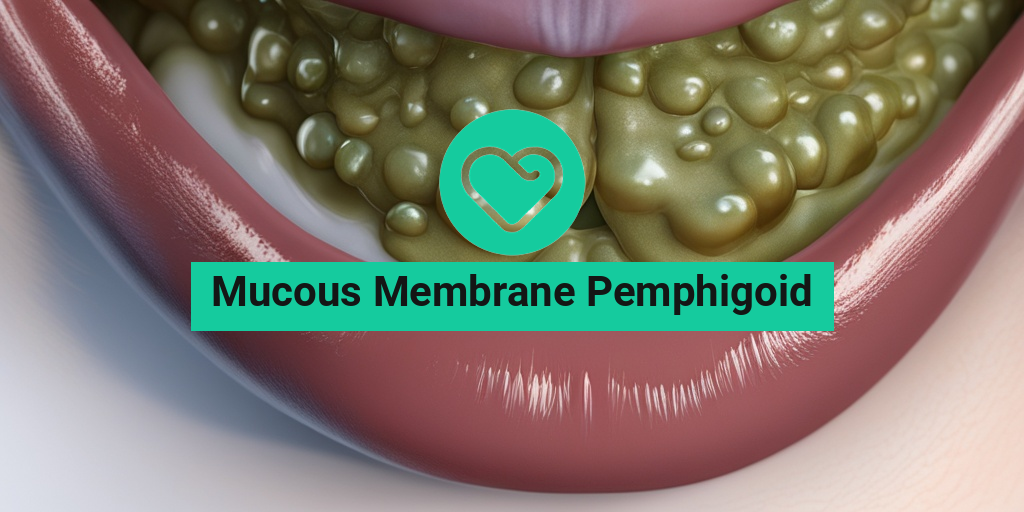
What Is Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the mucous membranes, which are the thin layers of tissue that line various body cavities, such as the mouth, nose, eyes, and genitals. In MMP, the immune system mistakenly attacks the mucous membranes, leading to inflammation and blistering.
What Causes Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
The exact cause of MMP is still unknown, but research suggests that it may be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential triggers include:
- Infections, such as herpes simplex or HIV
- Certain medications, such as blood pressure medications or antibiotics
- Other autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
- Genetic predisposition
It’s essential to note that MMP is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
How Is Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Diagnosed?
Diagnosing MMP can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and conduct various tests, including:
- Blood tests to rule out other autoimmune disorders
- Biopsies of affected tissue to examine the skin and mucous membranes
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, to rule out other conditions
If you’re experiencing symptoms of MMP, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Symptoms
The symptoms of MMP can vary in severity and location, but common signs include:
Oral Symptoms
Many people with MMP experience oral symptoms, such as:
- Blisters or sores on the lips, tongue, or inside the mouth
- Painful eating or swallowing
- Dry mouth or altered taste
Ocular Symptoms
MMP can also affect the eyes, leading to:
- Redness, itching, or burning sensations in the eyes
- Discharge or crusting around the eyes
- Vision problems or sensitivity to light
Genital and Skin Symptoms
In some cases, MMP can affect the genital area, causing:
- Blisters or sores on the genitals or anus
- Painful urination or sexual intercourse
- Itching or burning sensations in the genital area
MMP can also cause skin symptoms, such as:
- Blisters or rashes on the skin
- Itching or burning sensations on the skin
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, MMP is a rare condition, and an accurate diagnosis can only be made by a qualified healthcare professional.
For more information on MMP and other health topics, consider consulting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. 🏥
Causes and Risk Factors of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the mucous membranes, which are the thin layers of tissue that line various body cavities, such as the mouth, nose, eyes, and genitals. While the exact causes of MMP are still not fully understood, research has identified several risk factors that may contribute to its development.
Autoimmune Response
The primary cause of MMP is an abnormal autoimmune response, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the mucous membranes, leading to inflammation and blistering. In people with MMP, the immune system produces antibodies that target the proteins that hold the mucous membranes together, causing them to separate and form blisters.
