What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the skin cells, primarily due to the skin’s exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. It is one of the most common forms of cancer, affecting millions of people worldwide each year. Understanding skin cancer is crucial for early detection and effective skin cancer treatment.
Skin cancer occurs when the DNA in skin cells becomes damaged, leading to uncontrolled growth. This can result in the formation of tumors, which can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The earlier skin cancer is detected, the higher the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Types of Skin Cancer
There are three primary types of skin cancer, each with distinct characteristics and treatment options. Understanding these types can help you recognize symptoms and seek appropriate skin cancer treatment when necessary.
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, accounting for about 80% of all cases. It typically appears as a small, shiny bump or a pinkish patch on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, neck, and ears. BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, making it highly treatable.
Skin cancer treatment for BCC often involves surgical removal of the tumor, but other options like topical creams and photodynamic therapy may also be effective.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore that crusts or bleeds. SCC can develop on sun-exposed areas but can also occur in other parts of the body. While it is more aggressive than BCC, it is still highly treatable when detected early.
Common skin cancer treatment options for SCC include surgical excision, cryotherapy, and radiation therapy. In some cases, topical chemotherapy may be recommended.
3. Melanoma
Melanoma is the least common but most dangerous type of skin cancer. It develops in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. Melanoma can appear as a new mole or a change in an existing mole, often characterized by asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, and a diameter larger than a pencil eraser.
Early detection is critical for successful skin cancer treatment. Treatment options for melanoma may include surgical removal, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the stage of the cancer.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of skin cancer is essential for early detection and effective treatment. If you notice any unusual changes in your skin, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and potential skin cancer treatment. Resources like Yesil Health AI can provide valuable information and guidance on skin cancer and its treatment options.
Remember, protecting your skin from UV exposure and performing regular skin checks can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer. Stay informed, stay safe, and prioritize your skin health! 🌞
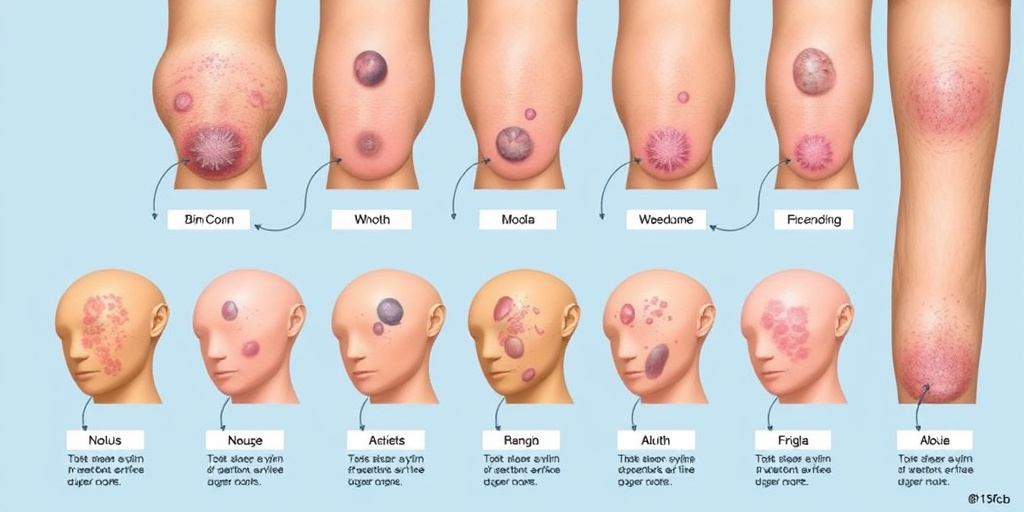
Skin Cancer Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of skin cancer early can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Skin cancer can manifest in various forms, and being aware of the signs is crucial for timely intervention. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
Changes in Moles
One of the most common indicators of skin cancer is a change in existing moles or the appearance of new ones. Look for the following characteristics:
- Asymmetry: If one half of a mole doesn’t match the other, it could be a warning sign.
- Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges may indicate a problem.
- Color: Moles that have multiple colors or an uneven distribution of color should be examined.
- Diameter: Moles larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser) warrant attention.
- Evolving: Any change in size, shape, or color over time is a cause for concern.
New Growths or Sores
New growths on the skin or sores that do not heal can also be symptoms of skin cancer. These may appear as:
- Red patches: Often itchy or painful, these can be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Open sores: Sores that bleed or crust over and do not heal may indicate basal cell carcinoma.
- Shiny bumps: A pearly or waxy bump on the skin can be a sign of basal cell carcinoma.
