What Is Impetigo?
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects infants and young children, although it can occur in individuals of any age. This bacterial infection is most commonly caused by two types of bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Impetigo is characterized by the formation of red sores or blisters, which can quickly rupture, ooze, and form a yellowish crust. Understanding impetigo is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
How Does Impetigo Spread?
Impetigo spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. It can also spread through:
- Scratches or cuts: Bacteria can enter the skin through minor injuries.
- Shared items: Towels, clothing, or bedding can harbor the bacteria.
- Close contact: Children in daycare or school settings are particularly at risk due to close interactions.
Because of its contagious nature, it’s essential to take precautions to prevent the spread of impetigo, especially in communal environments. 🏫
Impetigo Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of impetigo is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can vary depending on the type of impetigo, but common signs include:
Common Symptoms
- Red sores: These typically appear around the nose and mouth but can occur anywhere on the body.
- Blisters: The sores may develop into fluid-filled blisters that can burst.
- Crust formation: After the blisters burst, they often ooze and form a honey-colored crust.
- Itching or discomfort: The affected area may be itchy or painful, leading to scratching and further spread of the infection.
Types of Impetigo
There are two main types of impetigo:
- Non-bullous impetigo: This is the most common form, characterized by small red sores that quickly rupture and crust over.
- Bullous impetigo: This type features larger blisters filled with fluid, which can be more severe and may occur on other parts of the body.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you or your child exhibits symptoms of impetigo, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Early treatment can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others. Signs that warrant immediate medical attention include:
- Worsening symptoms despite home care
- Fever or other systemic symptoms
- Signs of infection spreading, such as increased redness or swelling
For more detailed information on impetigo and its treatment options, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. 🩺
In conclusion, understanding what impetigo is and recognizing its symptoms can help in managing this common skin infection effectively. With prompt treatment and proper hygiene practices, you can minimize the impact of impetigo and protect yourself and others from its spread. 🌟
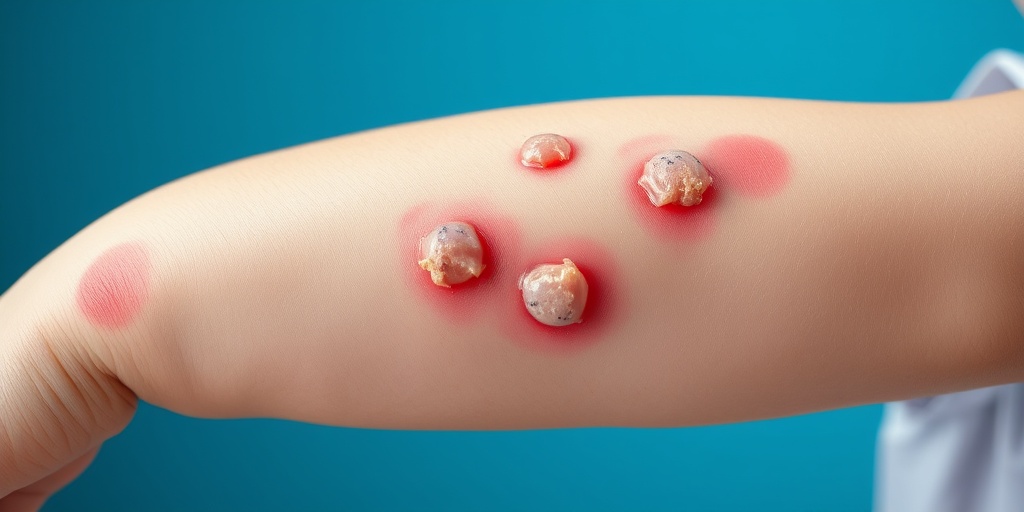
Types of Impetigo
Impetigo is a common and highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects infants and young children, although it can occur in individuals of any age. Understanding the different types of impetigo is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. There are two main types of impetigo:
1. Non-Bullous Impetigo
Non-bullous impetigo is the most prevalent form of the infection. It typically begins as small red spots that quickly develop into blisters. These blisters then burst, leaving behind a characteristic honey-colored crust. This type of impetigo is often caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria.
- Symptoms: Red sores, blisters, and honey-colored crusts.
- Common Locations: Face, especially around the nose and mouth, as well as on the hands and arms.
- Contagiousness: Highly contagious, spreading through direct contact with sores or contaminated objects.
2. Bullous Impetigo
Bullous impetigo is less common but can be more severe. It is characterized by larger blisters filled with clear fluid that can easily rupture. This type is primarily caused by Staphylococcus aureus and is often associated with a more systemic infection.
