What Is Tuberous Sclerosis?
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple systems in the body. It is characterized by the growth of non-cancerous tumors, known as hamartomas, in various organs, including the brain, skin, kidneys, heart, and lungs. These tumors can lead to a variety of health issues, making early diagnosis and management crucial.
Understanding the Genetics of Tuberous Sclerosis
TSC is caused by mutations in either the TSC1 or TSC2 genes, which are responsible for regulating cell growth and division. When these genes are mutated, it can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, resulting in the formation of tumors. The condition follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene is needed for a person to be affected. However, many cases arise from new mutations, meaning they occur in families with no prior history of the disorder.
How Common Is Tuberous Sclerosis?
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex affects approximately 1 in 6,000 live births, making it a relatively rare condition. It can occur in individuals of any ethnicity or gender. Due to its varied symptoms and manifestations, TSC is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed, which can complicate treatment and management.
Tuberous Sclerosis Symptoms
The symptoms of Tuberous Sclerosis can vary widely from person to person, depending on the organs affected and the severity of the condition. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others may face significant health challenges. Here are some common symptoms associated with Tuberous Sclerosis:
Neurological Symptoms
- Seizures: One of the most common neurological symptoms, affecting about 80% of individuals with TSC. Seizures can vary in type and severity.
- Cognitive Impairment: Some individuals may experience developmental delays or intellectual disabilities.
- Behavioral Issues: Conditions such as autism spectrum disorder are more prevalent in individuals with TSC.
Skin Symptoms
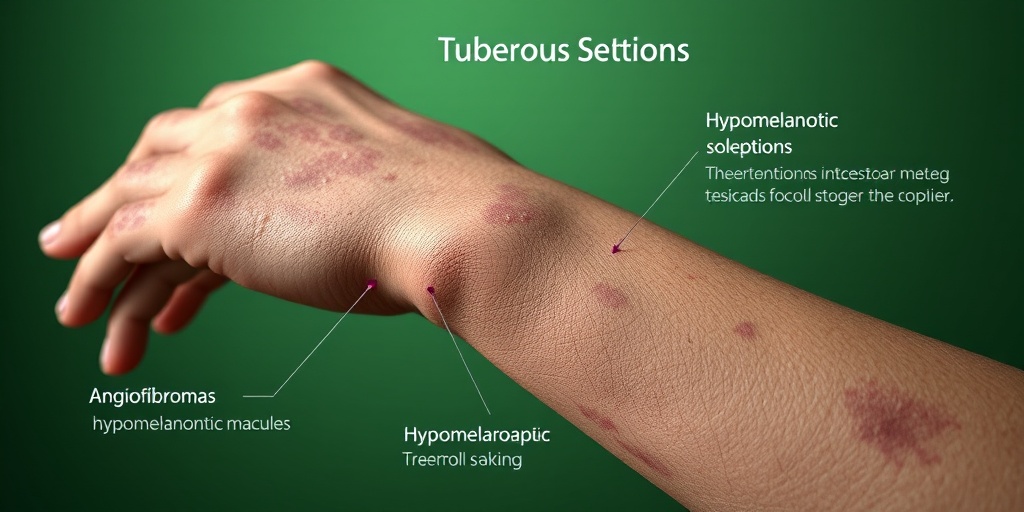
- Facial Angiofibromas: Small, reddish-brown bumps that typically appear on the face.
- Hypomelanotic Macules: Light-colored patches on the skin that may be present at birth.
- Shagreen Patches: Thickened, dimpled skin that often appears on the lower back.
Organ-Specific Symptoms
- Kidney Tumors: Renal angiomyolipomas are common in TSC and can lead to kidney dysfunction.
- Cardiac Rhabdomyomas: These benign tumors can affect heart function, particularly in infants.
- Lung Issues: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) can occur in women with TSC, leading to respiratory problems.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing. The diagnostic criteria include the presence of specific symptoms and the identification of tumors in affected organs. Radiological imaging, such as MRI or CT scans, plays a crucial role in monitoring tumor growth and assessing organ function.
Management of TSC is multidisciplinary, often involving neurologists, dermatologists, nephrologists, and other specialists. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Anti-seizure medications for seizure management and mTOR inhibitors like everolimus for tumor control.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove tumors or address complications.
- Supportive Therapies: Occupational and speech therapy can help address developmental delays and improve quality of life.
For more information on Tuberous Sclerosis Complex and its management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
Understanding Tuberous Sclerosis Complex is essential for early diagnosis and effective management. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms associated with TSC, it is crucial to seek medical advice promptly. 🌟
Tuberous Sclerosis Causes
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disorder that can affect multiple systems in the body. Understanding the causes of TSC is crucial for early diagnosis and management. The primary cause of TSC is a mutation in one of two genes: TSC1 or TSC2. These genes are responsible for producing proteins that help regulate cell growth and division. When these genes are mutated, it can lead to the formation of benign tumors in various organs, including the brain, kidneys, heart, and skin.
