What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the skin cells, primarily due to excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. It is one of the most common forms of cancer, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding skin cancer is crucial for early detection and effective skin cancer treatment.
Skin cancer typically manifests as changes in the skin, such as new growths or sores that do not heal. While it can occur anywhere on the body, it is most commonly found in areas that are frequently exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and arms. Early diagnosis is vital, as skin cancer can be highly treatable when caught in its initial stages.
Types of Skin Cancer
There are three primary types of skin cancer, each with distinct characteristics and treatment options. Understanding these types can help you recognize symptoms and seek appropriate skin cancer treatment when necessary.
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, accounting for about 80% of all cases. It originates in the basal cells, which are located in the lower part of the epidermis. BCC typically appears as a small, shiny bump or a pinkish patch on the skin. It grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, making it highly treatable.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. It arises from squamous cells, which are flat cells found in the outer layer of the skin. SCC may present as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore that crusts or bleeds. While it is more aggressive than BCC, it is still highly treatable, especially when detected early.
3. Melanoma
Melanoma is the least common but most dangerous type of skin cancer. It develops in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Melanoma can appear as a new mole or a change in an existing mole, often characterized by irregular borders, multiple colors, and a larger diameter. Early detection is crucial, as melanoma can spread rapidly to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
Recognizing Symptoms
Being aware of the symptoms of skin cancer is essential for early detection. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- New growths: Any new mole or growth on the skin should be examined.
- Changes in existing moles: Look for changes in size, shape, or color.
- Non-healing sores: Sores that do not heal within a few weeks may be a sign of skin cancer.
- Itching or tenderness: Persistent itching or tenderness in a specific area can also indicate a problem.
Seeking Treatment
If you suspect you have skin cancer, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Treatment options vary depending on the type and stage of skin cancer and may include:
- Surgery: The most common treatment for skin cancer, where the cancerous tissue is removed.
- Radiation therapy: Often used for cancers that are difficult to remove surgically.
- Chemotherapy: May be used for advanced cases, particularly melanoma.
- Topical treatments: Creams and ointments can be effective for superficial skin cancers.
For those seeking information on skin cancer treatment options, resources like Yesil Health AI can provide evidence-based answers tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Understanding skin cancer and its types is the first step toward prevention and early detection. Regular skin checks and awareness of changes in your skin can significantly impact your health. If you notice any concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Remember, early intervention is key to successful skin cancer treatment! 🌞
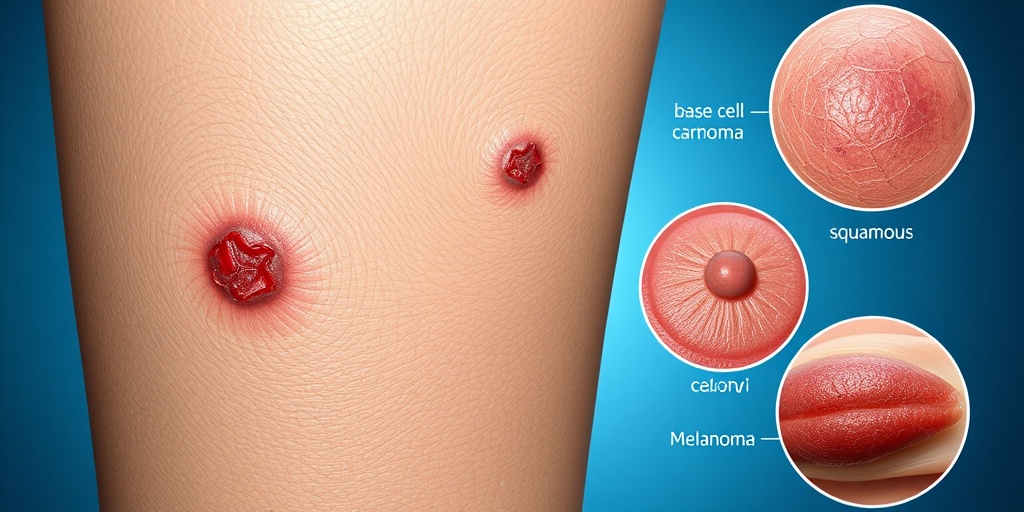
Skin Cancer Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of skin cancer early can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Skin cancer can manifest in various forms, and being aware of the signs is crucial for timely intervention. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
Changes in Moles
One of the most common indicators of skin cancer is changes in existing moles or the appearance of new ones. Look for the following characteristics, often summarized by the ABCDE rule:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other.
- Border: The edges are irregular, ragged, or blurred.
- Color: The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown, black, or even red, white, or blue.
- Diameter: The mole is larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
New Growths or Sores
New growths on the skin or sores that do not heal can also be signs of skin cancer. These may appear as:
- Red patches that may be itchy or painful.
- Open sores that bleed or crust over and do not heal.