- Symptoms: Larger blisters, often on the trunk and extremities, that can be painful.
- Common Locations: Trunk, arms, and legs.
- Contagiousness: Also highly contagious, particularly in crowded settings like schools or daycare centers.
Both types of impetigo can lead to complications if left untreated, including deeper skin infections or scarring. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment is essential. 🩺
Causes of Impetigo
Understanding the causes of impetigo is vital for prevention and management. Impetigo is primarily caused by bacteria that invade the skin, often through breaks or cuts. Here are the main factors contributing to the development of this infection:
1. Bacterial Infection
The primary culprits behind impetigo are two types of bacteria:
- Staphylococcus aureus: This bacterium is responsible for many skin infections, including impetigo. It can thrive in warm, moist environments, making it particularly dangerous in crowded settings.
- Streptococcus pyogenes: Known for causing strep throat, this bacterium can also lead to impetigo, especially in children.
2. Skin Breaks
Impetigo often occurs when bacteria enter the skin through:
- Cuts or Scrapes: Minor injuries can provide an entry point for bacteria.
- Insect Bites: Bites can lead to breaks in the skin, making it easier for bacteria to invade.
- Rashes: Conditions like eczema can compromise the skin barrier, increasing the risk of infection.
3. Contagion
Impetigo is highly contagious and can spread through:
- Direct Contact: Touching an infected person or their belongings can transmit the bacteria.
- Shared Items: Towels, clothing, and bedding can harbor bacteria, facilitating the spread of impetigo.
- Crowded Environments: Schools and daycare centers are common places for outbreaks due to close contact among children.
4. Environmental Factors
Certain environmental conditions can increase the risk of developing impetigo:
- Warm Weather: Bacteria thrive in warm, humid conditions, making summer months more prone to outbreaks.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate handwashing and personal hygiene can contribute to the spread of bacteria.
By understanding the causes of impetigo, individuals can take proactive measures to reduce their risk of infection. Maintaining good hygiene, treating skin injuries promptly, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are essential steps in prevention. 🧼✨

Risk Factors for Impetigo
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects children but can also occur in adults. Understanding the risk factors associated with impetigo is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Here are some key factors that can increase the likelihood of developing this infection:
Age
Children aged 2 to 6 years are particularly susceptible to impetigo. Their developing immune systems and tendency to engage in close contact with other children make them prime candidates for this infection. However, adults can also contract impetigo, especially if they have compromised immune systems.
Skin Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, are at a higher risk of developing impetigo. These conditions can create breaks in the skin, providing an entry point for bacteria. Maintaining healthy skin is essential to reduce the risk of infection.
Close Contact
Impetigo spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. Children in daycare or school settings are particularly vulnerable due to close interactions with peers. Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can help mitigate this risk.
Environmental Factors
Living in crowded conditions or areas with poor sanitation can increase the risk of impetigo. Bacteria thrive in environments where hygiene practices are lacking. Ensuring a clean living space and promoting hygiene can significantly reduce the chances of infection.
Weather Conditions
Hot, humid weather can create an ideal environment for bacteria to flourish. During these conditions, the skin may become more susceptible to infections. It’s essential to keep the skin clean and dry, especially in warmer climates.
Injury to the Skin
Any break in the skin, whether from cuts, insect bites, or abrasions, can serve as an entry point for bacteria. Individuals who engage in activities that may lead to skin injuries should take extra precautions to protect their skin and prevent infections.
Impetigo Diagnosis
Diagnosing impetigo typically involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. Here’s what you can expect during the diagnostic process:
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing impetigo is a physical examination of the affected skin. A doctor will look for characteristic symptoms, such as:
- Red sores or blisters: These may ooze and form a honey-colored crust.
- Itching or discomfort: The affected area may be itchy or painful.
- Location: Impetigo commonly appears on the face, especially around the nose and mouth, but can occur anywhere on the body.
Medical History
In addition to a physical examination, the healthcare provider will ask about the patient’s medical history. This includes:
- Any recent skin injuries or conditions.
- Exposure to others with impetigo or similar infections.
- Current symptoms and their duration.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, a doctor may perform laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis. This could involve:
- Swabbing the sores: A sample may be taken from the infected area to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Blood tests: While not commonly needed for impetigo, blood tests may be conducted if there are concerns about a more serious infection.
Distinguishing from Other Conditions
It’s important to differentiate impetigo from other skin conditions that may present similar symptoms, such as:
- Herpes simplex: This viral infection can cause sores that may resemble impetigo.
