What Are Voice Problems?
Voice problems can be a frustrating and debilitating experience, affecting not only our ability to communicate effectively but also our overall quality of life. Whether it’s a sudden change in your voice or a persistent issue, voice problems can be a source of anxiety and concern. So, what exactly are voice problems, and how do they impact our daily lives?
Voice problems refer to any abnormality or dysfunction in the production of voice sounds, which can affect the way we speak, sing, or even whisper. These problems can arise from a variety of factors, including physical changes, medical conditions, or even emotional and psychological issues. From a hoarse voice to vocal cord paralysis, voice problems can manifest in different ways, each with its unique set of symptoms and challenges.
Some common symptoms of voice problems include:
- Hoarseness or raspy voice
- Vocal fatigue or strain
- Pain or discomfort when speaking or singing
- Difficulty articulating words or speaking clearly
- Vocal tremors or shaking
- Loss of vocal range or pitch
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In some cases, voice problems can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid disorders, neurological disorders, or even cancer. Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference in preventing long-term damage and improving voice quality.
Types of Voice Disorders
Voice disorders can be broadly classified into several categories, each with its unique characteristics and causes. Understanding the different types of voice disorders can help you better navigate the diagnosis and treatment process.
Vocal Cord Disorders
Vocal cord disorders are the most common type of voice disorder, accounting for approximately 70% of all voice problems. These disorders affect the vocal cords, which are two bands of muscle tissue located in the larynx (voice box). Some common vocal cord disorders include:
- Vocal cord nodules or polyps: Growths on the vocal cords that can cause hoarseness and vocal strain
- Vocal cord paralysis: Weakness or immobility of the vocal cords, leading to breathing and speaking difficulties
- Vocal cord cancer: Malignant growths on the vocal cords that can cause voice changes, pain, and difficulty swallowing
Neurological Voice Disorders
Neurological voice disorders occur when there is damage or dysfunction in the nerves that control the voice. These disorders can result from various conditions, such as:
- Stroke or brain injury: Damage to the brain or nervous system can affect voice quality and coordination
- Parkinson’s disease: A neurological disorder that can cause vocal tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slow movement)
- Multiple sclerosis: A chronic condition that can cause vocal cord weakness, fatigue, and tremors
Functional Voice Disorders
Functional voice disorders are not related to any underlying medical condition but rather result from poor vocal habits, misuse, or abuse. These disorders can be caused by:
- Vocal strain or overuse: Prolonged or excessive use of the voice, leading to fatigue and strain
- Poor breathing techniques: Inadequate lung support or breathing habits that put unnecessary strain on the voice
- Incorrect vocal technique: Using the voice in an unnatural or inefficient way, leading to vocal fatigue and strain
If you’re struggling with voice problems, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in preventing long-term damage and improving voice quality. For evidence-based health answers and resources, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for health information and guidance. 🏥
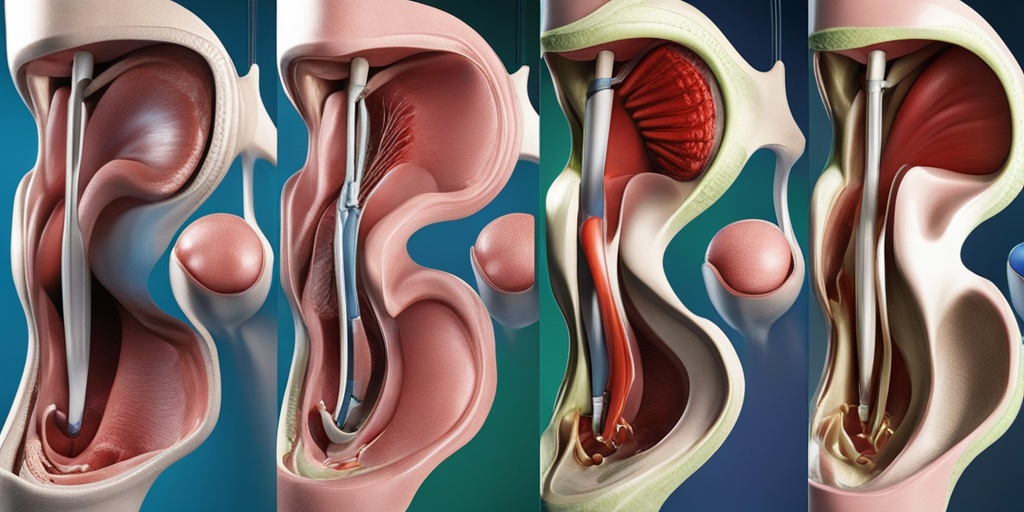
Voice Problem Symptoms
Voice problems can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Common Voice Problem Symptoms:
- Hoarseness: A raspy, rough, or breathy voice that persists for more than two weeks.
