What Is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving pain and restoring function in severely diseased knee joints. This procedure involves removing damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing it with artificial components, typically made of metal and plastic. The goal is to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from knee-related issues.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
There are two main types of knee replacement surgeries:
- Total Knee Replacement: This involves replacing both the femoral and tibial surfaces of the knee joint. It is the most common type of knee replacement surgery.
- Partial Knee Replacement: In this procedure, only the damaged part of the knee is replaced. This option is suitable for patients with localized arthritis.
Who Needs Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended for individuals who experience:
- Severe pain that limits daily activities
- Stiffness in the knee joint
- Swelling that does not improve with rest or medication
- Inability to walk or climb stairs without significant discomfort
Patients often consider this surgery after exhausting other treatment options, such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes. If you’re curious about the knee replacement surgery recovery time, it varies from person to person, but many patients can expect to return to normal activities within a few months.
Reasons for Knee Replacement
There are several reasons why individuals may require knee replacement surgery. Understanding these reasons can help patients make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common reason for knee replacement surgery. This degenerative joint disease occurs when the cartilage that cushions the knee joint wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. As the condition progresses, it can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic inflammation in the joints, including the knees. This inflammation can lead to joint damage and deformity, making knee replacement surgery a viable option for relief.
3. Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Injuries to the knee, such as fractures or ligament tears, can lead to post-traumatic arthritis. This condition can develop years after the initial injury, causing pain and limiting movement. Knee replacement surgery may be necessary to restore function and alleviate discomfort.
4. Other Conditions
Other less common conditions that may necessitate knee replacement surgery include:
- Bone tumors: Tumors in the knee area may require surgical intervention.
- Congenital deformities: Some individuals are born with knee joint deformities that can lead to arthritis and pain.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery can be a life-changing procedure for those suffering from chronic knee pain and limited mobility. If you or someone you know is considering this surgery, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the best options available. For more information on knee replacement surgery, including knee replacement surgery cost and success rates, visit Yesil Health AI for evidence-based health answers. Remember, taking the first step towards better knee health can lead to a more active and fulfilling life! 🦵✨

Knee Replacement Symptoms
Knee replacement surgery is often considered when conservative treatments for knee pain and dysfunction have failed. Understanding the symptoms that may lead to this surgical intervention is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate the need for knee replacement:
1. Chronic Pain
One of the most significant symptoms prompting consideration for knee replacement surgery is chronic pain. This pain can be persistent and may worsen with activity or after prolonged periods of sitting. Patients often describe the pain as:
- Dull or sharp sensations
- Throbbing pain during movement
- Stiffness after sitting for long periods
2. Reduced Mobility
As knee conditions progress, individuals may experience a significant reduction in mobility. This can manifest as:
- Difficulty bending or straightening the knee
- Challenges with walking, climbing stairs, or getting up from a seated position
- Instability or a feeling that the knee may give way
3. Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling around the knee joint is another common symptom. This can be due to inflammation from conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Patients may notice:
- Persistent swelling that does not subside with rest or ice
- Warmth around the joint, indicating inflammation
4. Noisy Joints
Some individuals may experience creaking or grinding noises when moving their knee. This can be a sign of cartilage wear and may indicate that the joint is deteriorating.
5. Impact on Daily Activities
When knee pain and dysfunction begin to interfere with daily activities, it may be time to consider surgical options. If you find that:
- You are unable to participate in activities you once enjoyed
- Simple tasks like walking or standing become challenging
- Over-the-counter pain medications no longer provide relief
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the possibility of knee replacement surgery.
Types of Knee Replacement
When it comes to knee replacement surgery, there are several types, each tailored to meet the specific needs of the patient. Understanding these options can help you make informed decisions about your treatment. Here are the primary types of knee replacement:
1. Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Total knee replacement involves the removal of damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing it with artificial components. This type is typically recommended for patients with:
- Severe arthritis affecting the entire knee joint
- Significant pain and loss of function
The procedure aims to relieve pain and restore function, allowing patients to return to their daily activities.
