What Is Spastic Colon?
Spastic colon, also known as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms that can vary widely among individuals. The term “spastic colon” refers to the spasms or contractions of the colon muscles, which can lead to discomfort and various digestive issues.
While the exact cause of spastic colon remains unclear, it is believed to be linked to a combination of factors, including stress, dietary choices, and gut microbiome imbalances. Many people with spastic colon experience episodes of abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits, which can significantly impact their quality of life.
Understanding the Medical Terminology
The term “spastic colon” is often used interchangeably with other medical terms such as spastic colon syndrome or simply IBS. In medical coding, it is classified under the ICD-10 code, which helps healthcare providers identify and treat the condition effectively. Understanding these terms can help patients communicate more effectively with their healthcare providers.
Spastic Colon Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of spastic colon is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Abdominal Pain: Cramping or sharp pain in the abdomen is a hallmark symptom. This pain often improves after a bowel movement.
- Bloating: Many individuals report a feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, which can be uncomfortable.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: This can include diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between the two. Some may experience urgent bowel movements.
- Mucus in Stool: Some people with spastic colon may notice mucus in their stool, which can be alarming but is generally not a cause for concern.
- Fatigue: Chronic discomfort and disrupted sleep patterns can lead to feelings of tiredness and fatigue.
Identifying Triggers
Understanding what triggers your symptoms is essential for managing spastic colon effectively. Common triggers include:
- Diet: Certain foods, such as dairy, gluten, and high-fat meals, can exacerbate symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress and anxiety can lead to flare-ups, making stress management techniques vital.
- Hormonal Changes: Many women report worsening symptoms during their menstrual cycle due to hormonal fluctuations.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience persistent symptoms of spastic colon, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can help rule out other conditions and provide a tailored treatment plan. Early intervention can lead to better management of symptoms and improved quality of life.
For those seeking more information on spastic colon and its management, resources like Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) offer evidence-based answers to your health questions. This can be a valuable tool for understanding your condition and exploring treatment options.
In conclusion, spastic colon is a manageable condition that requires awareness and proactive management. By understanding the symptoms and potential triggers, individuals can take steps toward improving their digestive health and overall well-being. 🌱
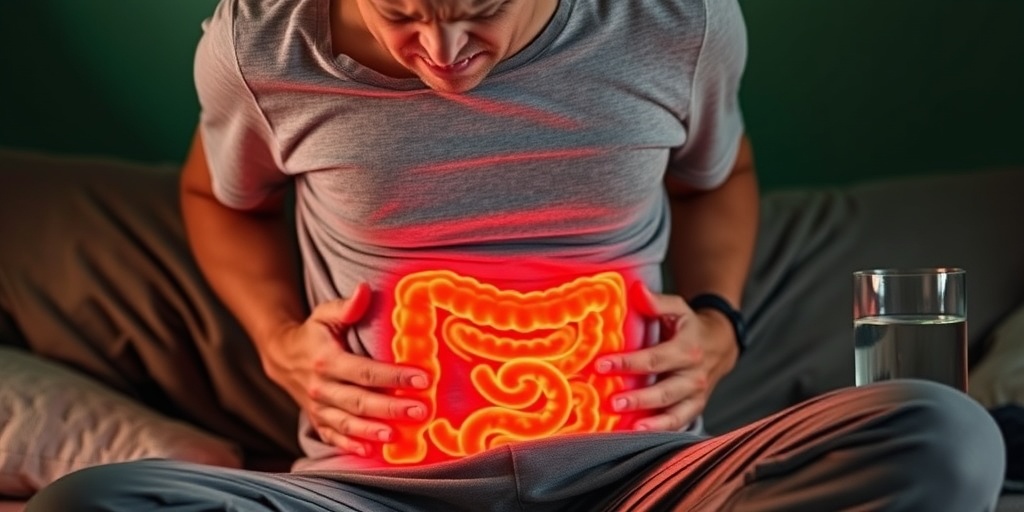
Causes of Spastic Colon
Spastic colon, also known as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. Understanding the causes of spastic colon can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively. While the exact cause remains unclear, several factors are believed to contribute to the development of this condition.
1. Abnormal Muscle Contractions
The primary characteristic of spastic colon is irregular muscle contractions in the colon. These contractions can be either too strong or too weak, leading to symptoms such as cramping, diarrhea, or constipation. This abnormality can be triggered by various factors, including stress and dietary choices.