Itching or Tenderness
Persistent itching or tenderness in a specific area of the skin can also be a symptom of skin cancer. If you notice these sensations accompanying any of the changes mentioned above, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Skin Color Changes
Changes in skin color, such as darkening or lightening of certain areas, can also be indicative of skin cancer. Pay attention to any unusual pigmentation or discoloration that appears suddenly.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Understanding the risk factors associated with skin cancer can help you take proactive measures to protect your skin. Here are some of the most significant risk factors:
Sun Exposure
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the leading cause of skin cancer. Individuals who spend a lot of time outdoors without proper sun protection are at a higher risk. Remember to:
- Use sunscreen with a high SPF.
- Wear protective clothing.
- Avoid tanning beds.
Skin Type
People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are more susceptible to skin cancer. This is because they have less melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation. If you have these characteristics, it’s crucial to be vigilant about skin checks and sun protection.
Family History
A family history of skin cancer can increase your risk. If your parents or siblings have had skin cancer, you should be more proactive in monitoring your skin and consulting with a dermatologist regularly.
Age
As we age, our skin becomes thinner and less resilient, making older adults more vulnerable to skin cancer. Regular skin examinations become increasingly important as you age.
Immune System Suppression
Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or medications, are at a higher risk for skin cancer. If you are immunocompromised, it’s essential to have regular skin checks and to be vigilant about any changes in your skin.
Previous Skin Cancer
If you have had skin cancer in the past, your risk of developing it again increases. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring your skin health.
By being aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with skin cancer, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin and seek treatment early if necessary. Remember, early detection is key! 🩺✨

Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
Diagnosing skin cancer is a crucial first step in ensuring effective treatment and recovery. Early detection can significantly improve the success rate of skin cancer treatments. Here’s what you need to know about the diagnosis process.
Understanding the Signs and Symptoms
Skin cancer can manifest in various forms, and recognizing the signs is essential. Common symptoms include:
- New growths or sores: Any new or changing growth on the skin should be examined.
- Changes in existing moles: Look for asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, or a diameter larger than a pencil eraser.
- Itching or bleeding: Persistent itching or bleeding from a mole or spot can be a warning sign.
Consultation with a Dermatologist
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. During your appointment, the doctor will:
- Conduct a thorough skin examination.
- Ask about your medical history and any risk factors, such as family history or excessive sun exposure.
- Perform a biopsy if necessary, where a small sample of skin is removed for laboratory analysis.
Biopsy and Laboratory Analysis
A biopsy is the definitive way to diagnose skin cancer. There are several types of biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A small section of skin is shaved off for testing.
- Excisional biopsy: The entire growth is removed for examination.
- Punch biopsy: A circular tool removes a deeper section of skin.
Once the biopsy is performed, the sample is sent to a laboratory where pathologists will analyze it for cancerous cells. The results will determine the type of skin cancer and the best course of action for skin cancer treatment.
Skin Cancer Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, understanding the various skin cancer treatment options available is vital for patients. Treatment plans can vary based on the type and stage of cancer, as well as individual patient factors.
Topical Treatments
For early-stage skin cancers, especially non-melanoma types, topical treatments can be effective. These include:
- Skin cancer treatment creams: Medications like imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil are applied directly to the skin to destroy cancer cells.
- Photodynamic therapy: This involves applying a photosensitizing agent to the skin, followed by exposure to a specific light to kill cancer cells.
Surgical Options
For more advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgical options include:
- Excisional surgery: The tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue are removed.
- Mohs surgery: A precise technique where cancerous skin is removed layer by layer, ensuring complete removal while preserving healthy tissue.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For patients who prefer to avoid surgery or for those with specific conditions, non-surgical treatments are available:
- Radiation therapy: High-energy rays are used to target and kill cancer cells, often used for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Systemic treatments that can be used for advanced skin cancers, often in combination with other therapies.
Cost and Accessibility of Treatments
The cost of skin cancer treatment can vary widely based on the type of treatment, location, and healthcare provider. Many insurance plans cover skin cancer treatments, but it’s essential to check with your provider. Additionally, seeking treatment at a specialized skin cancer treatment center can provide access to the latest therapies and clinical trials.
In conclusion, early diagnosis and understanding the available treatment options are key to effectively managing skin cancer. If you suspect you have skin cancer, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support. 🌞

Skin Cancer Surgery
When it comes to skin cancer treatment, surgery is often one of the most effective options available. It involves the removal of cancerous cells from the skin, and the type of surgery performed can vary based on the type and stage of skin cancer. Let’s explore the different surgical options and what you can expect during the process.
