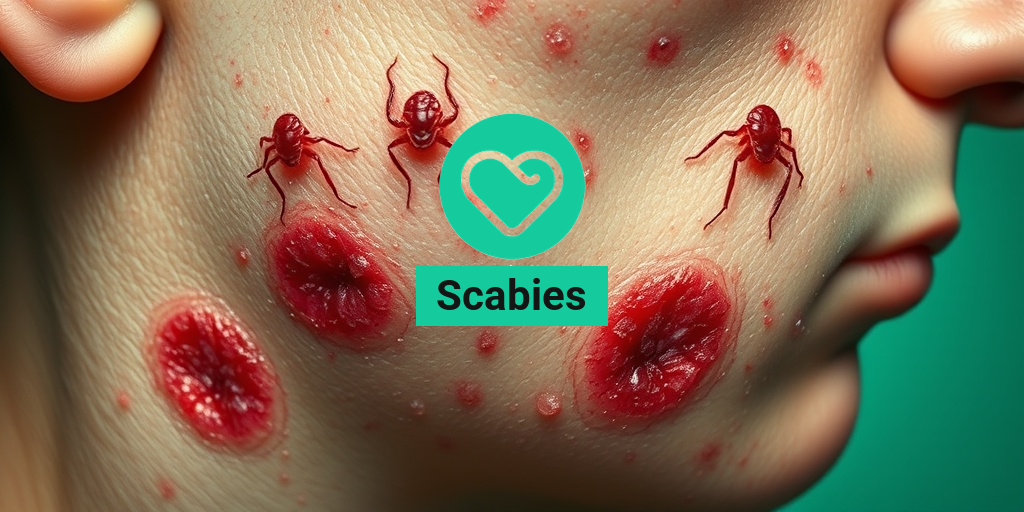
What Is Scabies?
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These microscopic parasites burrow into the outer layer of the skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort. Scabies can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or hygiene practices, and it often spreads in crowded conditions, such as schools, nursing homes, and shelters.
How Do Scabies Mites Spread?
The primary mode of transmission for scabies is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This can occur during activities such as:
- Close physical contact, including hugging or holding hands 🤝
- Sharing personal items like towels, bedding, or clothing 🛏️
- Living in close quarters with an infected individual
It’s important to note that scabies mites can survive for up to 48 hours on surfaces, making it possible to contract the condition from contaminated items. However, casual contact, such as shaking hands, is unlikely to spread the mites.
Understanding the Life Cycle of Scabies Mites
Scabies mites have a life cycle that includes several stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. The adult female mite burrows into the skin to lay eggs, which hatch within a few days. The newly hatched larvae then migrate to the skin’s surface, where they mature into adult mites. This cycle contributes to the rapid spread of scabies, as the itching and irritation often lead to scratching, which can further spread the mites to other areas of the body or to other individuals.
Scabies Symptoms
The symptoms of scabies can vary from person to person, but the most common signs include:
- Intense itching: This is often worse at night and can be extremely uncomfortable.
- Rash: A red, pimple-like rash may develop, often accompanied by small blisters or sores.
- Burrows: You may notice tiny, thread-like burrows on the skin, which are created by the mites as they tunnel beneath the surface.
- Secondary infections: Scratching the affected areas can lead to bacterial infections, resulting in additional symptoms like swelling and pus.
Common Areas Affected by Scabies
Scabies can occur anywhere on the body, but certain areas are more commonly affected, including:
- Between the fingers and toes
- Wrists and elbows
- Armpits
- Genital area
- Buttocks
- Scalp (in infants and young children)
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you suspect you have scabies or are experiencing severe itching and rash, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend effective scabies treatment. Early intervention can help prevent the spread of the condition to others and alleviate discomfort.
For more information on scabies and its treatment options, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. Remember, while scabies can be distressing, it is treatable, and with the right care, you can find relief and prevent further spread.
In conclusion, understanding scabies, its symptoms, and how it spreads is crucial for effective management and prevention. If you notice any signs of scabies, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for guidance. Your health and comfort are paramount! 🌟

Scabies Transmission
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. Understanding how scabies is transmitted is crucial for preventing its spread and protecting yourself and others. Let’s delve into the various ways scabies can be transmitted.
