What Is Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that affects the growth and development of nerve tissues. This condition leads to the formation of tumors on nerves, which can cause a variety of symptoms depending on their location and size. The tumors are usually benign, meaning they are not cancerous, but they can still lead to significant health issues and complications.
Neurofibromatosis is classified into three main types: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2), and Schwannomatosis. Each type has its own unique characteristics and symptoms, but they all share the common feature of tumor formation in the nervous system.
Individuals with neurofibromatosis may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Skin changes: Such as café-au-lait spots, which are light brown patches on the skin.
- Tumors: Neurofibromas can develop on or under the skin, and in some cases, they may affect internal organs.
- Neurological issues: Including learning disabilities, attention deficits, and other cognitive challenges.
- Bone deformities: Such as scoliosis or other skeletal abnormalities.
While neurofibromatosis is a lifelong condition, the severity and symptoms can vary widely from person to person. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for improving quality of life and addressing potential complications.
Neurofibromatosis Types
Understanding the different types of neurofibromatosis is essential for effective management and treatment. Here’s a closer look at the two most common types:
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
Neurofibromatosis Type 1, also known as NF1, is the most prevalent form of the disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 3,000 individuals. It is caused by mutations in the NF1 gene, which is responsible for producing a protein called neurofibromin that helps regulate cell growth.
Common symptoms of NF1 include:
- Café-au-lait spots: These are usually the first visible signs and can appear at birth or during early childhood.
- Neurofibromas: Soft, benign tumors that can develop on or under the skin.
- Freckling: Particularly in the armpits and groin area.
- Learning disabilities: Many individuals with NF1 may experience challenges in school.
While NF1 can lead to various complications, many individuals lead healthy, fulfilling lives with appropriate medical care and support.
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2)
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is less common than NF1, affecting about 1 in 25,000 individuals. It is primarily characterized by the development of bilateral vestibular schwannomas, which are tumors that affect the auditory nerve and can lead to hearing loss.
Key features of NF2 include:
- Bilateral vestibular schwannomas: These tumors can cause hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and balance issues.
- Other tumors: Individuals may also develop meningiomas and ependymomas, which can affect the brain and spinal cord.
- Skin tumors: Similar to NF1, individuals with NF2 may also develop skin tumors, but they are generally less common.
Management of NF2 often involves regular monitoring and surgical intervention when necessary to address tumor growth and associated symptoms.
Schwannomatosis
Schwannomatosis is the rarest form of neurofibromatosis and is characterized by the presence of multiple schwannomas, which are tumors that develop on the peripheral nerves. Unlike NF1 and NF2, schwannomatosis does not typically involve vestibular schwannomas, and individuals may experience chronic pain as a primary symptom.
Diagnosis and treatment for schwannomatosis can be complex, often requiring a multidisciplinary approach to manage symptoms effectively.
In conclusion, neurofibromatosis encompasses a spectrum of genetic disorders that can significantly impact individuals and their families. If you or someone you know is affected by neurofibromatosis, it’s essential to seek guidance from healthcare professionals who specialize in this area. For more information and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI. 🌟
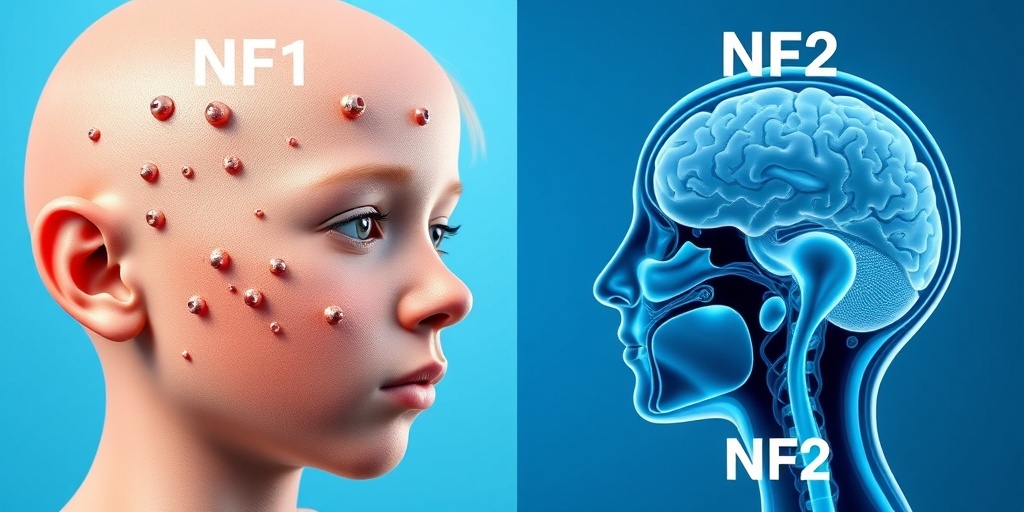
Neurofibromatosis Symptoms
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that affects the growth and development of nerve tissues. It can lead to the formation of tumors on nerves, skin changes, and various other symptoms. Understanding the symptoms of neurofibromatosis is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Here, we will explore the common symptoms associated with this condition.
