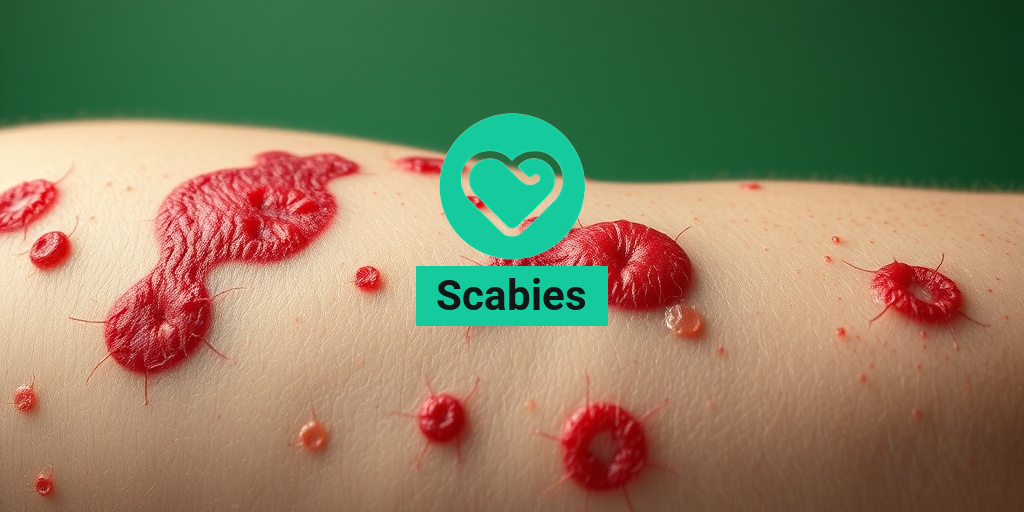
What Is Scabies?
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These microscopic parasites burrow into the upper layer of the skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort. Scabies can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or hygiene practices, making it a common concern in crowded living conditions such as schools, nursing homes, and shelters.
The primary mode of transmission is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This can occur during close physical interactions, such as hugging or sharing bedding. Additionally, scabies can spread through infested clothing, towels, or furniture, although this is less common.
Understanding scabies is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. The condition is often mistaken for other skin issues, which can delay proper care. If you suspect you have scabies, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Scabies Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of scabies is vital for early intervention. The most common signs include:
- Intense Itching: The hallmark symptom of scabies is severe itching, especially at night. This occurs due to an allergic reaction to the mites and their waste.
- Rash: A rash may develop, characterized by small red bumps, blisters, or sores. These can appear anywhere on the body but are often found in skin folds, between fingers, on the wrists, and around the waist.
- Burrows: You might notice tiny, thread-like burrows on the skin, which are created by the mites as they tunnel into the skin.
- Secondary Infections: Scratching the affected areas can lead to bacterial infections, resulting in additional symptoms like swelling, pus, and increased redness.
Identifying Scabies in Different Populations
Scabies can manifest differently depending on the individual. For instance:
- Children: In young children, scabies may present with a more widespread rash and can affect the scalp, face, and palms.
- Older Adults: Elderly individuals may experience a more severe form known as crusted scabies, which involves thick crusts of skin and a higher number of mites.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent itching or notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can perform a physical examination and may take a skin scraping to confirm the presence of mites. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of scabies to others and alleviate discomfort.
For those looking for reliable information on scabies and its treatment options, Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) is an excellent resource for evidence-based health answers. They provide comprehensive insights into various health conditions, including scabies, ensuring you have the information you need to make informed decisions about your health.
In conclusion, understanding what scabies is and recognizing its symptoms can empower you to take action quickly. If you suspect you have scabies, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and treatment. Remember, early intervention is key to managing this condition effectively! 🩺✨
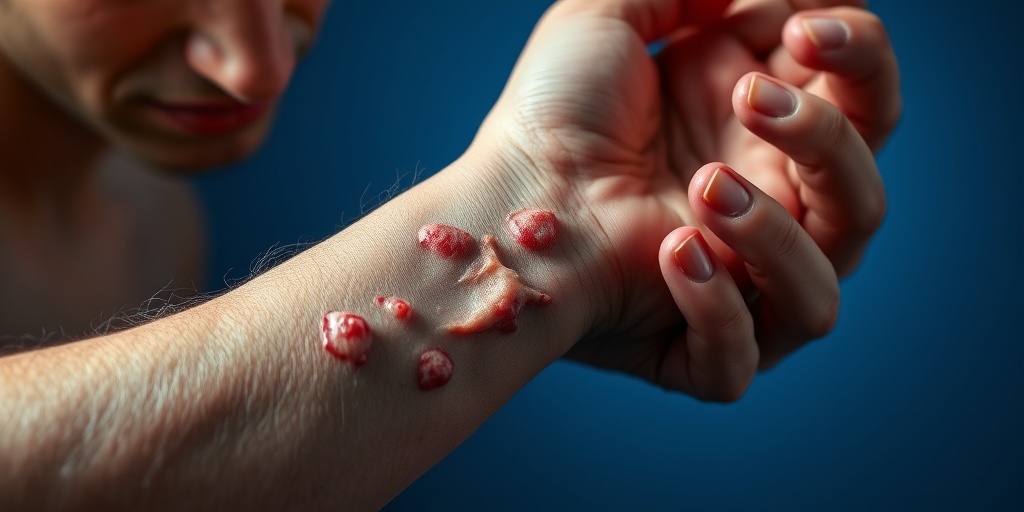
Scabies Transmission
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. Understanding how scabies spreads is crucial for prevention and control. Let’s delve into the various ways scabies can be transmitted.
