What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that primarily affects individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at an accelerated rate, leading to the production of ketones, which are acids that can accumulate in the bloodstream. This process typically happens when there is not enough insulin available to help glucose enter the cells for energy, causing the body to seek alternative energy sources.
In simpler terms, DKA is a metabolic state that arises when the body cannot utilize glucose effectively due to a lack of insulin. As a result, the body begins to burn fat for fuel, leading to an increase in ketone levels. If left untreated, DKA can lead to severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and even coma or death.
How Does DKA Occur?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) occurs when the body experiences a significant shortage of insulin. This can happen due to various reasons, including:
- Missed Insulin Doses: Skipping insulin injections or not taking enough insulin can trigger DKA.
- Illness or Infection: Physical stress from illness or infection can increase insulin requirements.
- Undiagnosed Diabetes: In some cases, DKA is the first sign of type 1 diabetes in individuals who have not yet been diagnosed.
- Insulin Pump Failure: Issues with insulin delivery systems can lead to insufficient insulin levels.
Understanding the underlying causes of DKA is crucial for prevention and management. If you or someone you know is at risk, it’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and seek medical advice when necessary.
DKA Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is vital for prompt treatment. Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. The symptoms of DKA can develop quickly, often within 24 hours, and may include:
Common Symptoms of DKA
- Excessive Thirst: Increased thirst is often one of the first signs, as the body attempts to combat dehydration.
- Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels lead to increased urination, which can further contribute to dehydration.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many individuals experience gastrointestinal distress, which can complicate the situation.
- Abdominal Pain: This can be a significant symptom, often mistaken for other conditions.
- Weakness or Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness can occur as the body struggles to function without adequate insulin.
- Rapid Breathing: As the body tries to compensate for the acidosis, breathing may become faster and deeper.
- Fruity-Scented Breath: The presence of ketones can give the breath a distinctive fruity odor.
- Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating: High levels of ketones can affect cognitive function.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of DKA, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment, typically involving intravenous fluids, insulin therapy, and electrolyte replacement. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to severe complications, including coma or death.
For more information on managing diabetes and understanding conditions like DKA, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, being aware of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) and its symptoms can save lives. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adhering to prescribed insulin regimens, and understanding the signs of DKA are essential steps in managing diabetes effectively. Stay informed and proactive about your health! 💙

DKA Causes and Risk Factors
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that primarily affects individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with DKA is crucial for prevention and timely intervention.
What Causes Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
DKA occurs when the body starts breaking down fats at an accelerated rate, leading to the production of ketones. This process typically happens when there is insufficient insulin in the body. Here are some common causes of DKA:
- Insulin Deficiency: The most significant cause of DKA is a lack of insulin. This can occur due to missed insulin doses, inadequate insulin therapy, or an increase in insulin resistance.
- Infection: Infections, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections, can increase the body’s demand for insulin, leading to DKA.
- Illness or Stress: Physical stress from illness or surgery can trigger DKA by raising blood sugar levels and increasing insulin requirements.
- Uncontrolled Blood Sugar Levels: Poorly managed diabetes, characterized by consistently high blood sugar levels, can lead to DKA.
- Substance Abuse: The use of drugs, particularly cocaine or alcohol, can disrupt normal metabolic processes and lead to DKA.
Risk Factors for Developing DKA
While anyone with diabetes can develop DKA, certain factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing this condition:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Individuals with type 1 diabetes are at a higher risk for DKA compared to those with type 2 diabetes.
- Young Age: Children and adolescents with diabetes are more susceptible to DKA, especially during growth spurts.
- Inadequate Education: Lack of knowledge about diabetes management and the importance of insulin therapy can lead to DKA.
- Previous DKA Episodes: A history of DKA increases the risk of future episodes, highlighting the need for vigilant management.
- Emotional Stress: Psychological factors, such as depression or anxiety, can affect diabetes management and increase the risk of DKA.
DKA Diagnosis
Diagnosing Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is essential for prompt treatment and recovery. The diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests.
Clinical Symptoms of DKA
Healthcare providers often begin the diagnosis of DKA by assessing the patient’s symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Excessive Thirst: Patients may experience extreme thirst due to dehydration.
- Frequent Urination: Increased urination is a result of high blood sugar levels.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms are common in DKA.
- Abdominal Pain: Many patients report abdominal discomfort.
- Fruity-Scented Breath: The presence of ketones can cause a distinctive fruity odor in the breath.
- Confusion or Altered Mental State: Severe cases may lead to confusion or loss of consciousness.
Laboratory Tests for DKA Diagnosis
In addition to clinical symptoms, laboratory tests are crucial for confirming a diagnosis of DKA. Key tests include:
- Blood Glucose Level: A blood glucose level greater than 250 mg/dL is indicative of DKA.