Genetic Factors
The majority of TSC cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in their child. However, about one-third of cases arise from new mutations, which means they occur spontaneously without a family history of the condition. This unpredictability can make it challenging for families to understand their risk of passing TSC to future generations.
Environmental Influences
While TSC is primarily a genetic disorder, some researchers are exploring potential environmental factors that may contribute to the severity of symptoms or the likelihood of developing TSC-related complications. Factors such as prenatal exposure to certain medications or toxins may play a role, although more research is needed to establish definitive links.
Understanding the Tumor Formation
The benign tumors associated with TSC, known as hamartomas, can develop in various organs. These tumors are not cancerous but can still cause significant health issues depending on their size and location. For instance:
- Brain: Tumors can lead to seizures, developmental delays, and cognitive impairments.
- Kidneys: Renal tumors can affect kidney function and may lead to hypertension.
- Heart: Cardiac rhabdomyomas can obstruct blood flow and cause heart problems.
- Skin: Skin lesions can vary in appearance and may require cosmetic treatment.
Understanding these causes is essential for managing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex effectively. Early intervention can help mitigate some of the complications associated with the disorder.
Tuberous Sclerosis Diagnosis
Diagnosing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex can be challenging due to the variability of symptoms and the fact that they can appear at different stages of life. However, early diagnosis is crucial for effective management and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Clinical Evaluation
The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough clinical evaluation. Healthcare providers will look for characteristic signs and symptoms of TSC, which may include:
- Skin lesions: These can include hypomelanotic macules, angiofibromas, and shagreen patches.
- Neurological symptoms: Seizures, developmental delays, and behavioral issues are common.
- Organ involvement: Symptoms related to kidney, heart, or lung function may also be assessed.
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex have been established by the International Tuberous Sclerosis Consortium. A diagnosis can be made if a patient meets the following:
- Presence of two major features (e.g., cardiac rhabdomyomas, facial angiofibromas) or one major feature and two minor features.
- Genetic testing confirming mutations in the TSC1 or TSC2 genes.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies play a vital role in the diagnosis of TSC. Common imaging techniques include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This is used to identify brain tumors and assess their impact on brain function.
- Ultrasound: This can help evaluate kidney tumors and other organ involvement.
- X-rays: These may be used to assess bone involvement or other complications.
In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the presence of hamartomas. However, this is less common due to the non-cancerous nature of the tumors associated with TSC.
Overall, a comprehensive approach combining clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and imaging studies is essential for accurately diagnosing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Early diagnosis can lead to timely interventions, improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by this complex disorder. 🧠💖

Tuberous Sclerosis Treatment Options
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disorder that can lead to the growth of non-cancerous tumors in various organs, including the brain, kidneys, heart, and skin. The treatment options for TSC are diverse and tailored to the individual needs of each patient. Understanding these options is crucial for effective management of the condition.
Medications
One of the primary treatment options for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex involves the use of medications. These can help manage symptoms and reduce the size of tumors. Some commonly prescribed medications include:
- Everolimus: This is an FDA-approved medication specifically for TSC. It works by inhibiting a protein that promotes tumor growth, thereby reducing the size of tumors in the brain and kidneys.
- Sirolimus: Similar to Everolimus, Sirolimus is used to manage kidney tumors and can also help with skin lesions.
- Antiepileptic drugs: Many individuals with TSC experience seizures. Medications such as lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and others are often prescribed to control seizure activity.
Interventional Procedures
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, especially if tumors are causing significant health issues. Options include:
- Laser therapy: This can be used to treat skin lesions associated with TSC.
- Resection: Surgical removal of tumors may be indicated if they are causing pain or dysfunction in organs.
- Embolization: This procedure involves blocking blood flow to a tumor, which can help shrink it.
Supportive Therapies
In addition to medications and surgical options, supportive therapies play a vital role in managing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. These may include:
- Physical therapy: Helps improve motor skills and coordination, especially in children.
- Occupational therapy: Assists individuals in developing skills for daily living and work.
- Speech therapy: Beneficial for those experiencing communication difficulties.
Tuberous Sclerosis Management
Managing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex requires a comprehensive approach that involves regular monitoring and a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers. Here are some key aspects of effective management:
Regular Monitoring
Due to the potential for tumor growth and associated complications, regular check-ups are essential. This may include:
- Imaging studies: MRI and CT scans are often used to monitor the size and number of tumors.
- Kidney function tests: Regular assessments help ensure that kidney function remains stable.
- Neurological evaluations: These are crucial for tracking seizure activity and cognitive development, especially in children.
Education and Support
Education about Tuberous Sclerosis Complex is vital for both patients and their families. Understanding the condition can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate care. Support groups and resources can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing daily challenges.
Personalized Care Plans
Each individual with TSC may experience a unique set of symptoms and challenges. Therefore, developing a personalized care plan is essential. This plan should be created in collaboration with healthcare providers and may include:
- Medication management: Tailoring medication types and dosages to the individual’s needs.
- Therapeutic interventions: Choosing the right combination of therapies based on symptoms and personal goals.
- Family involvement: Engaging family members in the care process can enhance support and understanding.
