What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist, resulting from pressure on the median nerve, which runs through the carpal tunnel—a narrow passageway in the wrist. This condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and even weakness in the hand, making daily activities challenging. Understanding the anatomy of the wrist and the factors that contribute to CTS is crucial for preventing carpal tunnel syndrome and maintaining overall hand health.
The Anatomy of the Carpal Tunnel
The carpal tunnel is formed by the carpal bones on the bottom and the transverse carpal ligament on the top. Within this tunnel, the median nerve and tendons that control finger movement pass through. When the tunnel becomes narrowed or inflamed, it can compress the median nerve, leading to the symptoms associated with CTS.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Several factors can contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, including:
- Repetitive Hand Movements: Activities that involve repetitive wrist motions, such as typing or using a mouse, can increase the risk of CTS.
- Wrist Position: Maintaining an awkward wrist position for extended periods can put pressure on the median nerve.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disorders can increase the likelihood of developing CTS.
- Injury: A wrist fracture or other injuries can lead to swelling and compression of the median nerve.
By understanding these causes, individuals can take proactive steps toward preventing carpal tunnel syndrome and protecting their wrist health.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Recognizing the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome early is essential for effective management and prevention of further complications. The symptoms can vary in intensity and may include:
Common Symptoms
- Numbness and Tingling: Many individuals experience a tingling sensation or numbness in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger. This sensation often worsens at night.
- Pain: Pain may radiate from the wrist up the arm or down into the fingers. It can be sharp or aching and may interfere with sleep.
- Weakness: Affected individuals may notice weakness in their grip or difficulty holding objects, which can impact daily tasks.
- Clumsiness: Some people report a feeling of clumsiness or a tendency to drop things due to decreased hand coordination.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from worsening and may include recommendations for lifestyle changes, ergonomic adjustments, or physical therapy. In some cases, surgical options may be considered if conservative treatments are ineffective.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Here are some effective strategies:
- Ergonomic Workstation: Ensure your workstation is set up to promote a neutral wrist position. Use ergonomic keyboards and mouse devices to minimize strain.
- Take Breaks: Regularly take breaks to stretch and rest your hands, especially during repetitive tasks.
- Wrist Exercises: Incorporate wrist and hand exercises into your daily routine to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Managing underlying health conditions, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying active can help reduce the risk of CTS.
For more personalized advice and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for understanding and managing health conditions.
By being aware of the symptoms and taking preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome and maintain healthy, functional hands for years to come! 🖐️✨

Causes and Risk Factors
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a condition that arises when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with CTS is crucial for preventing carpal tunnel syndrome and maintaining hand health.
Common Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Several factors can contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Repetitive Hand Movements: Engaging in repetitive tasks, such as typing or using a mouse, can lead to inflammation and swelling in the wrist, putting pressure on the median nerve.
- Wrist Position: Poor wrist positioning during activities can exacerbate the risk. For instance, bending the wrist while typing can increase pressure on the carpal tunnel.
- Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disorders, can increase the likelihood of developing CTS.
- Injury: A wrist fracture or injury can lead to swelling and changes in the wrist structure, contributing to nerve compression.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to fluid retention, which may increase pressure in the carpal tunnel.
Identifying Risk Factors
While anyone can develop carpal tunnel syndrome, certain factors can increase your risk:
- Age: CTS is more common in individuals aged 30 to 60.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop CTS, possibly due to smaller carpal tunnels.
- Occupation: Jobs that require repetitive wrist movements, such as assembly line work, data entry, or construction, can heighten the risk.
- Genetics: A family history of carpal tunnel syndrome may increase your susceptibility.
By being aware of these causes and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome from developing or worsening. Simple lifestyle changes and ergonomic adjustments can make a significant difference! 🖥️✨
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specific tests. Early diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and preventing carpal tunnel syndrome from worsening.
Medical History and Symptoms
Your healthcare provider will begin by asking about your symptoms and medical history. Common symptoms of CTS include:
- Numbness or Tingling: Often felt in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger.
- Pain: Discomfort may radiate up the arm or worsen at night.
- Weakness: Difficulty gripping objects or performing fine motor tasks.
It’s important to provide detailed information about your symptoms, including when they occur and any activities that exacerbate them. This information can help your doctor make an accurate diagnosis. 🩺
Physical Examination
During the physical examination, your doctor may perform specific tests to assess the function of the median nerve. These tests can include:
- Tinel’s Sign: Tapping over the median nerve at the wrist to see if it produces tingling in the fingers.
- Phalen’s Maneuver: Holding the wrists in a flexed position for about a minute to check for symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests
If the physical examination suggests carpal tunnel syndrome, your doctor may recommend additional tests, such as:
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Measuring the electrical activity of the median nerve to determine if it is functioning properly.
