What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common yet serious sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when a person’s breathing is interrupted during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and reduced oxygen levels in the body. This condition can have significant health implications if left untreated, including increased risks of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most prevalent form, caused by a blockage of the upper airway, often due to the relaxation of throat muscles and tissues during sleep.
- Central Sleep Apnea: Unlike OSA, this type occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. It is less common and often associated with underlying medical conditions.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: This is a combination of obstructive and central sleep apnea, where a person experiences both types of breathing interruptions.
What Causes Sleep Apnea?
Several factors can contribute to the development of sleep apnea, including:
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to fat deposits around the neck, which may obstruct the airway.
- Anatomical Features: Certain physical characteristics, such as a thick neck, enlarged tonsils, or a recessed chin, can increase the risk.
- Age: Sleep apnea is more common in older adults, as muscle tone decreases with age.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition can play a role in the likelihood of developing this condition.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Both can relax the throat muscles and exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms.
Understanding the underlying causes of sleep apnea is crucial for effective treatment and management. If you suspect you or a loved one may have this condition, consulting a sleep apnea doctor is essential for proper diagnosis and care.
Sleep Apnea Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea is vital for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Loud Snoring: This is often the most noticeable symptom, particularly in obstructive sleep apnea.
- Choking or Gasping During Sleep: Many individuals with sleep apnea experience episodes where they wake up gasping for air.
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Due to disrupted sleep, individuals may feel excessively tired during the day, impacting their daily activities.
- Morning Headaches: Frequent headaches upon waking can be a sign of sleep apnea, often due to low oxygen levels during the night.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Cognitive functions may be impaired due to poor sleep quality, leading to issues with focus and memory.
When to Seek Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. A sleep apnea test can help determine the severity of the condition and guide appropriate treatment options. This may include lifestyle changes, the use of a CPAP machine, or even surgical interventions in severe cases.
Innovative Treatments for Sleep Apnea
Recent advancements in sleep apnea treatment include options like Zepbound, a new device designed to help manage symptoms effectively. Additionally, specialized sleep apnea pillows and masks can enhance comfort and improve the effectiveness of treatment.
For more information on sleep apnea and its management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. Remember, addressing sleep apnea not only improves sleep quality but also enhances overall health and well-being. 🌙💤

Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when a person’s breathing is interrupted during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and reduced oxygen levels in the body. Understanding the different types of sleep apnea is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Here, we will explore the three main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, and complex sleep apnea syndrome.
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common form of sleep apnea, accounting for about 84% of cases. It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, causing a blockage in the airway. This blockage can lead to loud snoring and gasping for air, often waking the person up multiple times throughout the night.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include loud snoring, daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability.
- Risk Factors: Factors such as obesity, age, and a family history of sleep apnea can increase the risk of developing OSA.
2. Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Central sleep apnea is less common than OSA and occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Unlike OSA, there is no physical blockage of the airway. CSA is often associated with underlying medical conditions, such as heart failure or stroke.
- Symptoms: Symptoms may include sudden awakenings with shortness of breath, difficulty staying asleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Risk Factors: Conditions affecting the brainstem, such as stroke or certain neurological disorders, can increase the risk of CSA.
3. Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome
Complex sleep apnea syndrome, also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, is a combination of obstructive and central sleep apnea. It is characterized by the presence of both types of apnea, often identified during a sleep study. Patients may initially present with OSA, but upon treatment with a CPAP machine, central apnea episodes may emerge.
- Symptoms: Symptoms can include those of both OSA and CSA, leading to confusion in diagnosis.
- Management: Treatment may involve a combination of therapies tailored to address both obstructive and central components.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
Understanding the causes of sleep apnea is essential for effective treatment and management. The causes can vary depending on the type of sleep apnea, but several common factors contribute to the development of this disorder.
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Causes
The primary cause of obstructive sleep apnea is the relaxation of throat muscles during sleep. However, several factors can exacerbate this condition:
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can put pressure on the airway, leading to blockages.