Common Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
Neurofibromatosis Type 1, also known as NF1, is the most prevalent form of the disorder. The symptoms can vary widely among individuals, but some of the most common include:
- Café-au-lait spots: These are flat, pigmented birthmarks that are light brown in color. They often appear in childhood and can increase in number with age.
- Neurofibromas: These are benign tumors that develop on nerves. They can appear as small bumps on the skin or deeper within the body.
- Freckling: Individuals with NF1 may experience freckling in unusual areas, such as the armpits or groin.
- Optic gliomas: These are tumors that can affect the optic nerve, potentially leading to vision problems.
- Bone deformities: Some individuals may develop scoliosis or other bone abnormalities.
Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2)
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is less common than NF1 and primarily affects the nervous system. The symptoms typically manifest in late adolescence or early adulthood and include:
- Vestibular schwannomas: These are tumors that develop on the vestibular nerve, which can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and balance issues.
- Cataracts: Individuals with NF2 may develop cataracts at a younger age than the general population.
- Skin tumors: Similar to NF1, NF2 can also cause the formation of skin tumors, although they are less common.
Other Possible Symptoms
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, individuals with neurofibromatosis may experience:
- Learning disabilities: Some children with NF1 may face challenges in learning and attention.
- Seizures: Although less common, seizures can occur in some individuals with neurofibromatosis.
- Psychosocial issues: The visible symptoms of neurofibromatosis can lead to emotional and psychological challenges, including anxiety and depression.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely interventions and better management of the condition. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Neurofibromatosis Causes
Neurofibromatosis is primarily caused by genetic mutations. Understanding the underlying causes can help in managing the condition effectively. Let’s delve into the causes of neurofibromatosis and how they affect individuals.
Genetic Mutations
Neurofibromatosis is caused by mutations in specific genes:
- NF1 gene: Located on chromosome 17, mutations in the NF1 gene are responsible for Neurofibromatosis Type 1. This gene is crucial for producing a protein called neurofibromin, which helps regulate cell growth. A mutation can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, resulting in tumors.
- NF2 gene: Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is caused by mutations in the NF2 gene on chromosome 22. This gene produces a protein called merlin, which acts as a tumor suppressor. Mutations can lead to the development of tumors on the nerves.
Inheritance Patterns
Neurofibromatosis is typically inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in their offspring. However, in some cases, neurofibromatosis can occur spontaneously due to new mutations, even if there is no family history of the condition.
Environmental Factors
While neurofibromatosis is primarily genetic, some studies suggest that environmental factors may play a role in the expression of symptoms. Factors such as exposure to radiation or certain chemicals may influence the severity of the condition, although more research is needed in this area.