- Ketone Levels: Elevated levels of ketones in the blood or urine confirm the presence of ketoacidosis.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: This test assesses the acidity of the blood, with a pH level below 7.3 indicating acidosis.
- Electrolyte Levels: DKA can cause imbalances in electrolytes, particularly potassium, which must be monitored closely.
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process for DKA can empower individuals with diabetes and their caregivers to act swiftly in case of an emergency. Early detection and treatment are vital for preventing complications and ensuring a better outcome. 🩺

DKA Treatment Options
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the treatment options available can be crucial for managing this life-threatening situation effectively. Here, we’ll explore the primary treatment strategies used to address DKA.
1. Fluid Replacement
One of the first steps in treating DKA is fluid replacement. Patients often experience dehydration due to high blood sugar levels and the loss of fluids through urination. Administering intravenous (IV) fluids helps to:
- Restore hydration
- Dilute excess glucose in the bloodstream
- Support kidney function
Typically, isotonic saline solutions are used initially, and the rate of fluid administration is adjusted based on the patient’s needs and response to treatment.
2. Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is another critical component in the treatment of DKA. Insulin helps to:
- Lower blood glucose levels
- Stop the production of ketones
- Facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells
Insulin is usually administered through an IV drip, allowing for precise control over blood sugar levels. The dosage may be adjusted based on frequent blood glucose monitoring.
3. Electrolyte Management
During DKA, electrolyte imbalances can occur, particularly with potassium levels. Electrolyte management is essential to prevent complications such as cardiac arrhythmias. Healthcare providers will monitor:
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Chloride
Supplementation may be necessary to restore normal levels, especially as insulin therapy can cause potassium levels to drop.
4. Addressing Underlying Causes
Identifying and treating the underlying cause of DKA is vital for preventing recurrence. Common triggers include:
- Infection
- Insulin omission
- Illness or stress
Once the underlying issue is addressed, the risk of future DKA episodes can be significantly reduced.
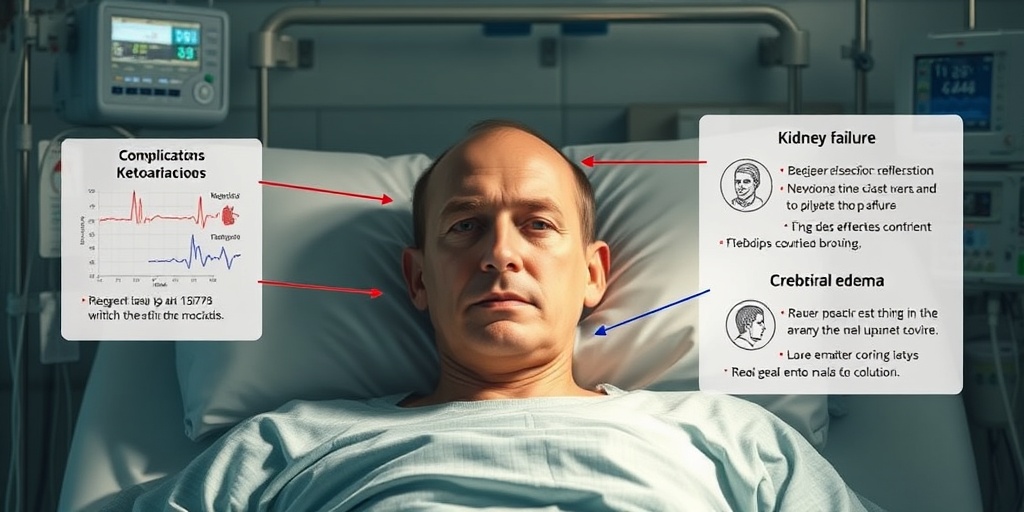
DKA Complications
While prompt treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) can save lives, it’s essential to be aware of potential complications that may arise during or after treatment. Understanding these complications can help in early detection and management.
1. Cerebral Edema
Cerebral edema, or swelling of the brain, is a rare but serious complication of DKA, particularly in children. Symptoms may include:
- Headache
- Confusion
- Seizures
This condition requires immediate medical intervention, as it can lead to long-term neurological damage.
2. Hypoglycemia
As insulin therapy is initiated, there is a risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This can occur if insulin is administered too aggressively or if the patient does not consume enough carbohydrates. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Confusion
Monitoring blood sugar levels closely during treatment is crucial to prevent this complication.
3. Acute Kidney Injury
DKA can lead to acute kidney injury due to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Symptoms may include:
- Decreased urine output
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Fatigue
Maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance during treatment is essential to protect kidney function.
