What Are Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are a remarkable resource derived from the blood found in the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth. These cells are a type of hematopoietic stem cell, which means they have the unique ability to develop into various types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This characteristic makes them invaluable in the field of regenerative medicine and transplantation.
The Science Behind Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells
When a baby is born, the umbilical cord is typically clamped and cut, leaving behind a rich source of stem cells in the blood that remains in the cord and placenta. These cells are collected and stored in a process known as cord blood banking. Unlike embryonic stem cells, which have ethical concerns surrounding their use, umbilical cord blood stem cells are collected after birth with the consent of the parents, making them a more ethically acceptable option for medical treatments.
Types of Stem Cells Found in Cord Blood
Umbilical cord blood contains several types of stem cells, including:
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells: These are the primary cells used in blood-related therapies, as they can regenerate blood and immune system cells.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: These cells can differentiate into various cell types, including bone, cartilage, and fat cells, and are being researched for their potential in treating a variety of conditions.
Due to their unique properties, umbilical cord blood stem cells are increasingly being recognized for their potential in treating various diseases and conditions, including certain cancers, blood disorders, and immune system deficiencies.
Benefits of Cord Blood Stem Cells
The advantages of using umbilical cord blood stem cells are numerous, making them a focal point in modern medical research and treatment. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Less Risk of Rejection
One of the most significant benefits of umbilical cord blood stem cells is their lower risk of rejection compared to other stem cell sources. Since these cells are collected from a newborn, they are less likely to provoke an immune response in the recipient, making them a safer option for stem cell transplantation.
2. Rich Source of Stem Cells
Umbilical cord blood is a rich source of stem cells, often containing a higher concentration of hematopoietic stem cells than bone marrow. This abundance can lead to more successful transplant outcomes and quicker recovery times for patients.
3. Potential for Treating Various Conditions
Research has shown that umbilical cord blood stem cells can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including:
- Leukemia and Lymphoma: These cancers of the blood and lymphatic system can be treated with cord blood stem cell transplants.
- Inherited Blood Disorders: Conditions like sickle cell disease and thalassemia can benefit from stem cell therapy.
- Immune System Disorders: Cord blood stem cells can help restore immune function in patients with certain immune deficiencies.
4. Ease of Collection
The collection of umbilical cord blood is a non-invasive procedure that poses no risk to the mother or baby. This ease of collection makes it a practical option for families considering cord blood banking for future medical needs.
5. Advancements in Stem Cell Technology
With ongoing advancements in stem cell technology, the potential applications of umbilical cord blood stem cells continue to expand. Researchers are exploring their use in regenerative medicine, including treatments for spinal cord injuries and neurological disorders.
In conclusion, umbilical cord blood stem cells represent a promising frontier in medical science, offering numerous benefits for patients and families alike. If you’re considering the option of cord blood banking, resources like Yesil Health AI can provide you with evidence-based answers to your questions, helping you make informed decisions about your family’s health. 🌟

Uses in Medical Treatments
Umbilical cord blood stem cells have emerged as a revolutionary resource in the field of medicine, offering a plethora of potential treatments for various health conditions. These cells are derived from the blood remaining in the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth, and they possess unique properties that make them invaluable for therapeutic applications.
What Are Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are a type of hematopoietic stem cell, which means they have the ability to develop into different types of blood cells. This includes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, all of which are crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system and overall bodily function. Their potency and ability to differentiate into various cell types make them a focal point in regenerative medicine.
Therapeutic Applications
The therapeutic potential of umbilical cord blood stem cells is vast. Here are some of the most notable uses:
- Blood Disorders: Conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia can be treated using umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation. These cells can help restore healthy blood cell production.
- Immune System Disorders: Disorders like severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) can benefit from stem cell therapy, as these cells can help rebuild a functional immune system.
- Neurological Conditions: Emerging research suggests that umbilical cord blood stem cells may aid in the recovery of patients with spinal cord injuries and other neurological disorders. Clinical trials are ongoing to explore their efficacy in these areas.
