What Is Blood Transfusion?
A blood transfusion is a medical procedure that involves transferring blood or blood components from one person (the donor) to another (the recipient). This process is crucial in various medical situations, such as surgeries, trauma care, and the treatment of certain medical conditions like anemia. The primary goal of a blood transfusion is to restore the recipient’s blood volume, improve oxygen delivery to tissues, and enhance overall health.
Blood transfusions can be life-saving, especially in emergencies where rapid blood loss occurs. They are also used to treat patients with chronic conditions that affect blood production, such as leukemia or sickle cell disease. Understanding the meaning and significance of blood transfusions can help demystify the process and alleviate any concerns patients may have.
Why Are Blood Transfusions Necessary?
Blood transfusions are necessary for several reasons:
- Trauma and Surgery: In cases of severe injury or during major surgeries, patients may lose significant amounts of blood, necessitating a transfusion to stabilize their condition.
- Anemia Treatment: Patients suffering from anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells, may require transfusions to increase their red blood cell count and improve oxygen delivery.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like hemophilia or thalassemia may require regular transfusions to manage symptoms and maintain health.
Types of Blood Transfusions
There are several types of blood transfusions, each tailored to meet specific medical needs. Understanding these types can help patients and their families make informed decisions regarding treatment options.
1. Whole Blood Transfusion
A whole blood transfusion involves the transfer of all components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets. This type of transfusion is less common today, as most transfusions are performed using specific blood components to target the patient’s needs more effectively.
2. Red Blood Cell Transfusion
This is the most common type of blood transfusion. It focuses on replenishing red blood cells, which are essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body. Red blood cell transfusions are often used in cases of severe anemia or significant blood loss.
3. Platelet Transfusion
Platelet transfusions are used to treat patients with low platelet counts, a condition known as thrombocytopenia. This can occur due to various reasons, including chemotherapy, certain diseases, or bone marrow disorders. Platelets are crucial for blood clotting, and their transfusion helps prevent excessive bleeding.
4. Plasma Transfusion
Plasma transfusions involve the transfer of the liquid portion of blood, which contains water, electrolytes, proteins, and waste products. Plasma is vital for maintaining blood pressure and volume, and it plays a significant role in the body’s immune response. This type of transfusion is often used in patients with liver disease or those undergoing major surgeries.
5. Cryoprecipitate Transfusion
Cryoprecipitate is a component derived from plasma that is rich in clotting factors. It is primarily used to treat patients with bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia or those who have experienced massive blood loss. This transfusion helps restore the body’s ability to form clots effectively.
6. Autologous Blood Transfusion
In an autologous blood transfusion, patients donate their own blood before a scheduled surgery. This method reduces the risk of transfusion reactions and infections since the blood is from the same individual. It is particularly beneficial for patients with specific blood type concerns or those who prefer to avoid donor blood.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of blood transfusions and their purposes can empower patients and their families to make informed decisions about their healthcare. If you have further questions about blood transfusions or need personalized health information, consider visiting Yesil Health AI for evidence-based answers. Remember, blood transfusions can be a vital part of medical treatment, helping to save lives and improve health outcomes. 🩸
Blood Transfusion Indications
A blood transfusion is a medical procedure that involves transferring blood or blood components from one person (the donor) to another (the recipient). This life-saving intervention is often necessary in various clinical situations. Understanding the indications for a blood transfusion can help patients and their families make informed decisions about their health. Here are some common indications:
1. Severe Anemia
One of the most common reasons for a blood transfusion is severe anemia. Anemia occurs when the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to tissues. This can result from various conditions, including:
- Chronic blood loss (e.g., from heavy menstruation or gastrointestinal bleeding)
- Bone marrow disorders
- Iron deficiency
In such cases, a blood transfusion can help restore the necessary red blood cell count and improve oxygen delivery to vital organs.
2. Surgical Procedures
Many surgical procedures, especially major surgeries like heart surgery or organ transplants, may require a blood transfusion. During surgery, significant blood loss can occur, and transfusions can help maintain blood volume and prevent complications.
