What Is Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects individuals with ovaries, often during their reproductive years. This condition is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, which can lead to a variety of health issues. The term “bilateral” indicates that cysts are present on both ovaries, which is a common finding in those diagnosed with this syndrome.
PCOS is not just about the presence of cysts; it involves a complex interplay of hormonal imbalances that can affect various bodily functions. The exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, but it is believed to be linked to genetic factors, insulin resistance, and inflammation. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Understanding the Hormonal Imbalance
In individuals with bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome, the ovaries produce an excess of androgens, which are male hormones that females also produce in smaller amounts. This hormonal imbalance can disrupt the normal ovulation process, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and fertility issues.
Diagnosis of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Diagnosing PCOS typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and imaging tests such as ultrasounds. Healthcare providers may look for specific criteria, including:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods.
- Excess androgen levels: Signs may include hirsutism (excess hair growth), acne, and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic ovaries: The presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries as seen on an ultrasound.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to rule out other conditions that may mimic PCOS symptoms.
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Symptoms
The symptoms of bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome can vary widely among individuals, making it a challenging condition to identify. Here are some of the most common symptoms associated with PCOS:
Irregular Menstrual Cycles
One of the hallmark symptoms of PCOS is irregular menstrual cycles. Individuals may experience:
- Infrequent periods: Menstruation may occur only a few times a year.
- Prolonged periods: Some may have heavy bleeding that lasts longer than usual.
Excess Androgen Levels
High levels of androgens can lead to various physical symptoms, including:
- Hirsutism: Unwanted hair growth on the face, chest, and back.
- Acne: Persistent breakouts, particularly on the face and back.
- Scalp hair thinning: Similar to male-pattern baldness.
Weight Gain and Insulin Resistance
Many individuals with bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome struggle with weight gain, particularly around the abdomen. This can be linked to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar levels. This can further complicate the symptoms of PCOS and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Other Symptoms
In addition to the above, other symptoms may include:
- Skin changes: Dark patches of skin, particularly in skin folds.
- Fatigue: Many individuals report feeling unusually tired.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving due to irregular ovulation.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and management of bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome. If you suspect you may have PCOS, it’s important to seek guidance from a healthcare provider.
For more information and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for understanding various health conditions, including PCOS. 🌼
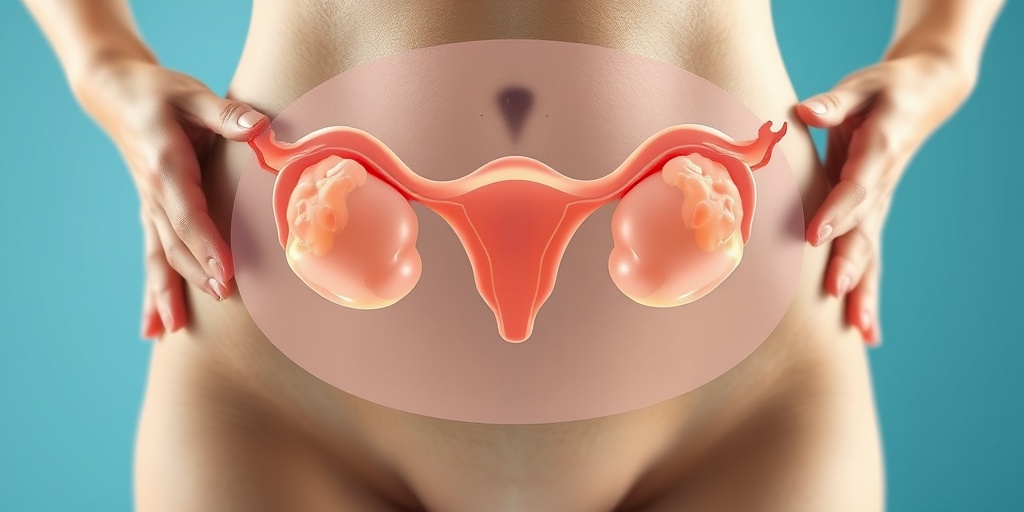
Causes of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder that affects many women of reproductive age. Understanding the causes of this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment. While the exact cause of bilateral PCOS remains unclear, several factors are believed to contribute to its development.
Hormonal Imbalances
One of the primary causes of bilateral PCOS is hormonal imbalance. Women with this condition often have elevated levels of androgens, which are male hormones that can disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries. This imbalance can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, ovulatory dysfunction, and the formation of cysts in the ovaries.