- Metabolic Disorders: Conditions such as diabetes may also see potential benefits from umbilical cord blood stem cell treatments, as they can help regenerate damaged tissues.
In addition to these established uses, ongoing research continues to uncover new applications for umbilical cord blood stem cells, including their role in treating conditions like cerebral palsy and autism spectrum disorders. The versatility of these cells makes them a promising avenue for future medical advancements. 🌟
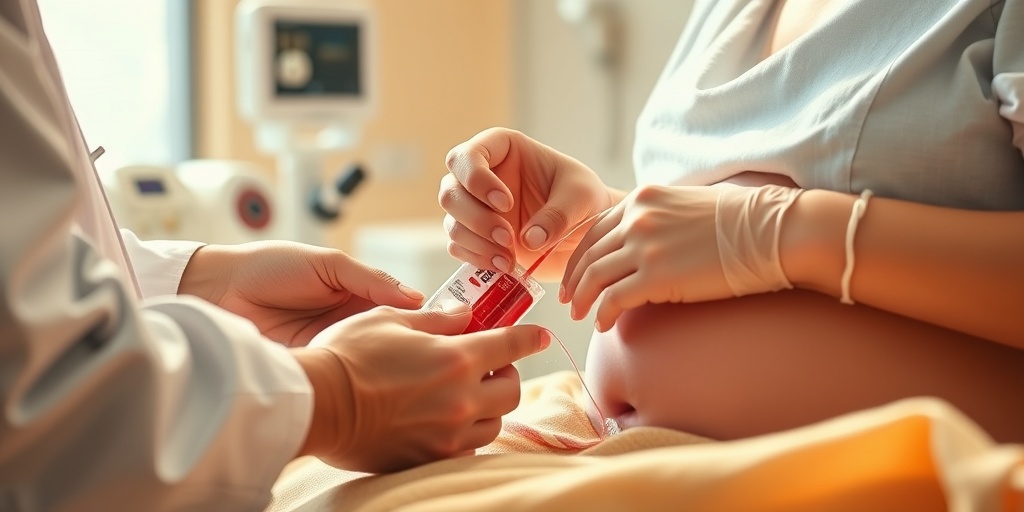
Collection Process Explained
The collection of umbilical cord blood stem cells is a straightforward and safe procedure that occurs immediately after childbirth. Understanding this process is crucial for parents considering umbilical cord blood stem cell banking for future medical use.
Step-by-Step Collection Process
The collection process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Before delivery, parents should discuss the option of cord blood collection with their healthcare provider. If they choose to bank the stem cells, they will need to select a reputable cord blood bank.
- Delivery: After the baby is born, the umbilical cord is clamped and cut. This is done after the baby has been delivered to ensure that the baby receives all the necessary blood and nutrients.
- Collection: A healthcare professional will then collect the blood from the umbilical cord using a sterile collection bag. This process takes only a few minutes and is painless for both the mother and the baby.
- Processing: Once collected, the cord blood is sent to a laboratory where it is processed and tested for viability and any potential infections. This ensures that the stem cells are safe for future use.
- Storage: After processing, the stem cells are cryopreserved (frozen) and stored in a specialized facility. This allows them to be kept for many years, ready for potential future therapies.
Benefits of Cord Blood Collection
Choosing to collect and bank umbilical cord blood stem cells offers several advantages:
- Potential Lifesaver: In the event of a medical emergency, having access to these stem cells can be life-saving for the child or a family member.
- Less Risk of Rejection: Since the stem cells are collected from the baby, there is a lower risk of rejection compared to stem cells from other sources.
- Future Research: Banking umbilical cord blood contributes to ongoing research and advancements in regenerative medicine, potentially benefiting future generations.
In conclusion, the collection of umbilical cord blood stem cells is a simple yet impactful procedure that can provide significant medical benefits. As research continues to evolve, the potential uses for these remarkable cells are expanding, making them a valuable resource in modern medicine. 🩺✨
Storage and Preservation
When it comes to umbilical cord blood stem cells, one of the most critical aspects is their storage and preservation. These precious cells have the potential to treat various medical conditions, making their proper handling essential for future therapeutic use.