Direct Skin-to-Skin Contact
The primary mode of transmission for scabies is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This can occur during:
- Close physical interactions, such as hugging or holding hands 🤝
- Sexual contact, which is a common way the mites spread among sexually active individuals
- Sharing a bed or sleeping in close quarters with someone who has scabies
It’s important to note that the mites can only survive for a short time away from human skin, so casual contact, like shaking hands, is less likely to result in transmission.
Indirect Transmission Through Contaminated Items
While direct contact is the most common way to contract scabies, it can also spread through contaminated items. The mites can survive for up to 72 hours on surfaces, which means:
- Sharing clothing, towels, or bedding with an infected person can lead to transmission
- Using furniture or bedding that has not been cleaned after an infected person has used it
To minimize the risk of indirect transmission, it’s essential to wash any potentially contaminated items in hot water and dry them on a high heat setting. 🧺
Scabies in Community Settings
Scabies can spread rapidly in crowded environments where close contact is common. This includes:
- Schools and daycare centers
- Nursing homes and assisted living facilities
- Military barracks
In these settings, outbreaks can occur quickly, making it vital for institutions to implement preventive measures and educate individuals about the signs and symptoms of scabies.
Scabies Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors associated with scabies can help you take proactive steps to avoid infection. Here are some key factors that increase the likelihood of contracting scabies:
Close Living Conditions
Individuals living in close quarters, such as dormitories, shelters, or crowded households, are at a higher risk of scabies transmission. The close proximity allows for easy skin-to-skin contact and increases the chances of spreading the mites. 🏠
Weakened Immune System
People with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to scabies. Their bodies may not be able to fight off the infestation as effectively, leading to more severe symptoms and complications.
Age and Gender
While scabies can affect anyone, certain demographics may be more vulnerable:
- Children and infants are often at higher risk due to their close contact with peers and caregivers
- Women may be more likely to contract scabies due to higher rates of close physical contact in caregiving roles
Previous Infestations
If you have had scabies in the past, you may be at a higher risk of reinfestation. This is particularly true if you have close contact with someone who is currently infected. It’s essential to ensure that all infected individuals are treated promptly to prevent recurrence.
Traveling to Endemic Areas
Traveling to regions where scabies is more prevalent can increase your risk of exposure. Areas with poor sanitation and crowded living conditions are often hotspots for scabies outbreaks. If you’re planning to travel, be aware of the risks and take necessary precautions.
By understanding how scabies is transmitted and recognizing the risk factors, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this uncomfortable condition. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to managing scabies effectively! 🌍✨

Scabies Diagnosis
Diagnosing scabies can sometimes be a challenge, as its symptoms can resemble those of other skin conditions. However, understanding the signs and seeking medical advice is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s what you need to know about the diagnosis process.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing scabies is recognizing its symptoms. Common signs include:
- Intense itching: This is often worse at night and can be quite distressing.
- Rash: A red, pimple-like rash may develop, often in clusters.
- Burrows: Tiny, thread-like lines on the skin, which are actually tunnels made by the scabies mites.
- Crusts: In severe cases, especially with scabies crustosa, the skin can become thick and crusty.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you suspect you have scabies, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They will typically perform a physical examination and may ask about your symptoms and any recent exposure to others with scabies. In some cases, they might take a skin scraping to examine under a microscope for the presence of scabies mites or their eggs.
Understanding the Importance of Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is vital because scabies can easily spread, especially in crowded living conditions. Early detection not only helps in managing your symptoms but also prevents further transmission to others. If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice! 🩺
Scabies Treatment Options
Once diagnosed, treating scabies effectively is crucial to alleviate symptoms and eliminate the mites. There are several treatment options available, and your healthcare provider will recommend the best course based on your specific situation.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are the most common approach for scabies. These include:
- Permethrin cream: This is a topical insecticide that is applied to the skin from the neck down and left on for 8-14 hours before washing off.
- Benzyl benzoate: Another effective topical treatment that can be used similarly to permethrin.
- Scabicide lotions: These are specifically formulated to kill scabies mites and are often recommended by healthcare providers.
Oral Medications
In more severe cases, or when topical treatments are ineffective, oral medications may be prescribed. Ivermectin is a common oral medication used to treat scabies, particularly in cases of crusted scabies or when the patient has difficulty applying topical treatments.
Home Remedies and Supportive Care
While medical treatments are essential, some home remedies and supportive care can help alleviate symptoms:
- Cool compresses: Applying cool, damp cloths to itchy areas can provide temporary relief.