3. Trauma and Emergency Situations
In cases of trauma, such as car accidents or severe injuries, rapid blood loss can lead to shock. A blood transfusion can be critical in stabilizing the patient and restoring blood volume, which is essential for survival.
4. Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatments, particularly chemotherapy, can lead to decreased blood cell production. Patients undergoing these treatments may require transfusions to manage low blood counts and alleviate symptoms like fatigue and weakness.
5. Blood Disorders
Certain blood disorders, such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia, may necessitate regular blood transfusions to manage symptoms and prevent complications. These transfusions can help maintain healthy hemoglobin levels and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Blood Transfusion Risks
While blood transfusions can be life-saving, they are not without risks. Understanding these risks is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. Here are some potential risks associated with blood transfusions:
1. Allergic Reactions
Some patients may experience allergic reactions to the donor blood. Symptoms can range from mild (itching, rash) to severe (anaphylaxis). It’s essential for healthcare providers to monitor patients closely during and after the transfusion.
2. Febrile Non-Hemolytic Reaction
This is one of the most common reactions to blood transfusions, characterized by fever and chills. It occurs when the recipient’s immune system reacts to white blood cells in the transfused blood. While generally not serious, it can be uncomfortable and may require treatment.
3. Hemolytic Reactions
A more severe risk is a hemolytic reaction, which occurs when the recipient’s immune system attacks the transfused red blood cells. This can happen if the blood types are not compatible. Symptoms may include fever, chills, back pain, and dark urine. Immediate medical attention is necessary in such cases.
4. Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)
TRALI is a rare but serious condition that can occur after a blood transfusion. It involves sudden lung injury, leading to difficulty breathing and low oxygen levels. This condition requires prompt medical intervention and can be life-threatening.
5. Infection Risk
Although blood screening and testing have significantly reduced the risk of infections, there is still a small chance of transmitting infections through transfusions. These can include viral infections like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV. Healthcare providers take extensive precautions to minimize this risk.
In summary, while blood transfusions are essential in many medical situations, they come with potential risks that must be carefully considered. Patients should discuss these risks with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about their treatment options. 🩸

Blood Transfusion Procedure
A blood transfusion is a medical procedure that involves transferring blood or blood components from one person (the donor) to another (the recipient). This procedure is often necessary for patients who have lost blood due to surgery, injury, or medical conditions such as anemia. Understanding the blood transfusion procedure is crucial for both patients and their families. Let’s break it down step by step.
Preparation for the Transfusion
Before the transfusion begins, several important steps are taken to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the procedure:
- Blood Type Matching: The recipient’s blood type is determined through a blood test. This is crucial to prevent any adverse reactions.
- Crossmatching: A small sample of the recipient’s blood is mixed with the donor’s blood to check for compatibility.
- Informed Consent: The healthcare provider will explain the procedure, including potential risks and benefits, and obtain consent from the patient.
The Transfusion Process
Once preparations are complete, the actual blood transfusion can begin. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
- IV Access: A healthcare professional will insert an intravenous (IV) line into a vein, usually in the arm.
- Blood Administration: The blood is then connected to the IV line and slowly infused into the recipient’s bloodstream. This process can take anywhere from 1 to 4 hours, depending on the volume of blood being transfused.
- Monitoring: Throughout the transfusion, the patient is closely monitored for any signs of reaction, such as fever, chills, or rash.
Types of Blood Products
There are various types of blood products that can be transfused, including:
- Whole Blood: Contains all components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets.
- Red Blood Cells: Primarily used to treat anemia or significant blood loss.
- Platelets: Often given to patients with low platelet counts, such as those undergoing chemotherapy.
- Plasma: Used to treat conditions that cause bleeding or clotting disorders.