- Fungal infections: Conditions like ringworm can also mimic the appearance of impetigo.
By accurately diagnosing impetigo, healthcare providers can recommend the most effective treatment options, ensuring a swift recovery and minimizing the risk of spreading the infection to others. 🩺

Impetigo Treatment Options
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects infants and young children, although it can occur in individuals of any age. If you or your child has been diagnosed with this condition, understanding the treatment options available is crucial for effective recovery. Here, we’ll explore various treatment methods, including topical and oral medications, as well as home care strategies.
Topical Antibiotics
For mild cases of impetigo, topical antibiotics are often the first line of treatment. These medications are applied directly to the affected area and can help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Common topical antibiotics include:
- Mupirocin (Bactroban): This is a popular choice for treating localized impetigo.
- Retapamulin (Altabax): Another effective topical option for mild infections.
It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding the application frequency and duration of treatment to ensure the best results.
Oral Antibiotics
In cases where the infection is more widespread or if the patient has a weakened immune system, oral antibiotics may be necessary. These medications work systemically to combat the infection from within. Common oral antibiotics prescribed for impetigo include:
- Cephalexin (Keflex): Often used for more severe cases.
- Dicloxacillin: Another effective option for treating impetigo.
- Clindamycin: This may be prescribed for patients allergic to penicillin.
As with topical treatments, it’s crucial to complete the entire course of oral antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Home Care Strategies
In addition to medical treatments, several home care strategies can help manage symptoms and promote healing:
- Keep the area clean: Gently wash the affected skin with soap and water to remove crusts and prevent further infection.
- Avoid scratching: This can spread the infection to other areas of the body or to other people.
- Cover the sores: Use a clean bandage to protect the sores and prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Practice good hygiene: Regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with others can help prevent transmission.
By combining medical treatments with effective home care, you can help ensure a swift recovery from impetigo. 🩹
Preventing Impetigo
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to a highly contagious condition like impetigo. Understanding how to minimize the risk of infection can protect not only you but also those around you. Here are some effective strategies for preventing impetigo.
Practice Good Hygiene
One of the most effective ways to prevent impetigo is through good hygiene practices. This includes:
- Regular handwashing: Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Keep nails trimmed: Short nails reduce the risk of scratching and spreading bacteria.
- Shower after sports: If your child participates in sports, ensure they shower immediately afterward to remove sweat and bacteria.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items
Impetigo can spread through direct contact or by sharing personal items. To minimize the risk:
- Do not share towels, clothing, or bedding: These items can harbor bacteria.
- Use separate personal items: Encourage family members to have their own toiletries and grooming tools.
Keep Skin Healthy
Maintaining healthy skin can also help prevent impetigo. Here are some tips:
- Moisturize: Keep skin hydrated to prevent cracks and breaks that can allow bacteria to enter.
- Treat cuts and scrapes promptly: Clean and cover any wounds to reduce the risk of infection.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of impetigo and keep your family healthy. Remember, awareness and proactive care are key! 🛡️

Frequently Asked Questions about Impetigo
What is Impetigo?
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection that primarily affects infants and young children, although it can occur in individuals of any age. It is characterized by red sores or blisters that can rupture, ooze, and form a yellowish crust.
How is Impetigo Spread?
Impetigo contagiosa spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. It can also spread through shared items like towels or clothing.
What are the Symptoms of Impetigo?
- Red sores or blisters, often around the nose and mouth
- Itching and discomfort
- Yellowish crust that forms over the sores
- Swollen lymph nodes in some cases
How is Impetigo Treated?
Treatment for impetigo typically involves:
- Topical antibiotics for mild cases
- Oral antibiotics for more severe infections
- Keeping the affected area clean and covered
Is Impetigo Contagious?
Yes, impetigo is highly contagious. It can spread through skin-to-skin contact or by touching items that have come into contact with the infection. It is important to practice good hygiene to prevent its spread.
Can Impetigo Be Prevented?
To help prevent impetigo, consider the following tips:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water
- Avoid sharing personal items
- Keep cuts and scrapes clean and covered
What Does Impetigo Look Like?
Images of impetigo typically show red sores that may ooze and develop a honey-colored crust. If you suspect you or your child has impetigo, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Is There a Specific Meaning for Impetigo?
The term impetigo comes from the Latin word “impetere,” which means “to attack.” This reflects the aggressive nature of the infection and its rapid spread among individuals.
What Should I Do If I Suspect Impetigo?
If you suspect that you or your child has impetigo, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. Early treatment can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others. 🩺