Direct Skin-to-Skin Contact
The primary mode of transmission for scabies is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This can occur during:
- Close physical interactions, such as hugging or holding hands 🤝
- Sexual contact, which is a common way for scabies to spread among sexually active individuals
- Living in the same household or sharing a bed with someone who has scabies
Indirect Transmission
While less common, scabies can also be transmitted indirectly through contaminated items. The scabies mites can survive for a short period outside the human body, which means they can be found on:
- Clothing, especially items that have been worn by an infected person
- Bedding and towels that have been used by someone with scabies
- Furniture or carpets where an infected person has sat or laid down
It’s important to note that scabies mites do not live long without a human host, typically dying within 48-72 hours. However, this is enough time for transmission to occur if precautions are not taken.
Environmental Factors
Scabies can thrive in crowded living conditions where close contact is unavoidable. This includes:
- Long-term care facilities
- Prisons
- Homeless shelters
In these environments, the risk of transmission increases significantly due to the close proximity of individuals. Awareness and prompt treatment are essential in such settings to prevent outbreaks.
Scabies Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors associated with scabies can help individuals take preventive measures. Here are some key factors that increase the likelihood of contracting scabies:
Close Contact with Infected Individuals
As mentioned earlier, direct contact with someone who has scabies is the most significant risk factor. This is particularly relevant for:
- Family members living in the same household
- Sexual partners
- Individuals in close-knit communities or institutions
Compromised Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are at a higher risk of developing scabies. Their bodies may not be able to fight off the infestation as effectively as those with healthy immune systems.
Age and Health Conditions
Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to scabies. In children, the skin may be more sensitive, making them more susceptible to irritation and infection. Additionally, individuals with certain skin conditions, like eczema, may also be at increased risk due to compromised skin barriers.
Living in Overcrowded Conditions
As previously mentioned, living in crowded environments can significantly increase the risk of scabies transmission. Overcrowding facilitates close contact, making it easier for the mites to spread. This is often seen in:
- Refugee camps
- Low-income housing
- Group homes
Traveling to Endemic Areas
Traveling to regions where scabies is more prevalent can also pose a risk. Areas with poor sanitation and crowded living conditions are often hotspots for scabies outbreaks. Travelers should be aware of these risks and take necessary precautions, such as avoiding close contact with locals who may show signs of infestation.
By understanding the transmission methods and risk factors associated with scabies, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones from this uncomfortable condition. 🛡️

Scabies Diagnosis
Diagnosing scabies can be a straightforward process, but it often requires a keen eye and a thorough understanding of the condition. Scabies is caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically diagnose this condition.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing scabies is recognizing its symptoms. Common signs include:
- Intense itching: This is often worse at night and can be quite distressing.
- Rash: A red, pimple-like rash may develop, often in areas like the hands, wrists, elbows, and between the fingers.
- Burrows: Tiny, thread-like lines on the skin where the mites have burrowed.
- Secondary infections: Scratching can lead to bacterial infections, which may complicate the diagnosis.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you suspect you have scabies, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They will typically perform a physical examination and may ask about your symptoms and any recent exposure to others with scabies. In some cases, they might:
- Take a skin scraping: This involves gently scraping the affected area to collect skin cells, which can be examined under a microscope for the presence of mites or their eggs.
- Conduct a visual examination: A thorough inspection of the skin can help identify characteristic signs of scabies.
Understanding the Importance of Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial because scabies can easily be mistaken for other skin conditions, such as eczema or allergic reactions. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the spread of scabies to others and alleviate discomfort. If you’re experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice! 🩺
Scabies Treatment Options
Treating scabies effectively is essential to eliminate the mites and relieve symptoms. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available, ranging from topical creams to oral medications. Here’s a closer look at the most common treatments.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against scabies. These include:
- Permethrin cream: This is a widely used topical treatment that is applied to the entire body, from the neck down, and left on for 8-14 hours before washing off.
- Benzyl benzoate: Another effective option, this lotion is applied similarly to permethrin and can help kill the mites.
- Crotamiton: This cream can relieve itching and kill mites, but it may be less effective than permethrin.
Oral Medications
In more severe cases or when topical treatments fail, oral medications may be prescribed. These include:
- Ivermectin: This oral medication is effective in treating scabies, especially in cases of crusted scabies, which is a more severe form of the condition.
- Antihistamines: While not a direct treatment for scabies, antihistamines can help alleviate itching and improve sleep during the healing process.