Post-Transfusion Care
After a blood transfusion, proper care is essential to ensure the recipient’s safety and well-being. Here are some key aspects of post-transfusion care:
Monitoring for Reactions
Patients are typically monitored for at least 30 minutes after the transfusion to watch for any immediate reactions. Common signs to look out for include:
- Fever or Chills: A sudden increase in temperature can indicate a reaction.
- Skin Reactions: Rashes, hives, or itching may occur.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing can be a sign of a serious reaction.
Hydration and Rest
Post-transfusion, it’s important for patients to stay hydrated and rest. Drinking fluids helps to flush out the system and can aid in recovery. Patients should also avoid strenuous activities for at least 24 hours following the transfusion.
Follow-Up Care
After the transfusion, follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor the patient’s blood levels and overall health. This is particularly important for those who received blood due to chronic conditions like anemia. Regular check-ups can help ensure that the transfusion was effective and that the patient is recovering well.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If any unusual symptoms arise after a blood transfusion, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms that warrant a call to a healthcare provider include:
- Severe headache
- Chest pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Severe abdominal pain
Understanding the blood transfusion procedure and the necessary post-transfusion care can significantly enhance patient safety and comfort. Always communicate openly with healthcare providers about any concerns or questions regarding the procedure. 🩸
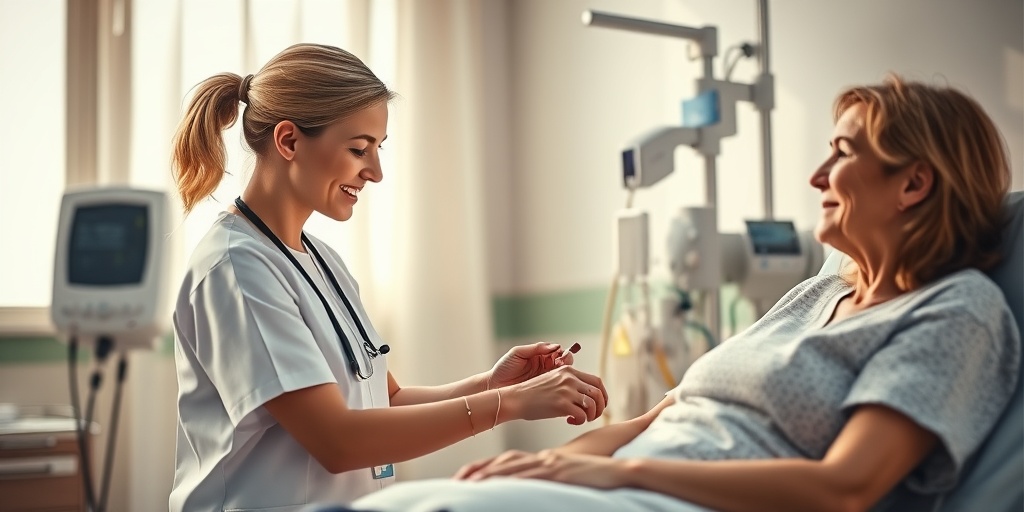

Blood Donation and Its Role
Blood donation is a vital process that plays a crucial role in saving lives. Every year, millions of people require blood transfusions due to various medical conditions, surgeries, or traumatic injuries. Understanding the importance of blood donation can help encourage more individuals to participate in this life-saving act.
What is Blood Donation?
Blood donation involves the voluntary process of giving blood, which can then be used for transfusions or medical research. Donated blood is separated into its components—red blood cells, plasma, and platelets—allowing healthcare providers to treat a variety of conditions effectively. Each donation can save up to three lives! 🩸
The Need for Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are essential for patients suffering from:
- Anemia: A condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells.
- Trauma: Injuries from accidents or surgeries that result in significant blood loss.
- Cancer: Patients undergoing chemotherapy often need transfusions to replenish their blood supply.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like sickle cell disease or thalassemia require regular transfusions.
With the increasing demand for blood, the role of blood donation becomes even more critical. Regular donations help maintain an adequate supply for hospitals and clinics, ensuring that patients receive the care they need promptly.