- Anatomical Features: Structural abnormalities, such as a thick neck, enlarged tonsils, or a deviated septum, can increase the likelihood of airway obstruction.
- Age: As people age, muscle tone decreases, making it more likely for the airway to collapse during sleep.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition can play a role, as sleep apnea often runs in families.
2. Central Sleep Apnea Causes
Central sleep apnea is often linked to underlying medical conditions that affect the brain’s ability to regulate breathing:
- Heart Conditions: Congestive heart failure and other heart-related issues can lead to CSA.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions such as stroke, brain tumors, or degenerative diseases can disrupt the brain’s signaling for breathing.
- High Altitude: Sleeping at high altitudes can sometimes trigger CSA due to lower oxygen levels.
3. Other Contributing Factors
In addition to the specific causes mentioned above, several lifestyle and environmental factors can contribute to sleep apnea:
- Smoking: Tobacco use can increase inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol relaxes the throat muscles, increasing the risk of airway obstruction.
- Medications: Certain medications, particularly sedatives, can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms.
Identifying the causes of sleep apnea is crucial for effective treatment. If you suspect you or a loved one may have sleep apnea, consult a sleep apnea doctor for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate testing, such as a sleep apnea test or a sleep apnea home test. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve quality of life and overall health. 🌙
Risk Factors for Sleep Apnea
Understanding the risk factors for sleep apnea is crucial for early detection and effective management of this common sleep disorder. Sleep apnea can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Here are some of the most significant risk factors:
1. Obesity
One of the most significant risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea is obesity. Excess body weight can lead to fatty deposits around the neck and throat, which can obstruct the airway during sleep. Studies show that even a modest weight gain can increase the risk of sleep apnea.
2. Age
As we age, the risk of developing sleep apnea increases. This is particularly true for individuals over the age of 40. The muscles in the throat can become weaker with age, making it easier for the airway to collapse during sleep.
3. Gender
Men are more likely to develop sleep apnea than women, with the ratio being approximately 2:1. However, the risk for women increases after menopause, suggesting hormonal changes may play a role in the development of this condition.
4. Family History
A family history of sleep apnea can increase your risk. Genetic factors may contribute to the structure of the airway and the likelihood of developing this disorder. If you have relatives with sleep apnea, it’s essential to be aware of the symptoms and seek evaluation if necessary.
5. Smoking and Alcohol Use
Both smoking and alcohol consumption can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. Smoking can increase inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway, while alcohol relaxes the throat muscles, increasing the likelihood of airway obstruction during sleep.
6. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also increase the risk of sleep apnea, including:
- Hypertension: High blood pressure is often associated with sleep apnea.
- Diabetes: There is a strong link between sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Disease: Individuals with heart conditions are at a higher risk for sleep apnea.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism can contribute to the development of sleep apnea.
7. Anatomical Features
Some individuals may have anatomical features that predispose them to sleep apnea, such as:
- Large Neck Circumference: A thicker neck can indicate excess fat around the throat.
- Enlarged Tonsils or Adenoids: These can block the airway, especially in children.
- Jaw Structure: A recessed jaw or a narrow airway can increase the risk.
Recognizing these risk factors can help in identifying individuals who may be at risk for sleep apnea. If you or someone you know exhibits these characteristics, it may be time to consult a sleep apnea doctor for further evaluation.
Sleep Apnea Diagnosis
Diagnosing sleep apnea is a multi-step process that typically begins with a thorough evaluation of symptoms and medical history. Here’s how the diagnosis usually unfolds:
1. Initial Consultation
The first step in diagnosing sleep apnea is a consultation with a healthcare provider. During this visit, you will discuss your symptoms, which may include:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Loud snoring
- Choking or gasping during sleep
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
2. Sleep Apnea Test
To confirm a diagnosis, a sleep apnea test is often required. There are two main types of tests:
- Polysomnography: This is an overnight sleep study conducted in a sleep clinic. It monitors various body functions, including brain activity, eye movement, heart rate, and oxygen levels.
