What Is Radiation?
Radiation is a form of energy that travels through space and can take various forms, including electromagnetic waves and particles. It is a natural phenomenon that occurs all around us, from the sunlight that warms our skin to the cosmic rays that bombard the Earth from outer space. Understanding radiation is crucial, especially when discussing its effects on the human body and the environment.
At its core, radiation can be categorized into two main types: ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Each type has different properties and effects on living organisms.
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, creating ions. This type of radiation can be harmful to living tissues and is associated with various health risks. Common sources of ionizing radiation include:
- X-rays
- Gamma rays
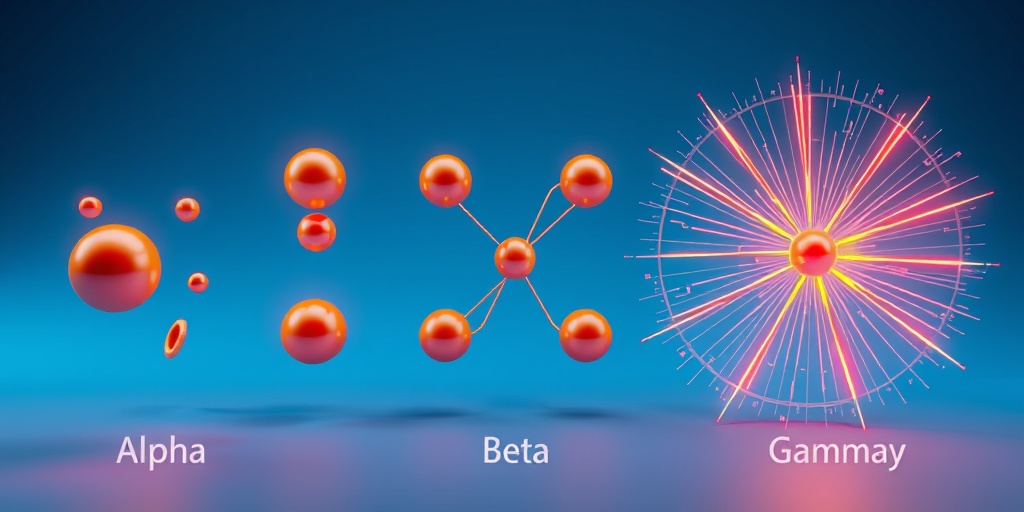
- Alpha particles
- Beta particles
Exposure to ionizing radiation can lead to significant radiation effects on the body, including cellular damage, increased cancer risk, and other health issues. For instance, the aftermath of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings highlighted the severe consequences of ionizing radiation exposure, leading to long-term health effects for survivors.
Non-Ionizing Radiation
Non-ionizing radiation, on the other hand, does not carry enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules. It includes lower-energy forms of radiation such as:
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared radiation
- Visible light
While non-ionizing radiation is generally considered less harmful than its ionizing counterpart, prolonged exposure can still have radiation effects on humans, such as skin burns from excessive UV exposure or potential risks associated with prolonged use of mobile phones.
Types of Radiation
Understanding the different types of radiation is essential for comprehending their potential effects on health and safety. Here, we delve deeper into the various forms of radiation and their implications.
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation encompasses a wide spectrum of energy waves, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays. This type of radiation is characterized by its wavelength and frequency. Key categories include:
- Radio Waves: Used in communication technologies, these waves are generally harmless.
- Microwaves: Commonly used in cooking and telecommunications, they can cause heating effects but are not ionizing.
- Infrared Radiation: Felt as heat, infrared radiation is used in various applications, including thermal imaging.
- Visible Light: The light we can see, essential for vision but can cause damage in excessive amounts (e.g., UV light).
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Known for its ability to cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
- X-rays: Used in medical imaging, they can penetrate tissues but pose risks of cellular damage.
- Gamma Rays: Emitted during radioactive decay, these rays are highly penetrating and can cause severe biological effects.