In conclusion, neurofibromatosis is a complex genetic disorder with a range of symptoms and causes. Understanding these aspects is vital for effective management and support for those affected by this condition. If you suspect you or a loved one may have neurofibromatosis, seeking medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and care. 🩺

Neurofibromatosis Diagnosis
Diagnosing neurofibromatosis can be a complex process, as it often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, family history, and genetic testing. This condition is characterized by the growth of tumors on nerves, and it can manifest in various forms, primarily neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing neurofibromatosis typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation by a healthcare professional. During this evaluation, the doctor will:
- Review the patient’s medical history and family history of neurofibromatosis.
- Conduct a physical examination to check for the presence of characteristic symptoms, such as:
- Café-au-lait spots: Light brown skin patches that are often the first visible sign of NF1.
- Neurofibromas: Soft, benign tumors that can develop on or under the skin.
- Freckling: Unusual freckling in areas such as the armpits or groin.
- Bone deformities: Such as scoliosis or tibial dysplasia.
Genetic Testing
If the clinical evaluation suggests neurofibromatosis, genetic testing may be recommended. This involves:
- Analyzing a blood sample to look for mutations in the NF1 or NF2 genes.
- Confirming the diagnosis, especially in cases where symptoms are not clearly defined.
Genetic counseling is often advised for patients and their families to understand the implications of the diagnosis, including inheritance patterns and potential risks for future generations.
Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans may be utilized to assess the presence and extent of tumors, particularly in the brain and spinal cord. These imaging techniques help in:
- Identifying the size and location of neurofibromas.
- Monitoring for complications, such as the development of malignant tumors.
Neurofibromatosis Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for neurofibromatosis, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. The choice of treatment often depends on the type of neurofibromatosis, the severity of symptoms, and individual patient needs.
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
For many individuals with neurofibromatosis, especially those with mild symptoms, the primary approach may involve regular monitoring. This includes:
- Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider to track any changes in symptoms.
- Periodic imaging studies to monitor the growth of tumors.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms associated with neurofibromatosis. These can include:
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers for discomfort caused by neurofibromas.
- Medication for associated conditions: Such as ADHD or learning disabilities, which are common in individuals with NF1.
Surgical Interventions
For patients with significant symptoms or complications, surgical options may be considered. These include:
- Removal of neurofibromas: Surgery may be performed to remove tumors that cause pain, discomfort, or cosmetic concerns.
- Corrective surgery: For bone deformities or other structural issues related to neurofibromatosis.
Supportive Therapies
In addition to medical treatments, supportive therapies can play a vital role in managing neurofibromatosis. These may include:
- Physical therapy: To improve mobility and strength, especially if there are associated musculoskeletal issues.
- Psychological support: Counseling or support groups to help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of living with neurofibromatosis.
Overall, the treatment plan for neurofibromatosis is highly individualized, and it is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best approach for their specific situation. With proper management, individuals with neurofibromatosis can lead fulfilling lives. 🌟

Living with Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a genetic disorder that affects the growth and development of nerve cell tissues. Living with this condition can present unique challenges, but understanding the types, symptoms, and management strategies can empower individuals and families affected by NF.
Understanding Neurofibromatosis Types
There are three main types of neurofibromatosis: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2), and Schwannomatosis. Each type has distinct characteristics and symptoms:
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1): This is the most common form, characterized by the presence of café-au-lait spots, neurofibromas (benign tumors), and potential complications such as learning disabilities and skeletal abnormalities.
- Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2): NF2 is less common and primarily involves the development of bilateral vestibular schwannomas, which can lead to hearing loss and balance issues.
- Schwannomatosis: This type is characterized by the presence of multiple schwannomas, which are tumors that develop on the nerves, often causing pain and discomfort.
Common Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis
Symptoms can vary widely among individuals with neurofibromatosis. Some common symptoms include:
- Café-au-lait spots: Light brown skin patches that can appear at birth or during childhood.
- Neurofibromas: Soft, benign tumors that can develop on or under the skin.
- Learning disabilities: Many individuals with NF1 may experience challenges in learning and attention.
- Bone deformities: Such as scoliosis or other skeletal abnormalities.