- Ultrasound: Imaging tests can help visualize the median nerve and assess any swelling or abnormalities.
By accurately diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome, healthcare providers can recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery. Early intervention is key to preventing carpal tunnel syndrome from becoming a chronic issue! 🌟
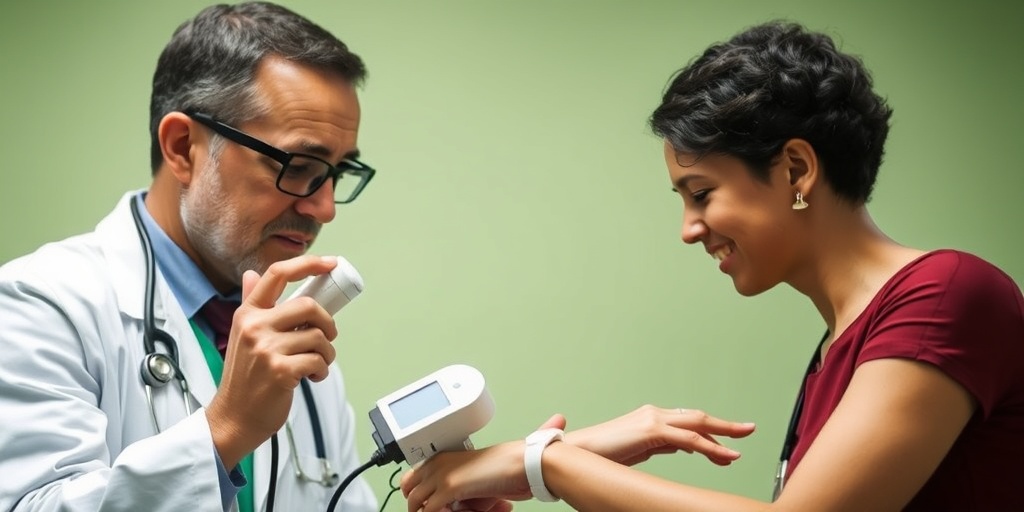
Treatment Options Available
When it comes to preventing carpal tunnel syndrome, understanding the available treatment options is crucial. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist. This can lead to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. Fortunately, there are several treatment options that can help alleviate these symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Many individuals find relief through non-surgical treatments, which are often the first line of defense against carpal tunnel syndrome. Here are some effective options:
- Wrist Splinting: Wearing a wrist splint, especially at night, can help keep the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can strengthen the muscles around the wrist and improve flexibility, which may alleviate symptoms.
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and relieve pressure on the nerve.
Surgical Treatments
If non-surgical treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgical options may be considered. The most common procedure is carpal tunnel release surgery, which involves cutting the ligament that is pressing on the median nerve. This surgery can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques. Recovery times vary, but many patients experience significant relief from symptoms after surgery.
Preventive Measures
In addition to treatment options, it’s essential to adopt preventive measures to avoid the onset of carpal tunnel syndrome. Here are some strategies:
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed. Adjust your chair, keyboard, and mouse to promote a neutral wrist position.
- Regular Breaks: Take frequent breaks during repetitive tasks to stretch and relax your hands and wrists.
- Hand Exercises: Incorporate hand and wrist exercises into your daily routine to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
Home Remedies for Relief
For those seeking natural ways to manage symptoms, several home remedies can provide relief from carpal tunnel syndrome. These remedies can be particularly useful for mild cases or as complementary treatments alongside medical interventions.
Cold and Heat Therapy
Applying cold or heat to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain:
- Cold Packs: Use a cold pack on your wrist for 15-20 minutes to numb the area and reduce swelling.
- Warm Compresses: After the initial inflammation has subsided, applying a warm compress can help relax the muscles and improve blood flow.
Herbal Remedies
Some herbal remedies may also help in managing symptoms:
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric can be consumed in food or taken as a supplement.
- Ginger: Ginger tea or supplements can help reduce inflammation and improve circulation.
Massage Therapy
Gentle massage of the wrist and hand can promote relaxation and improve blood flow. Consider visiting a licensed massage therapist who specializes in treating carpal tunnel syndrome or practicing self-massage techniques at home.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Incorporating mindfulness practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and promote overall well-being. 🧘♀️
By exploring these treatment options and home remedies, individuals can take proactive steps toward preventing carpal tunnel syndrome and managing its symptoms effectively. Remember, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. 🌟

Ergonomic Solutions
When it comes to preventing carpal tunnel syndrome, ergonomics plays a crucial role. By optimizing your workspace and the way you use your hands, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing this painful condition. Here are some effective ergonomic solutions to consider:
1. Proper Desk Setup
Your desk setup can greatly influence your wrist health. Here are some tips:
- Monitor Height: Ensure your monitor is at eye level to avoid straining your neck and wrists.