Genetic Predisposition
Research suggests that genetic factors may play a role in the development of MMP. People with a family history of autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, may be more likely to develop MMP.
Age and Gender
MMP typically affects older adults, with most cases diagnosed in people over the age of 60. Women are more likely to develop MMP than men, and the disorder is more common in people of European descent.
Environmental Triggers
Certain environmental factors, such as infections, injuries, or exposure to toxins, may trigger the onset of MMP in susceptible individuals. For example, some people may develop MMP after a viral or bacterial infection, while others may experience symptoms after exposure to certain chemicals or medications.
Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disease, may increase the risk of developing MMP. Additionally, people with a history of cancer, particularly lymphoma, may be more likely to develop MMP.
Diagnosing Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Diagnosing MMP can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions, such as oral lichen planus or pemphigus vulgaris. A diagnosis of MMP typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and biopsy.
Clinical Evaluation
A healthcare provider will typically begin by performing a thorough clinical evaluation, which includes a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. They will look for signs of blistering or scarring on the mucous membranes, as well as any other symptoms, such as oral ulcers, conjunctivitis, or genital lesions.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and skin biopsies, may be ordered to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis of MMP. These tests can help identify the presence of antibodies against the mucous membranes and detect any underlying autoimmune disorders.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from the affected area for examination under a microscope. This can help confirm the diagnosis of MMP and rule out other conditions, such as cancer or infection.
Early diagnosis and treatment of MMP are essential to prevent complications and improve outcomes. If you suspect you or a loved one may have MMP, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. 🏥

Treatment Options for Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the mucous membranes, causing blisters and sores on the skin and mucous membranes. While there is no cure for MMP, various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and prevent complications. In this section, we’ll explore the different treatment options for MMP.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the first line of treatment for MMP. These creams or ointments are applied directly to the affected areas to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. Mild to moderate cases of MMP can be effectively managed with topical corticosteroids. However, in more severe cases, oral corticosteroids may be necessary.
Immunosuppressive Medications
Immunosuppressive medications, such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide, are used to suppress the immune system and prevent it from attacking the mucous membranes. These medications are often prescribed in combination with corticosteroids to reduce the risk of side effects.
Rituximab
Rituximab is a biologic medication that targets the immune cells responsible for causing MMP. It has been shown to be effective in treating MMP, especially in cases that are resistant to other treatments.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
IVIG is a treatment that involves infusing antibodies into the bloodstream to help reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the mucous membranes. It is often used in combination with other treatments to manage MMP.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat MMP. For example, in cases where the disease affects the eyes, surgical procedures may be necessary to prevent vision loss.
Managing Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid Flares
MMP flares can be unpredictable and stressful, but there are ways to manage them effectively. Here are some tips to help you cope with MMP flares:
Identify Triggers
Identifying triggers that can cause MMP flares is crucial in managing the disease. Common triggers include stress, hormonal changes, and certain medications. Keeping a symptom journal can help you track your symptoms and identify patterns.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential in managing MMP flares. Brushing and flossing regularly can help prevent oral lesions and reduce the risk of infections. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and a gentle mouthwash can also help reduce irritation.
Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is essential in managing MMP flares. Drinking plenty of water can help thin out mucus and reduce the risk of dehydration. Avoiding spicy or acidic foods can also help reduce irritation.
Get Enough Rest
Getting enough rest is crucial in managing MMP flares. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night and take regular breaks throughout the day to reduce stress and fatigue.
Seek Support
Living with MMP can be challenging, but seeking support from family, friends, and support groups can make a big difference. Sharing your experiences and connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can help you feel less isolated and more empowered to manage your condition.
Remember, managing MMP requires a comprehensive approach that involves working closely with your healthcare provider, practicing good self-care, and staying informed about the latest treatment options. By taking control of your condition, you can reduce the frequency and severity of flares and improve your overall quality of life. 💊

Complications of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the mucous membranes, leading to blistering and scarring. While the condition itself can be challenging to manage, it’s essential to be aware of the potential complications that can arise if left untreated or poorly managed.