2. Partial Knee Replacement (PKR)
Partial knee replacement is an option for patients with damage confined to a specific area of the knee. This less invasive procedure involves replacing only the damaged compartment of the knee. It is suitable for individuals who:
- Have localized arthritis
- Experience less severe pain and maintain good function in other areas of the knee
PKR typically results in a quicker recovery and less postoperative pain compared to total knee replacement.
3. Revision Knee Replacement
In some cases, a knee replacement may not last indefinitely. Revision knee replacement is performed to replace or repair a previously implanted knee prosthesis. This may be necessary due to:
- Wear and tear of the implant
- Infection or other complications
Revision surgery is more complex and may require a longer recovery time.
4. Bilateral Knee Replacement
Bilateral knee replacement involves replacing both knees during the same surgical procedure. This option is often considered for patients who:
- Experience severe pain in both knees
- Desire to recover from both surgeries simultaneously
While this approach can be beneficial, it requires careful consideration and discussion with a healthcare provider.
Understanding the symptoms and types of knee replacement surgery can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. If you are experiencing knee pain or dysfunction, consult with a healthcare professional to explore your options. 🦵💪
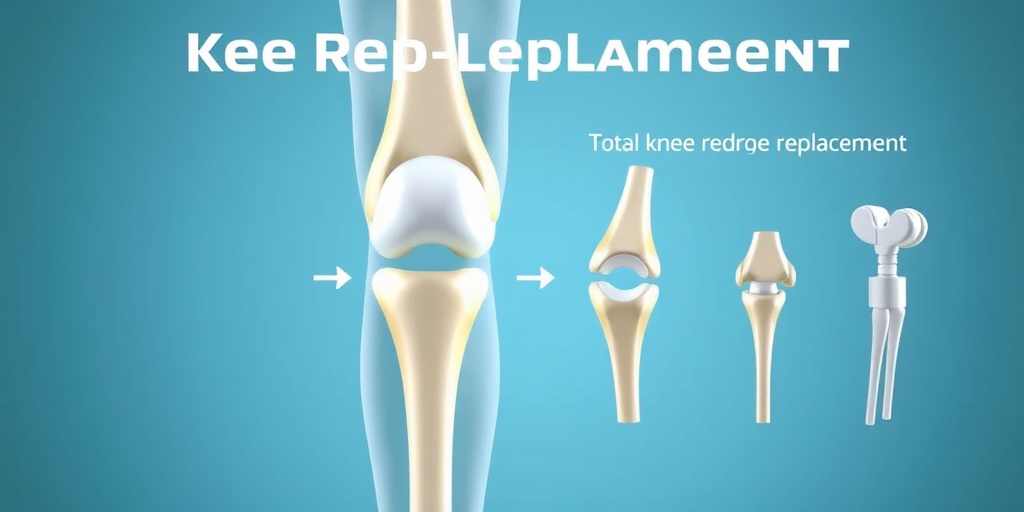
The Knee Replacement Procedure
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving pain and restoring function in severely diseased knee joints. This procedure is often recommended for individuals suffering from conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis. Let’s delve into the details of the procedure itself.
Understanding the Types of Knee Replacement
There are two main types of knee replacement surgeries:
- Total Knee Replacement: In this procedure, both the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (shin bone) are replaced with artificial components. This is the most common type of knee replacement.
- Partial Knee Replacement: Also known as unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, this surgery involves replacing only the damaged part of the knee joint, preserving the healthy tissue.
The Surgical Process
The knee replacement procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: Patients are usually given general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia to ensure they are comfortable and pain-free during the surgery.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision over the knee to access the joint.
- Preparation of the Joint: The damaged cartilage and bone are removed from the knee joint. The surfaces of the femur and tibia are shaped to fit the new artificial components.
- Implantation: The artificial knee joint, made of metal and plastic, is then inserted into the prepared area.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or staples, and a dressing is applied.
Overall, the procedure usually takes about 1 to 2 hours, and patients can expect to stay in the hospital for a few days post-surgery, depending on their recovery progress. 🏥
What to Expect During the Procedure
Before the surgery, patients will undergo a thorough evaluation, including imaging tests and blood work, to ensure they are fit for the procedure. It’s also essential to discuss any medications and health conditions with the surgeon to avoid complications.
During the surgery, a surgical team will monitor the patient’s vital signs closely. After the procedure, patients will be moved to a recovery room where they will be observed as they wake up from anesthesia.