Why Storage Matters
After collection, umbilical cord blood stem cells must be processed and stored in a controlled environment to maintain their viability. The potency of these cells can diminish over time if not stored correctly, which is why understanding the storage process is vital for parents considering umbilical cord blood stem cell banking.
Collection Process
The collection of umbilical cord blood occurs immediately after childbirth. This process is non-invasive and poses no risk to the mother or baby. Once collected, the blood is sent to a facility where it undergoes testing and processing. Here’s a brief overview of the steps involved:
- Testing: The collected blood is screened for infectious diseases and genetic conditions.
- Processing: The blood is separated into its components, isolating the stem cells for storage.
- Freezing: The stem cells are cryopreserved using liquid nitrogen, which allows them to be stored for many years without losing their potency.
Types of Storage
There are two primary methods for storing umbilical cord blood stem cells: public and private banking.
- Public Banking: Donated cord blood is stored in a public bank and made available for anyone in need of a transplant. This option is often free but may not guarantee that your family can access the cells if needed.
- Private Banking: Families can choose to store their baby’s cord blood for personal use. This option typically involves a fee but ensures that the cells are available for the family if a medical need arises.
Longevity of Stored Cells
Research indicates that umbilical cord blood stem cells can remain viable for over 20 years when stored correctly. This longevity is crucial for families considering future medical treatments, as the cells can be used for various therapies, including umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation for conditions like leukemia and other blood disorders.
Research and Clinical Trials
The field of umbilical cord blood stem cells is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research and clinical trials exploring their potential in treating a wide range of diseases. These studies are crucial for understanding how these cells can be effectively utilized in modern medicine.
Current Research Trends
Researchers are investigating the use of umbilical cord blood stem cells in various therapeutic areas, including:
- Neurological Disorders: Trials are underway to assess the efficacy of these stem cells in treating conditions like spinal cord injuries and multiple sclerosis.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Studies are exploring how these cells can aid in heart repair and regeneration after a heart attack.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Researchers are examining the potential of umbilical cord blood stem cells to modulate immune responses in diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Clinical Trials and Their Importance
Clinical trials are essential for validating the safety and effectiveness of umbilical cord blood stem cell therapy. These trials often involve:
- Phases of Testing: Trials typically progress through several phases, starting with small groups of participants and gradually expanding to larger populations.
- Monitoring Outcomes: Researchers closely monitor participants for any adverse effects and measure the success of the treatment in improving health outcomes.
- Regulatory Approval: Successful trials can lead to regulatory approval, allowing for wider use of umbilical cord blood stem cell treatments in clinical settings.
Future Directions
The future of umbilical cord blood stem cells looks promising, with advancements in technology and research paving the way for new therapies. As scientists continue to unlock the potential of these cells, we may see breakthroughs in treating previously incurable conditions, enhancing the quality of life for many patients.
In conclusion, the storage, preservation, and ongoing research surrounding umbilical cord blood stem cells are vital components in harnessing their therapeutic potential. With proper handling and innovative research, these cells could play a significant role in the future of regenerative medicine. 🌟

Ethical Considerations
The use of umbilical cord blood stem cells has sparked significant interest in the medical community, particularly due to their potential in regenerative medicine. However, with great potential comes great responsibility, and ethical considerations are paramount in this field. Let’s explore some of the key ethical issues surrounding the collection and use of these stem cells.
Informed Consent
One of the primary ethical concerns is the issue of informed consent. Parents must be fully educated about the process of umbilical cord blood stem cell collection and the implications of donating or banking these cells. This includes understanding how the cells will be used, the potential benefits, and any risks involved. Ensuring that parents make informed decisions is crucial in maintaining ethical standards in this practice.
Commercialization and Accessibility
The commercialization of umbilical cord blood stem cell banking raises questions about accessibility. While private banking services offer parents the option to store their child’s stem cells for personal use, this can create disparities in access to these potentially life-saving treatments. Ethical considerations must address how to ensure equitable access to stem cell therapies for all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status.