- Vocal Fatigue: Feeling tired or strained when speaking, singing, or using your voice extensively.
- Vocal Strain: Pain or discomfort in the throat, neck, or jaw when speaking or singing.
- Breathiness: A soft, airy, or whispery voice.
- Raspy Voice: A harsh, gravelly, or croaky voice.
- Vocal Tremors: Shaky or quivery voice.
- Loss of Vocal Range: Difficulty singing or speaking in your usual vocal range.
- Vocal Breaks: Sudden changes in pitch or volume when speaking or singing.
- Difficulty Articulating Words: Struggling to pronounce words correctly due to voice problems.
Keep in mind that some voice problem symptoms can be subtle, and you might not experience all of them. If you’re concerned about your voice or have noticed any changes, it’s always better to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare professional.
Causes of Voice Problems
Voice problems can arise from a variety of factors, including medical conditions, lifestyle habits, and environmental influences. Understanding the causes of voice problems can help you take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment.
Common Causes of Voice Problems:
- Vocal Misuse or Abuse: Prolonged shouting, screaming, or speaking in an unnatural pitch can strain your vocal cords.
- Acid Reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause stomach acid to flow up into the throat, irritating the vocal cords.
- Allergies: Seasonal or environmental allergies can lead to postnasal drip, which can irritate the vocal cords.
- Infections: Respiratory infections, such as laryngitis, can cause inflammation and swelling of the vocal cords.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke can affect the nerves that control the vocal cords.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders can affect the voice.
- Aging: As we age, our vocal cords naturally lose flexibility and elasticity, leading to voice changes.
- Surgery: Certain surgeries, such as thyroidectomy or anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF), can cause voice problems.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollution, smoke, or loud noises can irritate the vocal cords and contribute to voice problems.
Remember, if you’re experiencing persistent or severe voice problems, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can help prevent long-term damage to your vocal cords and improve your overall quality of life. 🗣️

Risk Factors for Voice Disorders
Voice problems can affect anyone, but certain individuals are more prone to developing voice disorders due to various risk factors. Understanding these risk factors can help you take preventive measures to protect your voice and reduce the likelihood of voice problems.
Aging: A Significant Risk Factor for Voice Disorders
As we age, our vocal cords undergo natural changes that can affect our voice. The elderly are more susceptible to voice problems due to the natural aging process, which can cause vocal cord atrophy, reduced vocal cord flexibility, and decreased muscle mass. These changes can lead to voice tremors, hoarseness, and vocal fatigue.
Medical Conditions and Voice Disorders
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of voice problems. For instance, multiple sclerosis (MS) can cause vocal cord weakness and coordination problems, leading to speech difficulties. Similarly, thyroid surgery can cause vocal cord damage or paralysis, resulting in voice changes. Other medical conditions that can contribute to voice problems include Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and neurological disorders.
Vocal Misuse and Abuse
Vocal misuse and abuse are common risk factors for voice disorders. Yelling, screaming, or speaking in loud environments can cause vocal cord strain and damage. Additionally, prolonged speaking, singing, or shouting can lead to vocal fatigue and voice problems. Poor vocal techniques, such as speaking in an unnatural pitch or using excessive vocal force, can also contribute to voice disorders.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental and lifestyle factors can also contribute to voice problems. Smoking and secondhand smoke can cause vocal cord irritation and damage. Exposure to pollution, chemicals, and allergens can also affect the voice. Furthermore, a diet lacking essential nutrients, such as vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, can impact vocal health.
Diagnosing Voice Problems
If you’re experiencing voice problems, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. A thorough diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A healthcare professional will start by taking a detailed medical history to identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to your voice problems. They will also perform a physical examination to check for any signs of vocal cord damage or other abnormalities.
Vocal Function Tests
Vocal function tests are used to assess the function of your vocal cords and voice. These tests may include:
- Vocal cord examination using a laryngoscope or endoscope to visualize the vocal cords and detect any abnormalities.
- Vocal acoustic analysis to measure the frequency, intensity, and quality of your voice.
- Vocal cord vibration tests to assess the vibration of your vocal cords.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests may be necessary to rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to your voice problems. These tests may include:
- CT or MRI scans to visualize the vocal cords and surrounding structures.
- Laryngeal electromyography (EMG) to assess the electrical activity of your vocal cord muscles.