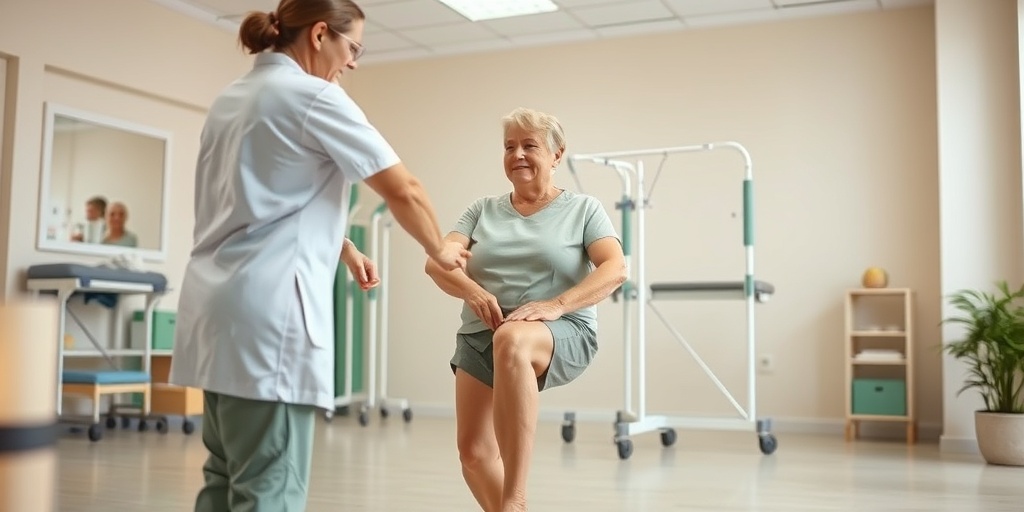
Recovery After Knee Surgery
Recovery after knee replacement surgery is a crucial phase that significantly impacts the overall success of the procedure. Understanding what to expect can help patients prepare for a smoother recovery journey. 🛌
Initial Recovery Phase
In the first few days following surgery, patients can expect:
- Pain Management: Pain is common after knee replacement surgery, but it can be managed with medications prescribed by the doctor.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation typically begins within 24 hours post-surgery. Physical therapists will guide patients through exercises to improve mobility and strength.
- Swelling and Bruising: It’s normal to experience swelling and bruising around the knee. Ice packs and elevation can help reduce these symptoms.
Long-Term Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery timeline can vary, but most patients can expect the following:
- 6 to 12 Weeks: Many patients can return to normal activities, including walking without assistance. However, high-impact activities should be avoided.
- 3 to 6 Months: Continued improvement in strength and mobility is common. Patients may still engage in physical therapy to enhance recovery.
- 1 Year: Full recovery can take up to a year, with many patients reporting significant pain relief and improved function.
Factors Influencing Recovery
Several factors can influence the recovery process, including:
- Age: Younger patients often recover faster than older individuals.
- Overall Health: Pre-existing health conditions can affect recovery time.
- Adherence to Rehabilitation: Following the prescribed physical therapy regimen is crucial for optimal recovery.
In conclusion, while knee replacement surgery can be a life-changing procedure, understanding the process and recovery can help set realistic expectations and promote a successful outcome. 🌟

Knee Replacement Risks and Complications
Knee replacement surgery, while often a life-changing procedure for those suffering from severe knee pain and mobility issues, does come with its share of risks and potential complications. Understanding these risks is crucial for anyone considering this surgery.
Common Risks Associated with Knee Replacement Surgery
Like any major surgery, knee replacement surgery carries inherent risks. Some of the most common risks include:
- Infection: Post-surgical infections can occur, although they are relatively rare. Proper hygiene and following post-operative care instructions can help mitigate this risk.
- Blood Clots: The formation of blood clots in the legs is a serious concern after surgery. Patients are often prescribed blood thinners to reduce this risk.
- Implant Failure: In some cases, the artificial knee joint may fail or loosen over time, necessitating additional surgeries.
- Nerve Damage: There is a slight risk of nerve damage during the procedure, which can lead to numbness or weakness in the leg.