Particle Radiation
Particle radiation consists of subatomic particles that can be emitted from radioactive materials. The main types include:
- Alpha Particles: Heavy and positively charged, alpha particles can be stopped by a sheet of paper but can cause significant damage if ingested or inhaled.
- Beta Particles: Lighter and negatively charged, beta particles can penetrate skin but are less harmful than alpha particles.
- Neutrons: Neutron radiation is highly penetrating and can cause significant biological damage, often found in nuclear reactions.
Each type of radiation has unique properties and potential radiation effects on the human body. Understanding these differences is vital for assessing risks and implementing safety measures.
For more detailed information on radiation and its effects, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. 🌟
In conclusion, radiation is a complex topic with significant implications for health and safety. By understanding the types of radiation and their effects, we can better protect ourselves and make informed decisions about exposure. Stay informed and stay safe! 🌍
Radiation Exposure Sources
Radiation is a natural part of our environment, and we are exposed to it from various sources every day. Understanding these sources is crucial for recognizing the potential radiation effects on our health. Here, we will explore the primary sources of radiation exposure.
Natural Sources of Radiation
Natural radiation comes from cosmic rays, terrestrial sources, and even our own bodies. Here are some key contributors:
- Cosmic Radiation: This type of radiation originates from outer space and interacts with the Earth’s atmosphere. High-altitude locations and air travel can increase exposure.
- Terrestrial Radiation: Certain rocks and soil contain radioactive materials like uranium, thorium, and radon. Radon gas, in particular, can accumulate in homes, especially in basements.
- Internal Radiation: Our bodies naturally contain radioactive isotopes, such as potassium-40, which contribute to our overall radiation exposure.
Man-Made Sources of Radiation
In addition to natural sources, human activities also contribute to radiation exposure. Some common man-made sources include:
- Medical Procedures: X-rays, CT scans, and radiation therapy for cancer treatment are significant sources of radiation exposure. While these procedures are essential for diagnosis and treatment, they do contribute to cumulative radiation doses.
- Industrial Applications: Certain industries use radioactive materials for various purposes, including gauging devices and radiography. Workers in these fields must adhere to strict safety protocols to minimize exposure.
- Nuclear Power Plants: While designed to be safe, accidents or leaks can lead to increased radiation exposure for nearby populations. The effects of such incidents can be long-lasting and severe.
Everyday Sources of Radiation
Even in our daily lives, we encounter radiation from various sources:
- Smoke Detectors: Many smoke detectors contain small amounts of radioactive material, which helps detect smoke particles.
- Televisions and Computers: Older models of these devices emit low levels of radiation, although modern technology has significantly reduced this risk.
- Air Travel: Frequent flyers are exposed to higher levels of cosmic radiation due to increased altitude.
Understanding these sources of radiation exposure is essential for making informed decisions about our health and safety. By being aware of where radiation comes from, we can take steps to minimize unnecessary exposure.
Short-Term Radiation Effects
When it comes to radiation effects, the short-term impacts can be quite significant, especially in cases of high exposure. These effects can manifest quickly and vary depending on the level of radiation received. Here’s a closer look at what happens in the short term.
Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Acute Radiation Syndrome, commonly known as ARS, occurs after a person receives a high dose of radiation in a short period. Symptoms can appear within hours or days and may include:
- Nausea and Vomiting: One of the first signs of ARS, often occurring within minutes to hours after exposure.
- Fatigue: A feeling of extreme tiredness can set in as the body begins to react to the radiation.
- Skin Damage: High doses can lead to burns or radiation sickness, affecting the skin’s integrity.
Effects on the Immune System
Short-term exposure to high levels of radiation can severely impact the immune system. This can lead to:
- Increased Infection Risk: A weakened immune response makes the body more susceptible to infections.
- Blood Cell Damage: Radiation can damage bone marrow, leading to a decrease in red and white blood cells, which are crucial for oxygen transport and immune defense.
Radiation Effects on the Eyes
Another notable short-term effect of radiation exposure is on the eyes. High doses can lead to:
- Cataracts: Radiation can cause clouding of the lens, leading to vision impairment.