- Keyboard Position: Keep your keyboard at elbow height, allowing your arms to rest comfortably at your sides.
- Mouse Placement: Position your mouse close to your keyboard to minimize reaching and strain.
2. Use Ergonomic Tools
Investing in ergonomic tools can make a significant difference:
- Ergonomic Keyboards: These keyboards are designed to reduce wrist strain by promoting a more natural hand position.
- Wrist Rests: A soft wrist rest can provide support and help maintain a neutral wrist position while typing.
- Adjustable Chairs: An adjustable chair can help you maintain proper posture, reducing the risk of strain on your wrists.
3. Regular Breaks and Stretching
Even with the best ergonomic setup, it’s essential to take regular breaks:
- Take Short Breaks: Every 30 minutes, take a 5-minute break to stretch and move around.
- Hand and Wrist Exercises: Incorporate simple stretches to relieve tension in your hands and wrists. For example, try wrist flexor and extensor stretches.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
In addition to ergonomic solutions, making certain lifestyle changes can further aid in preventing carpal tunnel syndrome. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can increase pressure on the median nerve in your wrist. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce this risk. Focus on:
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week.
2. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is key to overall health, including joint and nerve function. Make sure to drink enough water throughout the day. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily, and more if you’re active or in a hot environment. 💧
3. Mind Your Posture
Good posture can help prevent strain on your wrists and hands. Here are some tips:
- Sit Up Straight: Keep your back straight and shoulders relaxed while sitting.
- Feet Flat on the Floor: Ensure your feet are flat on the ground or on a footrest.
4. Limit Repetitive Motions
Repetitive motions can lead to strain and injury. To minimize this risk:
- Vary Your Tasks: If your job involves repetitive hand movements, try to switch tasks frequently.
- Use Voice Recognition Software: This can reduce the amount of typing you do, giving your hands a break.
5. Consider Your Activities
Some hobbies and activities can increase your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. If you engage in activities like knitting, playing musical instruments, or gaming, be mindful of:
- Taking Breaks: Regularly pause to stretch and rest your hands.
- Using Proper Technique: Ensure you’re using the correct technique to minimize strain.
By implementing these ergonomic solutions and lifestyle changes, you can take proactive steps toward preventing carpal tunnel syndrome and maintaining your wrist health. Remember, small adjustments can lead to significant improvements! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What are the best practices for preventing carpal tunnel syndrome?
To effectively prevent carpal tunnel syndrome, consider the following practices:
- Maintain proper wrist positioning while typing or using tools.
- Take regular breaks to stretch and rest your hands.
- Use ergonomic equipment, such as keyboards and mouse devices.
- Strengthen your wrist and hand muscles through targeted exercises.
How can I prevent carpal tunnel syndrome after a wrist fracture?
After a wrist fracture, it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s advice. To prevent carpal tunnel syndrome, focus on:
- Rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and flexibility.
- Avoiding repetitive motions that strain the wrist.
- Using wrist supports as recommended by your healthcare provider.
What steps can I take to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome in the workplace?
To avoid carpal tunnel syndrome at work, implement these strategies:
- Adjust your workstation to ensure your wrists are in a neutral position.
- Incorporate ergonomic tools and furniture.
- Schedule regular breaks to stretch and move around.
How can I prevent carpal tunnel syndrome during pregnancy?
Pregnant individuals can take steps to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome by:
- Wearing wrist braces to support the wrist during sleep.
- Limiting repetitive hand movements.
- Practicing gentle wrist and hand exercises.
What are some effective ways to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome while using keyboards?
To prevent carpal tunnel syndrome while typing, consider these tips:
- Keep your wrists straight and your hands slightly elevated.
- Use a padded wrist rest to support your wrists.
- Adjust your chair and desk height for optimal posture.
How can I stop carpal tunnel syndrome from worsening?
If you’re experiencing symptoms, it’s important to act quickly. Here are some ways to stop carpal tunnel syndrome from worsening:
- Seek medical advice for appropriate treatment options.
- Modify activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Engage in physical therapy to strengthen the wrist.
Are there any specific exercises to help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome?
Yes! Incorporating specific exercises can help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome. Some effective exercises include:
- Wrist flexor and extensor stretches.
- Hand and finger stretches.
- Wrist curls with light weights.
Can ergonomic tools really help in preventing carpal tunnel syndrome?
Absolutely! Using ergonomic tools can significantly prevent carpal tunnel syndrome by:
- Reducing strain on your wrists and hands.
- Promoting better posture while working.
- Encouraging natural hand movements.
Is it possible to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome through lifestyle changes?
Yes, making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome. Consider:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on nerves.
- Staying active to improve overall muscle strength.
- Avoiding smoking, which can impair blood flow.