- Shiny, pearly bumps that may be skin-colored, pink, or white.
Itching or Tenderness
While not all skin cancers cause discomfort, some may lead to itching or tenderness in the affected area. If you notice persistent itching or tenderness in a specific spot, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Changes in Skin Texture
Skin cancer can also cause changes in the texture of the skin. You may notice:
- Rough, scaly patches that may be red or brown.
- Thickened areas of skin that feel different from the surrounding skin.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Understanding the risk factors associated with skin cancer can help you take preventive measures. While anyone can develop skin cancer, certain factors can increase your likelihood:
Sun Exposure
One of the most significant risk factors for skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours, can damage the skin and increase the risk of developing skin cancer. It’s essential to use sunscreen with a high SPF and wear protective clothing when outdoors.
Skin Type
Your natural skin type plays a crucial role in your risk level. Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are at a higher risk for skin cancer. Those who sunburn easily or have a history of severe sunburns should be particularly vigilant.
Family History
A family history of skin cancer can increase your risk. If your parents or siblings have had skin cancer, it’s essential to discuss this with your healthcare provider and consider regular skin checks.
Age
As we age, our skin becomes more susceptible to damage. Most skin cancer cases are diagnosed in individuals over the age of 50, but younger people can also be affected, especially if they have other risk factors.
Immune System Suppression
Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or medications, are at a higher risk for skin cancer. This includes people undergoing treatments for autoimmune diseases or organ transplant recipients.
Exposure to Tanning Beds
Using tanning beds can significantly increase your risk of developing skin cancer. The UV radiation emitted by these devices can be more intense than natural sunlight, leading to skin damage and an increased likelihood of cancer.
By being aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with skin cancer, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin and seek medical advice when necessary. Regular skin checks and consultations with a dermatologist can help ensure early detection and effective skin cancer treatment. 🌞

Skin Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosing skin cancer is a crucial step in ensuring effective treatment and recovery. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes, making it essential to recognize the signs and seek medical advice promptly. Here’s what you need to know about the diagnosis process.
Understanding the Signs and Symptoms
Skin cancer can manifest in various forms, and being aware of the symptoms is vital. Common signs include:
- New Growths: Any new mole or growth on the skin that appears suddenly.
- Changes in Existing Moles: Moles that change in size, shape, or color.
- Itching or Bleeding: Moles that itch, bleed, or become crusty.
- Unusual Coloration: Moles that have multiple colors or an irregular border.
Consulting a Dermatologist
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. They will perform a thorough examination of your skin and may use a dermatoscope, a special tool that allows them to see the skin in greater detail.
Biopsy: The Definitive Test
To confirm a diagnosis of skin cancer, a biopsy is often necessary. This involves removing a small sample of skin tissue for laboratory analysis. There are several types of biopsies:
- Shave Biopsy: A small section of the skin is shaved off.
- Excisional Biopsy: The entire mole or growth is removed.
- Punch Biopsy: A circular tool is used to remove a deeper layer of skin.
The results will help determine whether cancer is present and, if so, what type it is. This information is crucial for deciding on the best skin cancer treatment options.
Skin Cancer Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, understanding the various skin cancer treatment options available is essential for effective management of the disease. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual, depending on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Topical Treatments
For some early-stage skin cancers, topical treatments may be effective. These include:
- Topical Chemotherapy: Creams containing chemotherapy agents can be applied directly to the skin.
- Immunotherapy Creams: These help stimulate the immune system to fight cancer cells.
Topical treatments are often preferred for superficial cancers and can be less invasive than other methods. 🧴
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For more advanced cases, minimally invasive procedures may be recommended:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the cancer cells with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrosurgery: Using electrical currents to destroy cancerous tissue.
These methods can be effective for certain types of skin cancer and often result in less scarring compared to traditional surgery.
Surgical Options
In cases where skin cancer is more aggressive or has spread, surgical options may be necessary:
- Excisional Surgery: Removing the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy skin.
- Mohs Surgery: A precise surgical technique that removes cancerous skin layer by layer.
Surgery is often the most effective way to ensure complete removal of cancerous cells, especially for melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer.
Radiation and Chemotherapy
For advanced skin cancers, especially those that have spread beyond the skin, radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be recommended. These treatments can help shrink tumors and manage symptoms.
Emerging Treatments
Research is ongoing, and new treatments are continually being developed. Options like targeted therapy and immunotherapy are showing promise in treating skin cancer, particularly melanoma. These therapies work by targeting specific pathways involved in cancer growth and can be less harmful to healthy cells.