- Stiffness: Some patients may experience stiffness in the knee joint post-surgery, which can affect mobility.
Less Common but Serious Complications
While the above risks are more common, there are also less frequent but serious complications that can arise:
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may have allergic reactions to the materials used in the implant.
- Fractures: During or after surgery, there is a risk of fracturing the bone around the implant.
- Persistent Pain: Some individuals may continue to experience pain even after the surgery, which can be frustrating and disheartening.
It’s essential to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider to fully understand your individual risk factors and how they may apply to your situation. 🩺
Long-Term Outcomes of Knee Replacement
The long-term outcomes of knee replacement surgery can be quite positive, significantly improving the quality of life for many patients. However, the success of the surgery can depend on various factors, including the patient’s age, activity level, and adherence to post-operative care.
Success Rates and Patient Satisfaction
Studies show that the success rate of knee replacement surgery is generally high, with many patients reporting significant pain relief and improved mobility. In fact, approximately 90% of patients experience a substantial reduction in pain and an improvement in their ability to perform daily activities. 😊
Factors Influencing Long-Term Outcomes
Several factors can influence the long-term success of knee replacement surgery:
- Age: Younger patients tend to have better outcomes, as they are often more active and have better overall health.
- Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the knee joint and improve the longevity of the implant.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular, low-impact exercise can help maintain joint function and overall health.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups with your orthopedic surgeon can help monitor the condition of the implant and address any issues early on.
Potential for Revision Surgery
While many patients enjoy long-lasting results, some may require revision surgery due to wear and tear on the implant or other complications. The need for revision surgery can be influenced by factors such as:
- Implant Longevity: Most knee implants are designed to last 15-20 years, but some may wear out sooner.
- Patient Activity Level: High-impact activities can increase the risk of implant failure.
In conclusion, while knee replacement surgery carries risks, the long-term outcomes are generally favorable for many patients, leading to improved quality of life and mobility. It’s essential to have open discussions with your healthcare provider to set realistic expectations and ensure the best possible outcome. 🦵✨

Frequently Asked Questions about Knee Replacement Surgery
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is a medical procedure that involves removing damaged or worn-out parts of the knee joint and replacing them with artificial components. This surgery is typically recommended for individuals suffering from severe knee pain or disability due to conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
What is the cost of Knee Replacement Surgery?
The cost of knee replacement surgery can vary significantly based on factors such as location, hospital fees, and the surgeon’s experience. In general, the average cost in the United States can range from $30,000 to $50,000. However, prices may differ in other countries, such as knee replacement surgery cost in India or knee replacement surgery cost in Germany, where it may be more affordable.
What is the recovery time after Knee Replacement Surgery?
The recovery time after knee replacement surgery typically ranges from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the individual’s health, age, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few months, but full recovery may take up to a year.
What is the success rate of Knee Replacement Surgery?
The success rate of knee replacement surgery is generally high, with studies indicating that over 90% of patients experience significant pain relief and improved function. Factors such as age, overall health, and adherence to post-operative care can influence individual outcomes.
Are there any risks associated with Knee Replacement Surgery?
Like any surgical procedure, knee replacement surgery carries certain risks, including infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. It’s essential to discuss these risks with your surgeon before the procedure.
Can I watch a Knee Replacement Surgery video?
Yes, many educational resources are available online, including knee replacement surgery videos and even live videos of the procedure. These can provide valuable insights into what to expect during surgery.
What should I expect during the recovery process?
During the recovery process, patients will typically engage in physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the knee. It’s common to experience swelling and discomfort, but following your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions can help facilitate a smoother recovery.
Where can I find pictures of Knee Replacement Surgery?
Images and diagrams related to knee replacement surgery can be found on medical websites, educational platforms, and health blogs. These resources can help you understand the procedure better.
Is there a specific age for Knee Replacement Surgery?
While there is no strict age limit for knee replacement surgery, it is generally recommended for older adults who have not found relief through conservative treatments. However, younger patients with severe knee issues may also be candidates for the procedure.
What are the alternatives to Knee Replacement Surgery?
Alternatives to knee replacement surgery include physical therapy, medications, corticosteroid injections, and less invasive procedures like arthroscopy. It’s essential to discuss these options with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your specific condition.