4. Infection
Patients with DKA are at an increased risk of infections, particularly if they have underlying conditions such as diabetes. Common infections include:
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections
- Skin infections
Monitoring for signs of infection and initiating appropriate treatment is vital for recovery.
In conclusion, understanding the treatment options and potential complications associated with Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is essential for effective management and prevention of this serious condition. Early intervention and comprehensive care can significantly improve outcomes for individuals experiencing DKA. 🌟
DKA Prevention Strategies
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can arise in individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes. Understanding how to prevent DKA is crucial for maintaining health and well-being. Here are some effective strategies to help you avoid this potentially life-threatening condition.
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
One of the most important steps in preventing DKA is to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. Keeping track of your glucose levels helps you identify any significant fluctuations that could lead to DKA. Aim to check your blood sugar at least four times a day, or more frequently if you are feeling unwell or are experiencing stress.
2. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can exacerbate the risk of DKA. Ensure you are drinking enough fluids throughout the day, especially water. If you are ill or experiencing high blood sugar levels, increase your fluid intake to help flush out excess glucose and prevent dehydration.
3. Understand the Symptoms of DKA
Being aware of the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can help you act quickly if you notice any warning signs. Common symptoms include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness or fatigue
- Fruity-smelling breath
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
4. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels and increase the risk of DKA. Implementing stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help you maintain stable glucose levels. Finding healthy outlets for stress is vital for overall well-being.
5. Follow Your Diabetes Management Plan
Adhering to your prescribed diabetes management plan is crucial in preventing DKA. This includes taking medications as directed, following a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity. Consult with your healthcare provider to ensure your plan is tailored to your needs.
6. Be Cautious During Illness
Illness can trigger DKA, especially if it leads to elevated blood sugar levels. If you become sick, monitor your blood sugar more frequently and stay in touch with your healthcare provider. They may recommend adjustments to your insulin regimen or other treatments to help manage your condition during illness.
Living with DKA
Living with the risk of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) can be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some insights into managing life with DKA.
1. Educate Yourself and Others
Knowledge is power when it comes to managing diabetes and preventing DKA. Educate yourself about the condition, its symptoms, and treatment options. Additionally, inform your family and friends about DKA so they can recognize the signs and assist you in an emergency.
2. Create a Support Network
Having a strong support network can make a significant difference in managing diabetes and preventing DKA. Connect with other individuals living with diabetes through support groups or online forums. Sharing experiences and tips can provide emotional support and practical advice.
3. Regular Check-Ups with Healthcare Providers
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your diabetes management and preventing complications like DKA. Discuss any concerns you have and ensure your treatment plan is up to date. Your provider can help you adjust your plan as needed based on your lifestyle and health changes.
4. Keep Emergency Supplies Handy
In case of a DKA episode, it’s wise to have emergency supplies readily available. This includes:
- Insulin
- Glucose monitoring supplies
- Hydration solutions
- Emergency contact information
Being prepared can help you respond quickly if symptoms arise.
5. Focus on a Balanced Lifestyle
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing DKA. This includes:
- Eating a nutritious diet rich in whole foods
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Getting adequate sleep
These factors contribute to overall health and can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Living with the risk of DKA requires vigilance and proactive management. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk and lead a healthier, more fulfilling life. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones due to a lack of insulin. This condition can lead to a dangerous buildup of acids in the blood, requiring immediate medical attention.
What are the symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Common symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) include:
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Weakness or fatigue
- Fruity-scented breath
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
What causes Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) occurs when the body does not have enough insulin to allow glucose to enter cells for energy. This can happen due to various factors, including:
- Infection or illness
- Missed insulin doses
- Severe dehydration
- Stress or trauma
How is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) treated?
Treatment for Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) typically involves:
- Administering insulin to lower blood sugar levels
- Rehydration with intravenous fluids
- Electrolyte replacement to restore balance
It is crucial to seek medical help immediately if DKA is suspected.
Can Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) occur in pets?
Yes, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) can also occur in dogs and cats. Symptoms in pets may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, lethargy, and vomiting. If you suspect your pet is experiencing DKA, consult a veterinarian promptly.
What should I do if I suspect DKA?
If you or someone you know is showing signs of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), it is essential to seek emergency medical care immediately. Early intervention can prevent severe complications and improve outcomes.
How can I prevent Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
To help prevent Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), consider the following tips:
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly
- Take insulin as prescribed
- Stay hydrated
- Manage stress and illness effectively
Is DKA reversible?
Yes, with prompt treatment, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is reversible. However, it is crucial to address the underlying causes and manage diabetes effectively to prevent future episodes.