- Retinal Damage: In severe cases, radiation can damage the retina, affecting vision quality.
Recognizing these short-term effects is vital for understanding the risks associated with radiation exposure. Whether from medical procedures or environmental sources, being informed can help individuals take necessary precautions to protect their health. 🌟

Long-Term Radiation Effects
Radiation exposure can have profound and lasting impacts on the human body. Understanding the long-term radiation effects is crucial for anyone who may be exposed to radiation, whether through medical treatments, occupational hazards, or environmental factors. Here, we delve into the various ways radiation can affect health over time.
Cellular Damage and Mutation
One of the primary long-term effects of radiation is cellular damage. When radiation interacts with cells, it can cause changes in the DNA structure, leading to mutations. These mutations can result in:
- Cancer: The most significant risk associated with long-term radiation exposure is the development of cancer. Studies have shown that individuals exposed to high levels of radiation, such as survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings, have a higher incidence of various cancers.
- Genetic Defects: Mutations can also be passed down to future generations, potentially leading to genetic defects in offspring.
Effects on Organs and Systems
Radiation can affect different organs and systems in the body, leading to chronic health issues. Some of the notable effects include:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Research indicates that radiation exposure can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
- Thyroid Dysfunction: The thyroid gland is particularly sensitive to radiation, which can lead to conditions such as hypothyroidism or thyroid cancer.
- Respiratory Problems: Inhalation of radioactive particles can cause long-term lung damage and increase the risk of respiratory diseases.
Neurological Effects
Long-term exposure to radiation can also impact the nervous system. Some potential neurological effects include:
- Cognitive Decline: Studies suggest that individuals exposed to high levels of radiation may experience cognitive decline and memory issues over time.
- Neuropathy: Radiation can lead to nerve damage, resulting in pain, tingling, or numbness in various parts of the body.
Radiation Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of radiation exposure is essential for early intervention and treatment. The symptoms can vary depending on the level and duration of exposure, as well as the individual’s health status. Here are some common radiation symptoms to be aware of:
Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Acute Radiation Syndrome occurs after a high dose of radiation exposure over a short period. Symptoms can appear within hours or days and may include:
- Nausea and Vomiting: One of the earliest signs, often occurring within minutes to hours after exposure.
- Fatigue: A profound sense of tiredness that can persist for days or weeks.
- Skin Burns: Radiation can cause severe skin damage, leading to burns or blistering.
Chronic Symptoms
For those exposed to lower levels of radiation over an extended period, chronic symptoms may develop, including:
- Skin Changes: Long-term exposure can lead to skin conditions such as dermatitis or increased pigmentation.
- Hair Loss: Radiation can cause hair thinning or loss, particularly in areas directly exposed.
- Increased Cancer Risk: As mentioned earlier, prolonged exposure can lead to various cancers, with symptoms depending on the type of cancer.
Psychological Effects
In addition to physical symptoms, radiation exposure can also have psychological effects. Individuals may experience:
- Anxiety and Depression: The fear of developing radiation-related illnesses can lead to significant mental health challenges.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Survivors of significant radiation events may experience PTSD, affecting their daily lives.
Understanding the radiation effects on the body is vital for prevention and treatment. Awareness of symptoms and long-term consequences can empower individuals to seek help and make informed decisions regarding their health.

Radiation Diagnosis
Radiation diagnosis plays a crucial role in modern medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to detect and diagnose various conditions effectively. This process involves the use of different types of radiation to visualize the internal structures of the body, helping to identify abnormalities that may not be visible through traditional examination methods.
What is Radiation Diagnosis?
Radiation diagnosis refers to the use of ionizing radiation to create images of the body. This technique is commonly employed in various imaging modalities, including:
- X-rays: One of the most common forms of radiation diagnosis, X-rays are used to view bones and certain tissues. They are particularly effective in identifying fractures, infections, and tumors.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans combine multiple X-ray images taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional images of the body. This method provides detailed information about organs, bones, and soft tissues.