Home Remedies and Supportive Care
In addition to medical treatments, some people seek scabies treatment at home. While these remedies may not eliminate the mites, they can provide relief from itching:
- Cold compresses: Applying a cold compress to the affected areas can soothe itching.
- Oatmeal baths: Soaking in an oatmeal bath can help calm irritated skin.
- Essential oils: Some essential oils, like tea tree oil, may have anti-parasitic properties, but always consult a healthcare provider before use.
Preventing Reinfestation
After treatment, it’s crucial to take steps to prevent reinfestation. This includes:
- Washing bedding and clothing: Use hot water and dry on high heat to kill any remaining mites.
- Avoiding close contact: Until treatment is complete, avoid close contact with others to prevent spreading scabies.
With the right diagnosis and treatment, scabies can be effectively managed, allowing you to return to your normal routine. If you suspect you have scabies, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance! 🌟

Scabies Home Remedies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin, leading to intense itching and discomfort. While medical treatments are often necessary, many people seek home remedies to alleviate symptoms and support healing. Here are some effective home remedies for scabies that you can try:
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is renowned for its natural antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. It can help reduce itching and kill scabies mites. To use:
- Mix a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil.
- Apply the mixture directly to the affected areas twice daily.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is another excellent remedy due to its soothing properties. It can help relieve itching and promote skin healing. Here’s how to use it:
- Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the affected skin.
- Leave it on for at least 30 minutes before rinsing off.
3. Neem Oil
Neem oil is known for its insecticidal properties and can be effective against scabies mites. To use neem oil:
- Mix neem oil with a carrier oil.
- Apply it to the affected areas and leave it on overnight.
4. Clove Oil
Clove oil has been shown to have strong anti-parasitic properties. It can help kill scabies mites and reduce itching. Here’s how to apply it:
- Mix a few drops of clove oil with a carrier oil.
- Apply it to the affected areas once a day.
5. Baking Soda
Baking soda can help soothe itching and irritation. To use it:
- Mix baking soda with water to create a paste.
- Apply the paste to the affected areas and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off.
6. Oatmeal Baths
Taking an oatmeal bath can provide relief from itching and irritation. Here’s how to prepare one:
- Grind plain oatmeal into a fine powder.
- Add it to a warm bath and soak for 15-20 minutes.
While these home remedies can help alleviate symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if symptoms persist. 🩺
Scabies Prevention Tips
Preventing scabies is crucial, especially if you or someone in your household has been diagnosed. Here are some effective prevention tips to help you avoid scabies:
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
Regular bathing and maintaining good personal hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of scabies. Make sure to:
- Shower daily and wash your hands frequently.
- Keep your nails trimmed and clean to avoid harboring mites.
2. Avoid Close Contact
Scabies spreads through close skin-to-skin contact. To minimize the risk:
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels, clothing, and bedding.
- Limit close contact with individuals who have scabies until they have been treated.
3. Wash Bedding and Clothing
Regularly washing bedding and clothing in hot water can help eliminate scabies mites. Follow these steps:
- Wash all clothing, towels, and bed linens in hot water (at least 130°F or 54°C).
- Dry them in a hot dryer to kill any remaining mites.
4. Vacuum Regularly
Vacuuming your home regularly can help remove any mites that may have fallen off from infected individuals. Make sure to:
- Vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture.
- Dispose of the vacuum bag or empty the canister outside to prevent re-infestation.
5. Educate Yourself and Others
Understanding how scabies spreads and recognizing its symptoms can help you take preventive measures. Share this knowledge with family and friends to promote awareness.
By following these prevention tips, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting scabies and protect your loved ones. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to managing this condition effectively! 🛡️

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of scabies? 🤔
The primary symptoms of this condition include:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Rash that may appear as small red bumps or blisters
- Burrows or tiny lines on the skin, often found between fingers, wrists, and other skin folds
How is scabies transmitted? 🔄
This condition is highly contagious and can be spread through:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person
- Sharing clothing, bedding, or towels with someone who has the condition
What are the treatment options for scabies? 💊
Treatment typically involves:
- Prescription creams or lotions that contain permethrin or lindane
- Oral medications, such as ivermectin, in severe cases
- Home remedies, though these should be discussed with a healthcare provider
Can scabies be treated at home? 🏠
While some home remedies may provide relief, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Over-the-counter creams may not be effective against the mites.
How long does it take for treatment to work? ⏳
Most treatments start to relieve symptoms within a few days, but it may take up to two weeks for the rash and itching to completely resolve. It’s important to follow the treatment plan as directed.
Is it possible to get scabies more than once? 🔁
Yes, individuals can get reinfected if they come into contact with an infected person or contaminated items after treatment. Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding close contact with infected individuals can help prevent reinfection.
What should I do if I suspect I have scabies? 🩺
If you suspect you have this condition, it is crucial to:
- Contact a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis
- Avoid close contact with others until you have been treated
- Wash all clothing and bedding in hot water to eliminate any mites