Types of Skin Cancer Surgery
- Excisional Surgery: This is the most common type of surgery for skin cancer. The surgeon removes the tumor along with a margin of healthy skin to ensure that all cancerous cells are eliminated.
- Mohs Surgery: This specialized technique is often used for non-melanoma skin cancers. It involves removing the cancerous skin layer by layer, examining each layer for cancer cells until no further cancerous cells are detected. This method is particularly effective for cancers located on the face, ears, and other sensitive areas.
- Curettage and Electrodessication: This method involves scraping away the cancerous tissue with a curette (a sharp instrument) and then using an electric current to destroy any remaining cancer cells. It’s often used for superficial skin cancers.
- Cryotherapy: In this procedure, liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and destroy abnormal skin cells. It’s typically used for precancerous lesions and some early-stage skin cancers.
What to Expect During Skin Cancer Surgery
Before the surgery, your doctor will discuss the procedure with you, including the type of anesthesia that will be used. Most skin cancer surgeries are performed on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day. Here’s a brief overview of what you can expect:
- Preparation: You may be asked to avoid certain medications or supplements before the surgery. Make sure to follow your doctor’s instructions closely.
- During the Procedure: The area around the tumor will be numbed, and the surgeon will remove the cancerous tissue. Depending on the type of surgery, this may take anywhere from a few minutes to a couple of hours.
- Recovery: After the surgery, you may experience some swelling, redness, or discomfort in the area. Your doctor will provide you with aftercare instructions, including how to care for the surgical site and when to return for follow-up visits.
Skin Cancer Surgery Success Rates
The success rate of skin cancer surgery is generally high, especially when the cancer is detected early. Factors that can influence the success rate include:
- The type of skin cancer
- The stage at which it was diagnosed
- The patient’s overall health
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence. 🩺
Skin Cancer Prevention Tips
Preventing skin cancer is crucial, especially for those at higher risk. Here are some effective skin cancer prevention tips to help you protect your skin:
1. Use Sunscreen Daily
Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 is one of the most effective ways to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. Make sure to apply it generously and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating. ☀️
2. Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing can be your first line of defense against UV rays. Consider wearing:
- Long-sleeved shirts
- Wide-brimmed hats
- Sunglasses with UV protection
3. Seek Shade
Whenever possible, seek shade, especially during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). This simple step can significantly reduce your exposure to harmful UV radiation.
4. Avoid Tanning Beds
Tanning beds can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. Opt for safer alternatives like self-tanning lotions or sprays if you desire a bronzed look.
5. Regular Skin Checks
Performing regular self-examinations of your skin can help you detect any unusual changes early. Look for new moles or changes in existing moles, and consult a dermatologist if you notice anything suspicious. 🕵️♀️
6. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking can also contribute to better skin health and lower your risk of skin cancer.
By following these prevention tips and staying vigilant about your skin health, you can significantly reduce your risk of skin cancer and promote overall well-being. Remember, early detection and prevention are key! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Skin Cancer Treatment
What are the common options for skin cancer treatment?
There are several skin cancer treatment options available, including:
- Topical treatments, such as creams and ointments
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery to remove cancerous cells
- Cryotherapy, which involves freezing the cancer cells
- Photodynamic therapy, using light to destroy cancer cells
Are there non-surgical treatments for skin cancer?
Yes, many patients seek skin cancer treatment without surgery. Options include:
- Topical chemotherapy creams
- Radiation therapy
- Cryotherapy
Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the best approach for your specific case. 🌟
What is the average cost of skin cancer treatment?
The skin cancer treatment cost can vary widely based on factors such as:
- Type of treatment
- Location of the treatment center
- Insurance coverage
It’s advisable to check with your insurance provider and treatment center for a detailed estimate. 💰
What is the success rate of skin cancer treatments?
The skin cancer treatment success rate largely depends on:
- The type and stage of cancer
- The treatment method used
- Overall health of the patient
Early detection typically leads to higher success rates. Always discuss your prognosis with your healthcare provider. 📈
How can I find a skin cancer treatment center near me?
To locate a skin cancer treatment center near you, consider:
- Asking your primary care physician for recommendations
- Searching online for local dermatology clinics
- Checking with local hospitals for specialized oncology departments
Utilizing online resources can help you find the best options available in your area. 🏥
What are the side effects of skin cancer treatment?
Side effects can vary based on the treatment method but may include:
- Skin irritation or redness
- Swelling at the treatment site
- Changes in skin pigmentation
- Fatigue or nausea (especially with systemic treatments)
Always discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider before starting treatment. ⚠️