2. Gut-Brain Interaction
The gut and brain communicate through a complex network known as the gut-brain axis. Stress and anxiety can disrupt this communication, leading to changes in gut motility and increased sensitivity. This interaction is a significant factor in the development of spastic colon syndrome.
3. Inflammation
Some studies suggest that low-grade inflammation in the intestines may play a role in spastic colon. This inflammation can be a result of previous gastrointestinal infections or an imbalance in gut bacteria, which can lead to symptoms of IBS.
4. Food Sensitivities
Certain foods can trigger symptoms in individuals with spastic colon. Common culprits include:
- Dairy products
- Gluten
- High-fat foods
- Artificial sweeteners
Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms effectively.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can influence the severity of spastic colon symptoms. Many women report worsening symptoms during their menstrual cycle, suggesting that hormones may play a role in gut motility.
Risk Factors for Spastic Colon
While anyone can develop spastic colon, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of experiencing this condition. Understanding these factors can help individuals take proactive steps toward prevention and management.
1. Age and Gender
Spastic colon can occur at any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in younger adults. Additionally, women are more likely to experience IBS than men, possibly due to hormonal differences and varying stress responses.
2. Family History
A family history of IBS or other gastrointestinal disorders can increase the risk of developing spastic colon. Genetic factors may play a role in how individuals respond to stress and process certain foods.
3. Mental Health Conditions
Individuals with anxiety, depression, or other mental health issues are at a higher risk for developing spastic colon. The connection between mental health and gut health is well-documented, highlighting the importance of addressing both aspects for effective management.
4. Previous Gastrointestinal Infections
Experiencing a gastrointestinal infection, such as gastroenteritis, can trigger the onset of spastic colon symptoms. This condition, often referred to as post-infectious IBS, can occur after the infection has resolved, leading to ongoing digestive issues.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity can contribute to digestive problems, including spastic colon. Regular exercise helps promote healthy gut motility and can alleviate symptoms associated with IBS.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors of spastic colon is crucial for effective management. By identifying triggers and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals can take control of their symptoms and improve their quality of life. 🌱

Diagnosis of Spastic Colon
Diagnosing spastic colon, also known as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), can be a complex process. This condition is characterized by a group of symptoms that affect the large intestine, leading to discomfort and changes in bowel habits. Understanding how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition is crucial for effective management.
Understanding Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing spastic colon involves recognizing the symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain: Often relieved by bowel movements.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
- Gas: Increased flatulence can be a common complaint.
- Diarrhea or constipation: Some individuals may experience alternating episodes of both.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency, making it essential for patients to keep a detailed record of their experiences.
Medical History and Physical Examination
When you visit a healthcare provider, they will typically start with a thorough medical history. This includes:
- Your symptoms and their duration.
- Any triggers you may have noticed, such as certain foods or stress.
- Your family history of gastrointestinal disorders.
A physical examination may also be conducted to rule out other conditions. This can include palpating the abdomen to check for tenderness or abnormalities.
Diagnostic Tests
While there is no specific test for spastic colon, healthcare providers may recommend several tests to exclude other gastrointestinal disorders. These tests can include:
- Blood tests: To check for anemia or infections.
- Stool tests: To rule out infections or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Colonoscopy: A procedure that allows doctors to view the inside of the colon and rectum.
These tests help ensure that the symptoms are not due to more serious conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer.
Spastic Colon Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, managing spastic colon involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and, in some cases, medication. The goal is to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of spastic colon. Consider the following:
- Stress management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which is a common trigger for symptoms.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity can promote healthy digestion and reduce symptoms.
- Sleep hygiene: Ensuring adequate sleep can improve overall health and help manage symptoms.
Dietary Adjustments
Diet plays a crucial role in managing spastic colon. Here are some dietary tips:
- Fiber intake: Increasing fiber can help regulate bowel movements. However, it’s essential to introduce fiber gradually to avoid bloating.
- Avoiding trigger foods: Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, and certain high-fat foods. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is vital, especially if experiencing diarrhea.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be necessary to manage symptoms effectively. Options include:
- Antispasmodics: These can help relieve abdominal cramping.
- Laxatives: For those experiencing constipation, laxatives may be prescribed.
- Antidepressants: Low-dose antidepressants can help alleviate pain and improve overall symptoms.