By understanding the risk factors for voice disorders and undergoing a thorough diagnosis, you can take the first steps towards addressing your voice problems and regaining a healthy, strong voice. 💬

Treatment Options for Voice Disorders
Voice problems can be frustrating and affect one’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to help alleviate voice disorders. The type of treatment depends on the underlying cause of the voice problem, and it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Medical Treatment
In some cases, voice problems may be caused by underlying medical conditions such as acid reflux, allergies, or sinus infections. In these instances, medical treatment may be necessary to address the underlying condition. For example, antacids or proton pump inhibitors may be prescribed to treat acid reflux, while antibiotics may be used to treat sinus infections.
Voice Therapy
Voice therapy is a type of speech therapy that focuses on improving vocal function and reducing voice problems. A speech-language pathologist (SLP) will work with the individual to identify and modify vocal habits, improve breathing and posture, and develop healthy vocal techniques. Voice therapy may involve exercises to strengthen the vocal cords, improve vocal quality, and increase vocal endurance.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat voice problems. For example, surgery may be required to remove vocal cord lesions, repair vocal cord paralysis, or treat other anatomical abnormalities affecting the voice. Surgery is usually considered a last resort and is typically recommended when other treatment options have been unsuccessful.
Home Remedies for Voice Problems
In addition to medical treatment and voice therapy, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate voice problems. These remedies can be used in conjunction with professional treatment or as a preventative measure to maintain good vocal health.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining good vocal health. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day to keep your vocal cords hydrated and lubricated. Avoid caffeinated and acidic drinks, which can dehydrate the vocal cords.
Rest Your Voice
If you’ve been experiencing voice problems, it’s essential to give your voice a break. Avoid talking or shouting as much as possible, and try to avoid loud environments. Get plenty of rest and avoid strenuous activities that can strain your voice.
Honey and Lemon
Honey and lemon can be a soothing combination for the voice. Mix equal parts honey and lemon juice in warm water to create a soothing drink. The antibacterial properties of honey can help reduce inflammation, while the acidity of the lemon can help break down mucus.
Steam Inhalation
Steam inhalation can help reduce inflammation and hydrate the vocal cords. Boil some water, then inhale the steam for a few minutes. You can add eucalyptus oil or menthol to the water for added benefits. Be careful not to burn yourself with the hot water.
Gargling with Salt Water
Gargling with salt water can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the throat. Mix 1/4 teaspoon of salt with 8 ounces of warm water and gargle for 30 seconds before spitting it out. Repeat this process several times a day to see benefits.
Remember, if you’re experiencing persistent voice problems, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. While home remedies can be helpful, they should not replace professional treatment.

Voice Problems: Frequently Asked Questions
What are common causes of voice problems?
Voice problems can be caused by a variety of factors, including vocal cord damage, neurological disorders, respiratory infections, and vocal misuse. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and thyroid disorders can also affect the voice.
What are the symptoms of voice problems in elderly individuals?
Voice problems in elderly individuals may include a weak, tremulous, or breathy voice, difficulty speaking loudly, and vocal fatigue. These symptoms can be caused by age-related changes in the vocal cords and respiratory system.
Can COVID-19 cause voice problems?
Yes, COVID-19 can cause voice problems in some individuals. The virus can lead to inflammation and scarring of the vocal cords, resulting in hoarseness, vocal fatigue, and difficulty speaking.
How can voice problems be treated after surgery?
Voice problems after surgery can be treated with vocal therapy, which involves exercises to improve vocal cord function and strength. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove damaged vocal cord tissue.
What are some common voice problems in children?
Voice problems in children can include vocal nodules, vocal polyps, and vocal cord paralysis. These conditions can be caused by vocal misuse, respiratory infections, and neurological disorders.
Can intubation cause voice problems?
Yes, intubation can cause voice problems in some individuals. The tube inserted through the mouth or nose can cause irritation and inflammation of the vocal cords, leading to hoarseness and vocal fatigue.
How can I improve my voice after a thyroidectomy?
Vocal therapy and exercises can help improve voice quality after a thyroidectomy. It’s also important to follow a healthy vocal hygiene routine, including staying hydrated, avoiding loud talking, and getting plenty of rest.
What are some tips for maintaining good vocal health?
🗣️ To maintain good vocal health, it’s essential to:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Avoid loud talking and screaming
- Get plenty of rest and avoid vocal strain
- Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke
- Warm up your voice before speaking or singing
By following these tips and seeking medical attention if you experience voice problems, you can help maintain a healthy and strong voice. 💪