- Fluoroscopy: This technique allows real-time imaging of the movement of internal structures, often used in procedures like barium swallows or catheter placements.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans: PET scans utilize radioactive tracers to visualize metabolic processes in the body, making them invaluable in cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
Benefits of Radiation Diagnosis
The use of radiation in diagnosis offers several advantages:
- Early Detection: Many diseases, including cancer, can be detected at an early stage, significantly improving treatment outcomes.
- Non-Invasive: Most radiation diagnostic procedures are non-invasive, meaning they do not require surgical intervention.
- Comprehensive Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques provide detailed views of internal structures, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
Safety Considerations
While radiation diagnosis is generally safe, it is essential to consider the radiation effects on the body. Healthcare providers take precautions to minimize exposure, including:
- Using the lowest effective dose of radiation.
- Employing protective measures, such as lead aprons.
- Limiting the number of scans when possible.
Patients should always discuss any concerns regarding radiation exposure with their healthcare provider to ensure informed decision-making. 🩺
Radiation Treatment Options
Radiation therapy is a cornerstone of cancer treatment, utilizing high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Understanding the various radiation treatment options available can empower patients to make informed choices about their care.
Types of Radiation Therapy
There are several types of radiation therapy, each tailored to the specific needs of the patient:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common form of radiation treatment, where high-energy beams are directed at the tumor from outside the body. It is often used for localized cancers.
- Brachytherapy: In this method, radioactive sources are placed directly inside or near the tumor. This allows for a higher dose of radiation to target the cancer while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Systemic Radiation Therapy: This involves administering radioactive substances through the bloodstream, targeting cancer cells throughout the body. It is commonly used for certain types of thyroid cancer and other conditions.
Benefits of Radiation Treatment
Radiation therapy offers numerous benefits, including:
- Targeted Treatment: Radiation can precisely target tumors, reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Combination Therapy: It can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy, to enhance overall effectiveness.
- Palliative Care: Radiation therapy can alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with advanced cancer.
Potential Side Effects
While radiation therapy is effective, it can also lead to side effects, which may vary depending on the treatment area and individual patient factors. Common side effects include:
- Fatigue: Many patients experience fatigue during and after treatment.
- Skin Reactions: The skin in the treatment area may become red, irritated, or sensitive.
- Changes in Appetite: Some patients may experience changes in taste or appetite during treatment.
It is essential for patients to communicate openly with their healthcare team about any side effects they experience, as there are often strategies to manage them effectively. 🌟
Frequently Asked Questions about Radiation Effects
What are the primary radiation effects on the human body?
The primary radiation effects on the human body can include a range of health issues, such as:
- Cellular damage
- Increased risk of cancer
- Radiation sickness
- Effects on reproductive health
How does radiation affect the skin?
Radiation effects on skin can manifest as burns, rashes, or long-term changes such as premature aging and increased risk of skin cancer. The severity often depends on the dose and duration of exposure.
What are the radiation effects on the eyes?
Exposure to high levels of radiation can lead to cataracts and other eye disorders. Radiation effects on eyes can be particularly concerning for those working in certain industries or undergoing specific medical treatments.
Can radiation effects cause genetic defects?
Yes, exposure to significant levels of radiation can lead to genetic mutations, which may result in radiation effects and defects in solids or hereditary conditions in future generations.
What historical events highlight the radiation effects?
The radiation effects of Hiroshima serve as a critical case study, illustrating the severe health impacts experienced by survivors, including increased cancer rates and other long-term health issues.
Is there ongoing research on radiation effects?
Yes, numerous organizations, including the radiation effects research foundation, continue to study the long-term impacts of radiation exposure to better understand its effects and improve safety standards.
How can I protect myself from radiation effects?
To minimize exposure, consider the following precautions:
- Limit time spent near radiation sources
- Increase distance from radiation sources
- Use protective shielding when necessary
What should I do if I suspect radiation exposure?
If you believe you have been exposed to harmful levels of radiation, seek medical attention immediately. Early intervention can help mitigate potential radiation effects.