In conclusion, managing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex involves a multifaceted approach that includes medication, interventional procedures, supportive therapies, and regular monitoring. By working closely with healthcare providers and utilizing available resources, individuals with TSC can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this complex condition. 🌟

Tuberous Sclerosis and Related Conditions
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disorder that can affect multiple organ systems in the body. It is characterized by the growth of benign tumors, known as hamartomas, in various tissues, including the brain, skin, kidneys, and lungs. Understanding TSC and its related conditions is crucial for effective management and support.
Understanding Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
TSC is caused by mutations in either the TSC1 or TSC2 genes, which are responsible for regulating cell growth and division. This genetic disorder can lead to a variety of symptoms, which may vary significantly from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Skin abnormalities: These may include facial angiofibromas, hypomelanotic macules, and shagreen patches.
- Neurological issues: Seizures are a common symptom, often occurring in early childhood. Other neurological manifestations can include developmental delays and intellectual disabilities.
- Kidney problems: Renal angiomyolipomas, which are benign tumors, can develop in the kidneys, potentially leading to complications.
- Lung involvement: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) can occur, particularly in women, leading to respiratory issues.
Related Conditions Associated with Tuberous Sclerosis
Individuals with TSC may also experience a range of related conditions that can complicate their health status. Some of these include:
- Epilepsy: A significant number of individuals with TSC experience seizures, which can be challenging to manage.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): There is a higher prevalence of ASD among individuals with TSC, necessitating tailored educational and therapeutic interventions.
- Cardiac rhabdomyomas: These benign tumors can develop in the heart, often detected in infants and young children.
- Vision problems: Retinal hamartomas can lead to vision impairment, requiring regular eye examinations.
Recognizing these related conditions is essential for comprehensive care and early intervention, which can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by TSC. Regular monitoring and a multidisciplinary approach are key to managing the complexities of this disorder.
Tuberous Sclerosis Support Resources
Living with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex can be challenging, but numerous resources are available to provide support and information. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, these resources can help navigate the complexities of TSC.
National and International Organizations
Several organizations focus on TSC, offering valuable resources, support groups, and educational materials:
- Tuberous Sclerosis Alliance (TSA): This organization provides a wealth of information on TSC, including treatment options, research updates, and community support.
- Tuberous Sclerosis Complex International (TSCi): An international network that connects families and individuals affected by TSC, promoting awareness and research.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD): NORD offers resources for rare diseases, including TSC, and advocates for patients’ rights.
Online Support Groups and Forums
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of TSC can be incredibly beneficial. Online support groups and forums provide a platform for sharing experiences, advice, and emotional support:
- Facebook Groups: There are several active Facebook groups dedicated to TSC, where members share personal stories, tips, and resources.
- Reddit Communities: Subreddits related to TSC can be a source of information and community support, allowing individuals to ask questions and share experiences.
Healthcare Provider Resources
For healthcare professionals, staying informed about the latest research and treatment options for TSC is crucial. Resources include:
- Medical Journals: Journals such as Pediatrics and Neurology often publish studies related to TSC, providing insights into new treatments and management strategies.
- Continuing Medical Education (CME): Many organizations offer CME courses focused on TSC, helping healthcare providers stay current with best practices.
In conclusion, while Tuberous Sclerosis Complex presents unique challenges, a wealth of resources and support systems are available to help individuals and families navigate this condition. By leveraging these resources, patients can enhance their quality of life and access the care they need. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
What is Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of non-cancerous tumors in various organs, including the brain, skin, kidneys, and heart. These tumors can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, depending on their location and size.
What are the common symptoms of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
Symptoms of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex can vary widely among individuals but may include:
- Seizures
- Developmental delays
- Skin abnormalities, such as facial angiofibromas
- Kidney tumors
- Behavioral issues
How is Tuberous Sclerosis Complex diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex is typically based on clinical criteria, which may include:
- Presence of characteristic skin lesions
- Imaging studies showing tumors in the brain or other organs
- Family history of TSC
Genetic testing can also confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the TSC1 or TSC2 genes.
What are the treatment options for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
Treatment for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex focuses on managing symptoms and may include:
- Medications for seizures
- Regular monitoring of tumors
- Surgical interventions for significant tumors
- Supportive therapies, such as physical or occupational therapy
What is the life expectancy for individuals with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
With appropriate management and care, many individuals with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex can lead fulfilling lives. Life expectancy can vary based on the severity of symptoms and complications, but advancements in treatment have significantly improved outcomes.
What is the ICD-10 code for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
The ICD-10 code for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex is Q85.1. This code is used for billing and documentation purposes in healthcare settings.
Are there any recent advancements in the treatment of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
Yes, recent advancements include the FDA approval of medications like Everolimus, which has shown effectiveness in treating certain tumors associated with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Ongoing research continues to explore new treatment options and therapies.
Where can I find support for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex?
Support for individuals and families affected by Tuberous Sclerosis Complex can be found through various organizations and online communities. These resources provide information, advocacy, and connections to others facing similar challenges.