- Oatmeal baths: Soaking in an oatmeal bath can soothe irritated skin.
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines may help reduce itching and improve sleep.
Preventing Reinfestation
After treatment, it’s important to take steps to prevent reinfestation. This includes:
- Washing bedding and clothing: Use hot water and dry on high heat to kill any remaining mites.
- Avoiding close contact: Until treatment is complete, avoid close contact with others to prevent spreading the mites.
- Informing close contacts: Letting those you’ve been in close contact with know about your diagnosis is crucial for preventing further outbreaks.
In conclusion, while scabies can be uncomfortable and distressing, effective treatment options are available. If you suspect you have scabies, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, early intervention is key to managing this condition effectively! 🌟

Scabies Home Remedies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort. While medical treatments are often necessary, many people seek home remedies to alleviate symptoms and support healing. Here are some effective home remedies you can try:
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is renowned for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It can help reduce itching and irritation caused by scabies. To use:
- Mix a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil.
- Apply the mixture directly to the affected areas.
- Leave it on for at least 30 minutes before rinsing off.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is another natural remedy that can soothe the skin and reduce inflammation. Its cooling effect can provide relief from itching. To use:
- Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the affected areas.
- Let it sit for about 30 minutes before washing it off.
3. Neem Oil
Neem oil is known for its insecticidal properties and can help kill scabies mites. It also has anti-inflammatory effects that can soothe the skin. To use:
- Mix neem oil with a carrier oil.
- Apply it to the affected areas twice daily.
4. Oatmeal Baths
Taking an oatmeal bath can help relieve itching and soothe irritated skin. Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can calm the skin. To prepare:
- Grind plain oats into a fine powder.
- Add the powder to warm bath water and soak for 15-20 minutes.
5. Cold Compress
A cold compress can provide immediate relief from itching and inflammation. To use:
- Wrap ice cubes in a clean cloth or use a cold pack.
- Apply it to the affected areas for 10-15 minutes.
Scabies Prevention Tips
Preventing scabies is crucial, especially if you or someone in your household has been diagnosed. Here are some effective prevention tips to help you avoid scabies:
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene is essential in preventing scabies. Regularly wash your hands and body, and keep your living environment clean. This includes:
- Showering daily.
- Washing clothes and bedding frequently in hot water.
2. Avoid Close Contact
Scabies spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact. To minimize the risk:
- Avoid close physical contact with someone who has scabies.
- Refrain from sharing personal items like towels, clothing, or bedding.
3. Treat Infected Individuals Promptly
If someone in your household is diagnosed with scabies, it’s important to treat them promptly to prevent the spread. Ensure that:
- Everyone in close contact with the infected person is treated.
- Follow the treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare professional.
4. Vacuum and Clean Your Home
Scabies mites can survive on surfaces for a short time. To reduce the risk of reinfestation:
- Vacuum carpets and upholstery thoroughly.
- Wash all bedding and clothing in hot water.
5. Educate Yourself and Others
Understanding scabies and its transmission can help you take proactive measures. Share information with family and friends to raise awareness and prevent outbreaks.
By following these home remedies and prevention tips, you can effectively manage and reduce the risk of scabies. Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. 🩺✨

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of scabies?
The primary symptoms of scabies include:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Rash that may appear as red bumps or blisters
- Burrows or tiny lines on the skin, often found between fingers and on wrists
- Thickened skin in severe cases, known as crusted scabies
How is scabies transmitted?
Scabies is primarily spread through prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. It can also be transmitted through sharing personal items such as clothing, bedding, or towels.
What treatments are available for scabies?
There are several effective treatments for scabies, including:
- Topical creams and lotions, such as permethrin or benzyl benzoate
- Oral medications like ivermectin for severe cases
- Antihistamines to relieve itching
Can scabies be prevented?
To prevent scabies, consider the following tips:
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals
- Do not share personal items
- Wash clothing and bedding in hot water regularly
Is scabies contagious?
Yes, scabies is highly contagious. It can spread quickly in crowded conditions, such as schools or nursing homes. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent outbreaks.
What should I do if I suspect I have scabies?
If you suspect you have scabies, it is important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and prevent spreading the condition to others.
Are there any home remedies for scabies?
While medical treatments are the most effective, some people explore home remedies such as:
- Tea tree oil for its potential anti-parasitic properties
- Neem oil which may help soothe the skin
However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any home remedies.