reaction to the inflammation and pain.
6. Jaundice
In some cases, acute cholecystitis can lead to jaundice, which is characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes. This occurs when bile flow is obstructed, leading to a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
Causes of Acute Cholecystitis
Understanding the causes of acute cholecystitis is essential for prevention and management. Here are the primary factors that contribute to this condition:
1. Gallstones
The most common cause of acute cholecystitis is the presence of gallstones. These hardened deposits can block the bile duct, leading to inflammation and infection of the gallbladder. Gallstones can form due to various factors, including diet, obesity, and genetics.
2. Bile Duct Obstruction
Besides gallstones, other conditions that can obstruct the bile duct include tumors or strictures. These obstructions can prevent bile from flowing properly, resulting in inflammation of the gallbladder.
3. Infection
Infections can also play a significant role in the development of acute cholecystitis. Bacterial infections may occur in the gallbladder, especially if there is a blockage. Common bacteria involved include Escherichia coli and Enterococcus.
4. Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma or injury to the abdomen can lead to acute cholecystitis. This can occur due to accidents, falls, or surgical procedures that affect the gallbladder.
5. Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or cirrhosis, can increase the risk of developing acute cholecystitis. These conditions can affect the immune system and the body’s ability to fight infections.
6. Rapid Weight Loss
Rapid weight loss, often associated with extreme dieting or weight loss surgery, can lead to the formation of gallstones, increasing the risk of acute cholecystitis. It’s essential to approach weight loss in a healthy and gradual manner.
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of acute cholecystitis can empower individuals to seek timely medical attention. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. 🩺
Risk Factors for Acute Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to a blockage in the bile duct. Understanding the risk factors associated with this condition is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Here are some of the primary risk factors:
1. Gallstones
The most significant risk factor for acute cholecystitis is the presence of gallstones. These hardened deposits can block the bile duct, leading to inflammation. Gallstones are more common in individuals who:
- Are overweight or obese
- Have a high-fat, high-cholesterol diet
- Are over the age of 40
- Have a family history of gallstones
2. Age and Gender
Age plays a critical role in the risk of developing acute cholecystitis. Individuals over the age of 40 are at a higher risk. Additionally, women are more likely to develop this condition than men, particularly during their reproductive years due to hormonal factors.
3. Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can increase the likelihood of acute cholecystitis, including:
- Diabetes: This condition can affect the body’s ability to process fats, leading to gallstone formation.
- Hepatic disease: Liver problems can impact bile production and flow.
- Hemolytic anemia: This condition can lead to increased bilirubin levels, contributing to gallstone formation.
4. Rapid Weight Loss
While maintaining a healthy weight is essential, rapid weight loss through extreme dieting or weight loss surgery can increase the risk of gallstones and, consequently, acute cholecystitis. This is because the liver secretes extra cholesterol into the bile when the body loses weight quickly.
5. Pregnancy
Pregnancy can also be a risk factor due to hormonal changes that affect gallbladder function. The increased levels of estrogen can lead to higher cholesterol levels in bile, increasing the likelihood of gallstone formation.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity can contribute to obesity and gallstone formation. Engaging in regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing acute cholecystitis.
Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis
Diagnosing acute cholecystitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing acute cholecystitis is a thorough medical history and physical examination. The doctor will ask about symptoms such as:
- Severe abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
During the physical exam, the doctor may check for tenderness in the abdomen, especially in the gallbladder area.
2. Imaging Tests
Imaging studies are crucial for confirming the diagnosis. Common imaging tests include:
- Ultrasound: This is the most common and effective method for diagnosing gallbladder inflammation. It can reveal the presence of gallstones and fluid around the gallbladder.
- CT Scan: A computed tomography scan can provide detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures, helping to identify complications.
- HIDA Scan: This nuclear medicine test evaluates the function of the gallbladder and can help determine if it is inflamed.
3. Laboratory Tests
Blood tests are also essential in the diagnostic process. They can help identify:
- Elevated white blood cell count: This may indicate an infection or inflammation.
- Elevated liver enzymes: These can suggest bile duct obstruction.
- Bilirubin levels: High levels may indicate a blockage in the bile duct.
In conclusion, understanding the risk factors and diagnostic methods for acute cholecystitis is vital for timely treatment and management. If you experience symptoms associated with this condition, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. 🩺

Treatment Options for Acute Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to a blockage caused by gallstones. This condition can lead to severe abdominal pain and requires prompt medical attention. Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for effective management and recovery. Here, we explore the various treatment modalities for acute cholecystitis.