Eye Complications
One of the most significant concerns with MMP is the risk of eye complications. The condition can cause scarring on the conjunctiva, leading to dry eye syndrome, which can further increase the risk of corneal ulcers and vision loss. In severe cases, MMP can even lead to blindness. It’s crucial to work closely with an ophthalmologist to monitor eye health and address any issues promptly.
Oral Complications
MMP can also affect the oral mucosa, leading to painful blisters and ulcers. These lesions can make eating and speaking difficult, and in severe cases, can lead to malnutrition and dehydration. Additionally, the constant inflammation can increase the risk of oral infections, which can spread to other parts of the body.
Respiratory Complications
In some cases, MMP can affect the respiratory tract, leading to bronchial stenosis, a narrowing of the airways that can cause breathing difficulties. This can increase the risk of respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, which can be life-threatening.
Other Complications
Other potential complications of MMP include:
- Genital lesions, which can lead to painful urination and sexual dysfunction
- Esophageal involvement, which can cause difficulty swallowing and lead to malnutrition
- Intestinal involvement, which can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and malabsorption
It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare team to monitor for these complications and address them promptly to prevent long-term damage.
Living with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
While MMP can be a challenging condition to live with, there are ways to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some tips for living with MMP:
Work with a Healthcare Team
Collaborating with a healthcare team, including a dermatologist, ophthalmologist, and other specialists, is crucial for managing MMP. They can help develop a personalized treatment plan and monitor for any complications.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is essential for managing MMP. This includes:
- Brushing teeth gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Avoiding spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the mouth
- Rinsing with saltwater or a mild mouthwash to reduce inflammation
Additionally, using a humidifier can help soothe dry mouth and reduce the risk of oral infections.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for managing MMP. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day to help keep the mucous membranes hydrated and reduce the risk of dehydration.
By being aware of the potential complications of MMP and taking steps to manage the condition, it’s possible to improve quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term damage. 💊

Frequently Asked Questions about Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
What is Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
Mucous membrane pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the mucous membranes, which are the thin layers of tissue that line the inside of the mouth, nose, throat, and other organs.
What are the symptoms of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
The symptoms of mucous membrane pemphigoid can vary depending on the location and severity of the disease. Common symptoms include:
- Blisters or sores on the mucous membranes
- Pain or discomfort in the affected areas
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membranes
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Eye problems, such as conjunctivitis or dry eyes
How is Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid diagnosed?
Mucous membrane pemphigoid is typically diagnosed through a combination of:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Biopsy of the affected tissue
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans
- Lab tests, such as blood tests or skin tests
What is the treatment for Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
Treatment for mucous membrane pemphigoid usually involves a combination of:
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Immunosuppressive medications to suppress the immune system
- Pain relief medications to manage discomfort
- Topical treatments, such as creams or ointments, to soothe the affected areas
What is the life expectancy of someone with Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
The life expectancy of someone with mucous membrane pemphigoid is generally good, but it can vary depending on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With proper treatment, most people with mucous membrane pemphigoid can lead active and normal lives.
How does Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid differ from Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Mucous membrane pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris are both autoimmune disorders that affect the skin and mucous membranes, but they have some key differences:
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid primarily affects the mucous membranes, while pemphigus vulgaris affects the skin and mucous membranes.
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid tends to be less severe than pemphigus vulgaris.
Is there a specific diet for Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
While there is no specific diet for mucous membrane pemphigoid, a healthy and balanced diet can help manage the symptoms of the disease. It’s recommended to:
- Avoid spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the mucous membranes
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
What is the ICD-10 code for Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
The ICD-10 code for mucous membrane pemphigoid is L12.0.
What are the oral manifestations of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
The oral manifestations of mucous membrane pemphigoid can include:
- Blisters or sores on the lips, tongue, or inside the mouth
- Pain or discomfort when eating or speaking
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
Can Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid be cured?
While there is no cure for mucous membrane pemphigoid, treatment can help manage the symptoms and prevent complications. With proper treatment, many people with mucous membrane pemphigoid can lead active and normal lives. 💊