- Home Sleep Apnea Test: This is a simplified version that can be done at home. It typically measures airflow, breathing patterns, and oxygen levels.
3. Interpretation of Results
Once the test is completed, the results will be analyzed by a sleep specialist. They will look for patterns that indicate the presence of sleep apnea, such as:
- Apneas (pauses in breathing)
- Hypopneas (shallow breathing)
- Oxygen desaturation levels
4. Treatment Options
If diagnosed with sleep apnea, various treatment options are available, including:
- CPAP Machine: The most common treatment, a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine keeps the airway open during sleep.
- Oral Appliances: These devices reposition the jaw to keep the airway open.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options may be considered to remove excess tissue or correct anatomical issues.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, quitting smoking, and avoiding alcohol can significantly improve symptoms.
Early diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea are essential for preventing complications such as cardiovascular issues, diabetes, and impaired cognitive function. If you suspect you have sleep apnea, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance. 💤

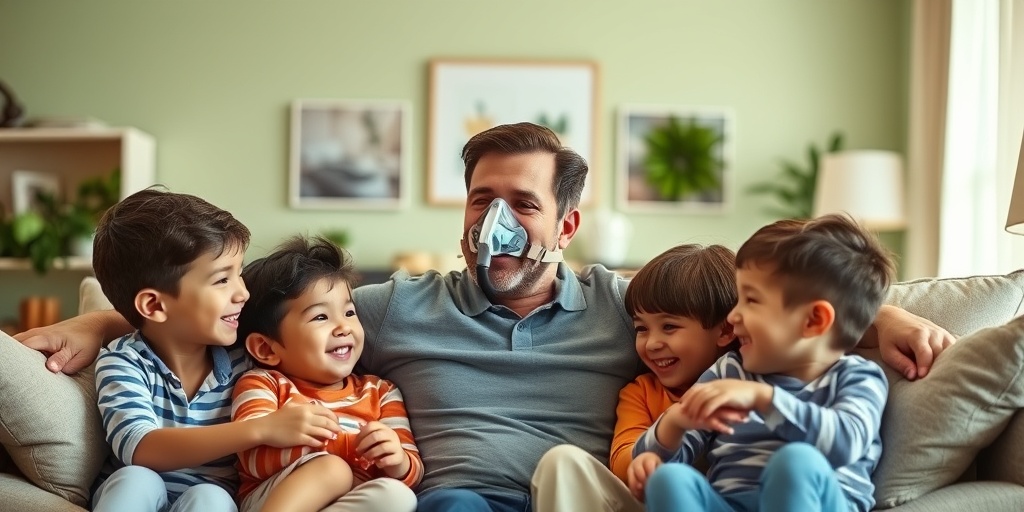
Sleep Apnea Treatment Options
Sleep apnea is a common yet serious sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with this condition, understanding the various sleep apnea treatment options available can be crucial for improving your quality of life. Let’s explore some of the most effective treatments for sleep apnea.
1. Lifestyle Changes
For many individuals, making simple lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms. Here are some effective changes to consider:
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can alleviate pressure on the airway, reducing the frequency of apnea episodes.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your side instead of your back can help keep the airway open.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax the throat muscles, which can worsen sleep apnea.
2. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy
One of the most common treatments for obstructive sleep apnea is the CPAP machine. This device delivers a steady stream of air through a mask that keeps the airway open during sleep. Here’s what you need to know:
- How It Works: The CPAP machine prevents airway collapse by providing continuous airflow.
- Benefits: Many users report improved sleep quality and reduced daytime fatigue.
- Considerations: Some may find it uncomfortable initially, but adjustments can be made for a better fit.