In conclusion, understanding the skin cancer treatment options available is crucial for anyone diagnosed with this condition. Early detection and a tailored treatment plan can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. If you suspect you may have skin cancer, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance. 🌟
Skin Cancer Surgery
When it comes to skin cancer treatment, surgery is often one of the most effective options available. This procedure involves the removal of cancerous cells from the skin, and it can vary in complexity depending on the type and stage of the cancer. Understanding the different surgical options can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
Types of Skin Cancer Surgery
There are several types of surgical procedures used to treat skin cancer, including:
- Excisional Surgery: This is the most common type of surgery for skin cancer. The surgeon removes the tumor along with a margin of healthy skin to ensure all cancerous cells are eliminated.
- Mohs Surgery: This technique is particularly effective for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It involves removing the cancerous skin layer by layer, checking each layer for cancer cells until no further cancerous cells are detected.
- Curettage and Electrodessication: This method involves scraping away the cancerous tissue and using electrical currents to destroy any remaining cancer cells. It is often used for superficial skin cancers.
- Laser Surgery: This technique uses focused light to remove cancerous cells. It is less invasive and can be used for certain types of skin cancers.
Preparing for Skin Cancer Surgery
Preparation for surgery is crucial for a successful outcome. Here are some steps to consider:
- Consultation: Meet with your dermatologist or oncologist to discuss the best surgical option for your specific type of skin cancer.
- Medical History: Provide a complete medical history, including any medications you are taking, to ensure the surgical team is fully informed.
- Preoperative Instructions: Follow any preoperative instructions given by your healthcare provider, such as avoiding certain medications or fasting before the procedure.
What to Expect During and After Surgery
During the surgery, you will receive local anesthesia to numb the area, ensuring you remain comfortable throughout the procedure. The duration of the surgery can vary based on the complexity of the case.
After the surgery, you may experience some swelling, redness, or discomfort in the treated area. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s aftercare instructions to promote healing and minimize the risk of infection.
Skin Cancer Aftercare
Proper aftercare following skin cancer surgery is vital for recovery and reducing the risk of recurrence. Here are some essential aftercare tips to keep in mind:
Wound Care
Taking care of the surgical site is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently clean the area with mild soap and water as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Apply Dressings: If instructed, apply any prescribed dressings to protect the wound.
- Avoid Scratching: It’s important to avoid scratching or picking at the surgical site to prevent infection.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
It’s normal to experience some pain or discomfort after surgery. Here are some ways to manage it:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress can reduce swelling and provide relief.
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your recovery and checking for any signs of recurrence. During these visits, your doctor may:
- Examine the surgical site for proper healing.
- Discuss any concerns or symptoms you may have.
- Schedule additional treatments if necessary.
Sun Protection
After skin cancer surgery, protecting your skin from the sun is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Long sleeves, hats, and sunglasses can help shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Stay away from tanning beds, as they can increase the risk of skin cancer.
By following these aftercare guidelines and maintaining regular check-ups, you can support your healing process and reduce the risk of future skin cancer issues. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to successful outcomes in skin cancer management! 🌞

Frequently Asked Questions about Skin Cancer Treatment
What are the common options for skin cancer treatment?
Skin cancer treatment options vary based on the type and stage of cancer. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: Removal of cancerous tissue.
- Radiation therapy: Using high-energy rays to target cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Medications that kill cancer cells.
- Topical treatments: Creams or ointments applied directly to the skin.
What is the cost of skin cancer treatment?
The cost of skin cancer treatment can vary widely depending on the type of treatment, location, and healthcare provider. In general, treatments can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. It’s advisable to consult with your healthcare provider and insurance company for specific estimates.
Are there skin cancer treatment creams available?
Yes, there are various skin cancer treatment creams that are used for superficial skin cancers. These topical treatments can be effective for certain types of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Always consult a dermatologist to determine the best option for your condition.
Can skin cancer be treated without surgery?
Yes, there are skin cancer treatment options that do not involve surgery. These may include:
- Topical chemotherapy: Creams that treat cancerous cells.
- Photodynamic therapy: A treatment that uses light to activate a drug that kills cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: Effective for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
What are the treatment options for skin cancer on the face?
Treating skin cancer on the face requires careful consideration to minimize scarring. Options include:
- Mohs surgery: A precise surgical technique that removes cancerous skin layer by layer.
- Topical treatments: Creams specifically designed for facial skin.
- Radiation therapy: Often used for non-surgical candidates.
Where can I find skin cancer treatment near me?
To find skin cancer treatment near you, consider the following steps:
- Consult your primary care physician for referrals.
- Search online for local dermatology clinics or cancer treatment centers.
- Check with your health insurance provider for in-network specialists.
What is the NHS approach to skin cancer treatment?
The NHS provides comprehensive care for skin cancer, including diagnosis, treatment options, and follow-up care. Patients can expect a multidisciplinary approach, involving dermatologists, oncologists, and other specialists to ensure the best outcomes.
What is the skin cancer treatment cost in India?
The skin cancer treatment cost in India is generally lower compared to many Western countries. Costs can vary based on the type of treatment and the facility, but many patients find affordable options available. It’s best to consult local healthcare providers for specific pricing.