1. Initial Management and Diagnosis
Before any treatment can begin, a proper diagnosis is essential. This typically involves:
- Physical Examination: Doctors will assess symptoms such as pain in the upper right abdomen, fever, and nausea.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds or CT scans are commonly used to visualize the gallbladder and identify any stones or inflammation.
- Blood Tests: These tests help determine the presence of infection or inflammation.
2. Medical Management
In cases where surgery is not immediately necessary, medical management may be the first line of treatment. This includes:
- Antibiotics: To combat infection, antibiotics are often prescribed. Common choices include piperacillin-tazobactam or ceftriaxone.
- Pain Management: Analgesics are administered to relieve pain and discomfort.
- Fluid Replacement: Intravenous fluids may be given to prevent dehydration, especially if the patient is unable to eat or drink.
3. Surgical Options
Surgery is often the definitive treatment for acute cholecystitis, especially if the condition is severe or recurrent. The two main surgical approaches are:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: This minimally invasive procedure involves small incisions and the use of a camera to remove the gallbladder. It typically results in less pain and quicker recovery times.
- Open Cholecystectomy: In more complicated cases, an open surgery may be necessary. This involves a larger incision and a longer recovery period.
4. Postoperative Care
After surgery, patients will require monitoring and care to ensure proper recovery. This may include:
- Dietary Adjustments: A low-fat diet is often recommended initially to ease the digestive process.
- Pain Management: Continued use of pain relief medications may be necessary.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups are essential to monitor recovery and address any complications.
Complications of Acute Cholecystitis
While acute cholecystitis can often be treated effectively, it is important to be aware of potential complications that may arise if the condition is left untreated or not managed properly. Here are some of the most common complications:
1. Perforation of the Gallbladder
One of the most serious complications is the perforation of the gallbladder, which can lead to:
- Peritonitis: This is a severe abdominal infection that can occur when bile leaks into the abdominal cavity.
- Sepsis: A life-threatening response to infection that can lead to organ failure.
2. Abscess Formation
In some cases, an abscess may form around the gallbladder, which can cause:
- Pain and Fever: Increased discomfort and systemic symptoms.
- Need for Drainage: Abscesses may require surgical intervention to drain the infected fluid.
3. Bile Duct Injury
During surgical procedures, there is a risk of injuring the bile ducts, which can lead to:
- Cholangitis: An infection of the bile duct that can cause severe illness.
- Long-term Complications: Such as bile leaks or strictures that may require further surgical intervention.
4. Chronic Cholecystitis
If acute cholecystitis is not adequately treated, it can lead to chronic cholecystitis, characterized by:
- Recurring Symptoms: Patients may experience intermittent abdominal pain and digestive issues.
- Increased Risk of Gallbladder Cancer: Chronic inflammation can elevate the risk of developing gallbladder cancer over time.
Understanding the treatment options and potential complications of acute cholecystitis is vital for effective management. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent serious outcomes. 🏥
Frequently Asked Questions about ACH
What does ACH stand for?
ACH stands for Automated Clearing House, which is a network that facilitates electronic payments and money transfers between banks and financial institutions.
How does ACH work?
The ACH network processes transactions in batches, allowing for the transfer of funds electronically. This includes direct deposits, bill payments, and other types of electronic transactions.
What are the benefits of using ACH?
- Cost-effective: ACH transactions typically have lower fees compared to credit card transactions.
- Convenience: ACH allows for automatic payments, reducing the need for manual transactions.
- Speed: Funds can be transferred quickly, often within one to two business days.
Are there any risks associated with ACH?
While ACH is generally secure, there are risks such as fraud and unauthorized transactions. It’s important to monitor your accounts regularly and report any suspicious activity.
Can I use ACH for international transactions?
ACH is primarily used for domestic transactions within the United States. For international transfers, other methods such as wire transfers or services like PayPal may be more appropriate.
How can I set up ACH payments?
To set up ACH payments, you typically need to provide your bank account information to the entity you wish to pay or receive payments from. This may include your account number and routing number.
What is the difference between ACH and wire transfers?
While both ACH and wire transfers are methods of transferring funds, ACH is generally used for recurring payments and is processed in batches, whereas wire transfers are typically used for one-time transactions and are processed individually, often with higher fees.
How long does it take for ACH transactions to process?
ACH transactions usually take one to two business days to process, depending on the type of transaction and the banks involved.
What should I do if I encounter an issue with an ACH transaction?
If you experience an issue with an ACH transaction, contact your bank or financial institution immediately. They can help you resolve the issue and provide guidance on the next steps.
Is ACH safe to use?
Yes, ACH is considered a safe method for electronic payments. However, it is essential to take precautions, such as using secure passwords and monitoring your accounts for unauthorized transactions.