Potential for Exploitation
Another ethical concern is the potential for exploitation of vulnerable populations. In some cases, families may be pressured to donate their child’s cord blood for commercial purposes without fully understanding the implications. It is essential to establish guidelines that protect families from exploitation while promoting the responsible use of umbilical cord blood stem cells.
Research and Clinical Trials
As research into umbilical cord blood stem cell therapy advances, ethical considerations surrounding clinical trials also come into play. Participants must be adequately informed about the nature of the research, potential risks, and benefits. Additionally, the ethical treatment of participants, especially vulnerable populations, is critical to maintaining integrity in scientific research.
Future of Cord Blood Stem Cells
The future of umbilical cord blood stem cells is bright, with ongoing research and advancements in technology paving the way for innovative therapies. Here are some exciting developments and potential future applications:
Advancements in Stem Cell Technology
Recent advancements in stem cell technology have opened new avenues for the use of umbilical cord blood. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance the potency of these stem cells, making them more effective for various treatments. Techniques such as genetic modification and reprogramming are being investigated to improve the therapeutic potential of cord blood stem cells.
Expanded Treatment Options
As our understanding of umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation grows, so does the range of conditions that can be treated. Currently, these stem cells are primarily used for blood disorders, but ongoing research is exploring their potential in treating neurological conditions, autoimmune diseases, and even certain types of cancer. The future may hold groundbreaking therapies that utilize these cells in ways we have yet to imagine.
Integration into Regenerative Medicine
The integration of umbilical cord blood stem cells into regenerative medicine is another exciting prospect. As scientists continue to uncover the mechanisms behind stem cell differentiation and regeneration, we may see these cells being used to repair damaged tissues and organs. This could revolutionize treatment for conditions such as heart disease, spinal cord injuries, and degenerative diseases.
Global Collaboration and Standardization
Efforts to standardize the use of umbilical cord blood stem cells across the globe are gaining momentum. Organizations and researchers are collaborating to establish best practices for collection, storage, and application of these cells. This global approach aims to ensure that the benefits of cord blood stem cell therapy are accessible to all, regardless of geographical location.
As we look to the future, the potential of umbilical cord blood stem cells is immense. With continued research, ethical considerations, and technological advancements, we are on the brink of a new era in medicine that could change lives for generations to come. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells
What are Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are stem cells collected from the blood remaining in the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth. These cells are rich in hematopoietic stem cells, which can develop into various types of blood cells, making them valuable for medical treatments.
What are the advantages of Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
- Less Risk of Rejection: Since these cells are often used in transplants, they have a lower risk of being rejected by the recipient’s immune system.
- Rich Source of Stem Cells: Umbilical cord blood is a potent source of stem cells, which can be used in various therapies.
- Potential for Regenerative Medicine: These stem cells have the potential to treat a range of conditions, including blood disorders and certain cancers.
How is Umbilical Cord Blood Collected?
The collection of umbilical cord blood is a simple and painless procedure that occurs immediately after the baby is born. A healthcare professional will clamp the umbilical cord and use a needle to draw blood from the cord into a sterile bag.
What is Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking?
Umbilical cord blood stem cell banking involves storing the collected stem cells in a specialized facility for future use. This process ensures that the stem cells remain viable for potential medical treatments.
What conditions can be treated with Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
Umbilical cord blood stem cells can be used to treat various conditions, including:
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Sickle cell disease
- Thalassemia
- Some metabolic disorders
Are there any risks associated with Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Therapy?
While umbilical cord blood stem cell therapy is generally considered safe, there can be risks, including:
- Infection: As with any medical procedure, there is a risk of infection.
- Graft-versus-host disease: This occurs when the transplanted cells attack the recipient’s body.
How effective is Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Treatment?
The effectiveness of umbilical cord blood stem cell treatment varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient. Many patients have experienced positive outcomes, particularly in blood-related disorders.
Can Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells be used for future therapies?
Yes, ongoing research is exploring the potential of umbilical cord blood stem cells in treating a variety of conditions beyond blood disorders, including neurological diseases and regenerative medicine applications.
How can I learn more about Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
For more information, consult with a healthcare provider or a specialist in stem cell therapy. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your specific situation.