3. Oral Appliances
For those who cannot tolerate CPAP, sleep apnea devices such as oral appliances may be a viable alternative. These custom-made devices reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open. They are particularly effective for mild to moderate cases of sleep apnea.
4. Surgery
In severe cases of sleep apnea, surgical options may be considered. Sleep apnea surgery can involve removing excess tissue from the throat or repositioning anatomical structures. Here are some common surgical procedures:
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Removes excess tissue from the throat.
- Genioglossus Advancement: Repositions the tongue muscle attachment to prevent airway blockage.
- Maxillomandibular Advancement: Repositions the upper and lower jaw to enlarge the airway.
5. New Treatments: Zepbound
Recently, innovative treatments like zepbound for sleep apnea have emerged. This medication aims to reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms by targeting specific pathways in the brain. While still under research, it shows promise as a potential alternative for those who struggle with traditional treatments.
Living with Sleep Apnea
Living with sleep apnea can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can manage their condition effectively. Here are some tips for navigating daily life with sleep apnea:
1. Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
It’s essential to maintain regular check-ups with a sleep apnea doctor to monitor your condition and adjust treatments as necessary. This can help ensure that your treatment plan remains effective over time.
2. Support Groups and Resources
Connecting with others who have sleep apnea can provide emotional support and practical advice. Consider joining local or online support groups where you can share experiences and learn from others.
3. Education and Awareness
Understanding what causes sleep apnea and its symptoms can empower you to take control of your health. Educate yourself about the condition, treatment options, and lifestyle changes that can help.
4. Sleep Hygiene Practices
Implementing good sleep hygiene can improve your overall sleep quality. Here are some practices to consider:
- Establish a Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading or meditating.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
By understanding the treatment options available and adopting effective strategies for living with sleep apnea, you can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available! 🌙💤

Frequently Asked Questions about Sleep Apnea
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These pauses can last for a few seconds to minutes and may occur many times throughout the night, leading to disrupted sleep and reduced oxygen levels in the body.
What are the Symptoms of Sleep Apnea?
Common sleep apnea symptoms include:
- Loud snoring
- Choking or gasping during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
What Causes Sleep Apnea?
Several factors can contribute to sleep apnea, including:
- Obesity
- Age
- Family history
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Structural abnormalities in the airway
How is Sleep Apnea Diagnosed?
A sleep apnea test is typically conducted to diagnose the condition. This may involve an overnight sleep study in a sleep clinic or a sleep apnea home test that monitors your breathing patterns, heart rate, and oxygen levels while you sleep.
What are the Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea?
Treatment for sleep apnea varies based on severity and may include:
- CPAP machine: A device that delivers continuous air pressure to keep the airways open.
- Oral appliances: Devices that reposition the jaw to keep the airway open.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical options may be considered to remove excess tissue or correct structural issues.
- Lifestyle changes: Weight loss, quitting smoking, and avoiding alcohol can significantly improve symptoms.
What is Zepbound for Sleep Apnea?
Zepbound is a newer treatment option for sleep apnea that may help patients who do not respond well to traditional therapies. It is important to consult with a sleep apnea doctor to determine if this treatment is suitable for you.
How Does a CPAP Machine Work?
A CPAP machine works by providing a steady stream of air through a mask that you wear while sleeping. This air pressure keeps your airway open, preventing the pauses in breathing that characterize sleep apnea.
Can Sleep Apnea Affect Children?
Yes, sleep apnea in children can occur and may lead to behavioral issues, learning difficulties, and growth problems. If you suspect your child has sleep apnea, it is essential to seek evaluation and treatment from a qualified healthcare provider.
What is a Sleep Apnea Pillow?
A sleep apnea pillow is designed to support proper head and neck alignment, which can help keep the airways open during sleep. These pillows can be beneficial for individuals with mild to moderate sleep apnea.
Where Can I Find More Information?
If you have more questions about sleep apnea, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional or a sleep specialist for personalized advice and treatment options. 💤