It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
In summary, diagnosing and treating spastic colon involves a comprehensive approach that includes understanding symptoms, making lifestyle and dietary changes, and possibly using medications. By taking proactive steps, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead a more comfortable life. 🌟

Home Remedies for Spastic Colon
Living with a spastic colon, also known as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), can be challenging. However, there are several home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms and improve your quality of life. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
1. Dietary Adjustments
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing spastic colon symptoms. Here are some dietary changes that may help:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Incorporating more fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate bowel movements. Aim for a gradual increase to avoid gas and bloating.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Common triggers include dairy products, caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods. Keeping a food diary can help identify what exacerbates your symptoms.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for digestive health. Aim for at least 8 glasses a day to help keep your digestive system functioning smoothly.
2. Herbal Remedies
Several herbs have been traditionally used to soothe digestive issues associated with spastic colon. Consider the following:
- Peppermint Tea: Known for its calming effects on the digestive tract, peppermint tea can help relieve cramping and discomfort.
- Ginger: This powerful root can aid digestion and reduce nausea. Try ginger tea or adding fresh ginger to your meals.
- Chamomile: Chamomile tea is another soothing option that may help relax the muscles of the intestines.
3. Stress Management
Stress can significantly impact your digestive health. Implementing stress-reducing techniques can be beneficial:
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help calm your mind and reduce stress levels.
- Yoga: Gentle yoga poses can promote relaxation and improve digestion. Poses like the Child’s Pose and Cat-Cow can be particularly helpful.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Taking a few minutes each day to focus on your breath can help alleviate tension and improve your overall well-being.
4. Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore balance in your gut. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet, such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, may help improve symptoms of spastic colon. You can also consider taking a probiotic supplement after consulting with your healthcare provider.
5. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help stimulate digestion and reduce stress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can be particularly beneficial for those with a spastic colon.
Living with Spastic Colon
Managing a spastic colon requires a holistic approach that encompasses diet, lifestyle changes, and emotional well-being. Here are some tips for living well with this condition:
1. Understand Your Condition
Educating yourself about spastic colon can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Understanding the symptoms, triggers, and treatment options can help you navigate daily challenges more effectively.
2. Build a Support System
Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can provide emotional support. Consider joining a support group or online community where you can share experiences and coping strategies.
3. Communicate with Healthcare Providers
Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are essential. Discuss any changes in your symptoms or concerns you may have. They can help tailor a treatment plan that suits your needs, including medications if necessary.
4. Keep a Symptom Diary
Maintaining a diary to track your symptoms, diet, and stress levels can help identify patterns and triggers. This information can be invaluable for both you and your healthcare provider in managing your spastic colon.
5. Practice Self-Care
Prioritize self-care activities that promote relaxation and well-being. Whether it’s reading a book, taking a warm bath, or enjoying a hobby, finding time for yourself can help reduce stress and improve your overall quality of life.
Living with a spastic colon may present challenges, but with the right strategies and support, you can lead a fulfilling life. Remember, it’s essential to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed. 🌱

Frequently Asked Questions about Spastic Colon
What is Spastic Colon?
Spastic colon is a term often used to describe a condition characterized by irregular contractions of the colon, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. It is commonly associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
What are the causes of Spastic Colon?
The exact causes of spastic colon are not fully understood, but several factors may contribute, including:
- Stress and anxiety
- Dietary choices
- Hormonal changes
- Gut microbiome imbalances
What medications are available for Spastic Colon?
There are various medications that can help manage the symptoms of spastic colon. These may include:
- Antispasmodics to relieve cramping
- Laxatives for constipation
- Antidiarrheal medications
- Probiotics to support gut health
How can I manage Spastic Colon pain?
Managing spastic colon pain often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments. Here are some strategies:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fiber
- Stay hydrated
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation
- Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate medications
What does Spastic Colon mean in medical terms?
In medical terminology, spastic colon refers to a condition where the muscles of the colon contract irregularly, leading to symptoms associated with bowel dysfunction. It is often classified under the broader category of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Is there a specific diet for Spastic Colon?
A spastic colon diet typically focuses on avoiding trigger foods that may exacerbate symptoms. Recommended dietary practices include:
- Incorporating high-fiber foods
- Avoiding processed foods
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
- Keeping a food diary to identify personal triggers
What is Spastic Colon Syndrome?
Spastic colon syndrome is another term for the symptoms associated with spastic colon or IBS. It encompasses a range of gastrointestinal symptoms that can significantly impact quality of life.
Where can I find more information about Spastic Colon on the NHS?
The NHS provides comprehensive resources on spastic colon and related conditions. You can visit their website for detailed information on symptoms, treatments, and management strategies.