How Blood Donation Works
The blood donation process is straightforward and safe. Here’s a brief overview:
- Registration: Donors fill out a form with personal information and medical history.
- Health Screening: A healthcare professional checks vital signs and hemoglobin levels to ensure the donor is fit to give blood.
- Donation: The actual donation takes about 10-15 minutes, during which approximately one pint of blood is collected.
- Recovery: After donating, donors are advised to rest and hydrate for a short period.
It’s important to note that blood donation is a safe procedure, with strict protocols in place to ensure the health and safety of both donors and recipients. 💉
Future of Blood Transfusions
The future of blood transfusions is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in medical technology and research. As we look ahead, several trends and innovations are shaping the landscape of blood transfusion practices.
Artificial Blood Products
One of the most exciting developments in the field is the research into artificial blood products. Scientists are working on creating synthetic blood that can mimic the functions of human blood. This could potentially eliminate the need for human donors and address the ongoing blood shortages faced by many healthcare systems. Imagine a world where blood transfusions are no longer reliant on donations! 🧬
Improved Blood Screening Techniques
As technology advances, so do the methods for screening donated blood. Enhanced testing techniques can detect infections and diseases more accurately and quickly, ensuring that the blood supply remains safe for transfusions. This not only protects patients but also boosts public confidence in blood donation programs.
Personalized Medicine
The future of blood transfusions may also see a shift towards personalized medicine. With the rise of genetic testing and tailored treatments, healthcare providers may be able to match blood types and components more precisely to individual patients’ needs. This could lead to better outcomes and fewer transfusion reactions.
Education and Awareness Campaigns
To ensure a steady supply of blood, ongoing education and awareness campaigns are essential. These initiatives aim to inform the public about the importance of blood donation and dispel common myths surrounding the process. By fostering a culture of giving, we can encourage more people to step forward and donate blood.
In conclusion, the future of blood transfusions is bright, with numerous innovations on the horizon. As we continue to advance in medical science, the hope is that blood transfusions will become safer, more efficient, and more accessible to those in need. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Blood Transfusion
What is a Blood Transfusion?
A blood transfusion is a medical procedure that involves transferring blood or blood components from one person (donor) to another (recipient). This is often done to replace lost blood due to surgery, injury, or medical conditions.
What are the common reasons for needing a Blood Transfusion?
- Anemia: Blood transfusions can help treat severe anemia by increasing the number of red blood cells.
- Surgery: Patients undergoing major surgeries may require transfusions to replace blood lost during the procedure.
- Trauma: Individuals who have experienced significant blood loss due to accidents may need immediate transfusions.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as cancer or blood disorders, may necessitate transfusions.
What are the side effects of Blood Transfusion?
While blood transfusions are generally safe, some individuals may experience side effects, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Mild allergic reactions can occur, such as itching or rash.
- Fever: Some patients may develop a fever after receiving a transfusion.
- Transfusion Reactions: In rare cases, a more serious reaction can occur, which may require immediate medical attention.
How is a Blood Transfusion performed?
The blood transfusion procedure typically involves the following steps:
- The patient is prepared and an intravenous (IV) line is established.
- Blood is matched to ensure compatibility.
- The blood is transfused slowly while monitoring the patient for any reactions.
- Post-transfusion, the patient is observed for a period to ensure safety.
Can Jehovah’s Witnesses receive Blood Transfusions?
Many Jehovah’s Witnesses refuse blood transfusions based on their religious beliefs. However, they may accept certain blood components or alternative treatments. It is essential to discuss these preferences with healthcare providers beforehand.
What should I do if I experience a reaction after a Blood Transfusion?
If you experience any unusual symptoms after a blood transfusion, such as fever, chills, or rash, it is crucial to notify your healthcare provider immediately. Early intervention can help manage any potential complications.
Where can I find more information about Blood Transfusion?
For more detailed information, you can consult medical professionals or refer to reputable health websites that provide comprehensive resources on blood transfusions and related topics.