- Hearing loss: Particularly in those with NF2 due to tumors affecting the auditory nerves.
Managing Neurofibromatosis
While there is currently no cure for neurofibromatosis, effective management strategies can help improve quality of life. Here are some approaches:
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the growth of tumors and manage symptoms.
- Symptom Management: Pain management strategies, including medications and physical therapy, can help alleviate discomfort.
- Educational Support: For children with learning disabilities, individualized education plans (IEPs) can provide necessary support in school.
- Genetic Counseling: Families affected by NF may benefit from genetic counseling to understand the inheritance patterns and implications for future generations.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with neurofibromatosis can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to seek support from mental health professionals, support groups, or online communities. Connecting with others who understand the journey can provide comfort and valuable insights. 🌈
Neurofibromatosis Research and Future Directions
Research into neurofibromatosis is ongoing, with scientists and medical professionals striving to better understand the condition and develop new treatment options. Here are some exciting areas of research and future directions:
Genetic Research
Understanding the genetic mutations that cause neurofibromatosis is crucial for developing targeted therapies. Researchers are exploring the specific genes involved in NF1 and NF2, which could lead to innovative treatments that address the root causes of the disorder.
Targeted Therapies
Recent advancements in targeted therapies have shown promise in treating neurofibromatosis. For instance, MEK inhibitors have been studied for their potential to shrink neurofibromas in individuals with NF1. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of these treatments.
Improving Quality of Life
Research is also focused on improving the overall quality of life for individuals with neurofibromatosis. This includes:
- Developing better pain management strategies.
- Enhancing educational resources for children with learning disabilities.
- Creating comprehensive care models that address both physical and emotional health.
Community and Advocacy
Advocacy groups play a vital role in raising awareness about neurofibromatosis and supporting research initiatives. Organizations such as the Neurofibromatosis Network and Children’s Tumor Foundation are dedicated to funding research, providing resources, and connecting families affected by NF. 🤝
As research continues to evolve, there is hope for improved treatments and a better understanding of neurofibromatosis. The future looks promising, with the potential for breakthroughs that could significantly enhance the lives of those living with this condition.

Frequently Asked Questions about Neurofibromatosis
What is Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes tumors to form on nerve tissue. It primarily affects the nervous system, skin, and bones. There are three main types: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2), and Schwannomatosis.
What are the symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1?
Common symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 include:
- Multiple café-au-lait spots (light brown skin patches)
- Neurofibromas (benign tumors on nerves)
- Freckling in the armpits or groin
- Bone deformities
- Learning disabilities
How is Neurofibromatosis treated?
While there is no cure for Neurofibromatosis, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications. This may include:
- Surgical removal of tumors
- Regular monitoring of growths
- Physical therapy for mobility issues
- Medications for pain management
What is the difference between Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Type 2?
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 is more common and typically presents with skin changes and neurofibromas, while Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is characterized by bilateral vestibular schwannomas (tumors on the auditory nerve), leading to hearing loss and balance issues.
Are there any famous people with Neurofibromatosis?
Yes, several individuals have publicly shared their experiences with Neurofibromatosis, raising awareness about the condition. Some notable figures include:
- Actor and comedian Dan Aykroyd
- Author and activist Jesse Jackson
Can lifestyle changes help manage Neurofibromatosis symptoms?
While there is no specific diet for Neurofibromatosis, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall well-being. Some individuals have explored dietary changes, such as the Paleo diet, to see if it helps manage symptoms. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes.
Where can I find support for Neurofibromatosis?
Support groups and organizations dedicated to Neurofibromatosis can provide valuable resources and community connections. Consider reaching out to:
- The Neurofibromatosis Network
- The Children’s Tumor Foundation
Is Neurofibromatosis hereditary?
Yes, Neurofibromatosis is usually inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in their child.
What should I do if I suspect I have Neurofibromatosis?
If you suspect you have Neurofibromatosis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and management plan. Early intervention can help manage symptoms effectively.