Genetic Factors
Genetics also play a significant role in the development of bilateral PCOS. If a woman has a family history of PCOS, she may be at a higher risk of developing the condition herself. Research suggests that certain genes may influence the hormonal pathways involved in ovarian function, making some women more susceptible to this syndrome.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is another critical factor associated with bilateral PCOS. Many women with this condition have higher levels of insulin, which can lead to weight gain and further exacerbate hormonal imbalances. Insulin resistance can also contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, making it essential for women with PCOS to monitor their blood sugar levels.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle choices, can also influence the onset of bilateral PCOS. A diet high in processed foods and sugars can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of developing this syndrome. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate these issues, making it vital for women to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Risk Factors for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Identifying the risk factors for bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome can help in early diagnosis and management. While anyone can develop PCOS, certain factors may increase the likelihood of its occurrence.
Obesity
Obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for bilateral PCOS. Excess body weight can lead to increased insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, making it more challenging for women to manage their symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing PCOS.
Age
Age is another important factor. Women are more likely to develop bilateral PCOS during their reproductive years, typically between the ages of 15 and 44. However, symptoms may begin to appear during adolescence, making it essential for young women to be aware of the signs and seek medical advice if necessary.
Family History
A family history of PCOS or related conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, can increase the risk of developing bilateral PCOS. If a woman has relatives who have experienced PCOS, she should be vigilant about monitoring her health and discussing any concerns with her healthcare provider.
Ethnicity
Research indicates that certain ethnic groups may be more prone to developing bilateral PCOS. For instance, women of South Asian, Middle Eastern, and Hispanic descent may have a higher prevalence of this condition. Understanding these ethnic predispositions can help in tailoring prevention and treatment strategies.
Other Health Conditions
Women with other health conditions, such as metabolic syndrome, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, may also be at an increased risk for bilateral PCOS. These conditions often share common risk factors, such as obesity and insulin resistance, which can complicate the management of PCOS.
In conclusion, while the exact causes of bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome are still being studied, understanding the contributing factors and risk factors can empower women to take proactive steps in managing their health. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle can make a significant difference in the lives of those affected by this condition. 🌸

Diagnosis of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Diagnosing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) can be a complex process, as it often involves a combination of clinical evaluations, medical history, and imaging studies. Understanding the symptoms and the diagnostic criteria is crucial for effective management.
Common Symptoms to Look For
Women with bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: This is one of the hallmark signs of PCOS. Women may have infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles.
- Excess Androgen Levels: Symptoms such as acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness can indicate elevated androgen levels.
- Polycystic Ovaries: An ultrasound may reveal enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight management, which can exacerbate other symptoms.
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnosis of bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome typically follows the Rotterdam criteria, which require at least two of the following:
- Irregular or absent ovulation
- Clinical or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism
- Polycystic ovaries visible on ultrasound
Additionally, healthcare providers may conduct blood tests to measure hormone levels, including testosterone and insulin, to rule out other conditions that may mimic PCOS symptoms.
Imaging Studies
Ultrasound is a key tool in diagnosing bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome. A transvaginal ultrasound can help visualize the ovaries and identify the presence of cysts. Typically, the ovaries may appear enlarged and contain multiple small follicles, which is characteristic of PCOS.
Treatment Options for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Managing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s symptoms and health goals. Treatment options can range from lifestyle changes to medication and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications
One of the first lines of treatment for PCOS is often lifestyle modification. This includes:
- Dietary Changes: A balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage weight and insulin levels. Consider incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your meals.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce insulin resistance and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week.
- Weight Management: Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly improve symptoms and restore regular menstrual cycles.
Medications
For women who do not respond to lifestyle changes alone, medications may be necessary. Common options include:
- Hormonal Birth Control: Birth control pills can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptoms of hyperandrogenism, such as acne and excessive hair growth.
- Metformin: This medication is often prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity and can help with weight management and menstrual regularity.
- Anti-androgens: Medications like spironolactone can help reduce hair growth and acne by blocking the effects of androgens.
Surgical Options
In cases where other treatments are ineffective, surgical options may be considered. One such procedure is ovarian drilling, which involves making small holes in the ovaries to restore normal ovulation. This is typically reserved for women who are struggling with infertility and have not had success with other treatments.
In conclusion, the diagnosis and treatment of bilateral polycystic ovarian syndrome require a comprehensive approach that addresses both symptoms and underlying hormonal imbalances. By working closely with healthcare providers, women can find effective strategies to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. 🌼

Managing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome at Home
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects many women of reproductive age. Managing this condition at home can significantly improve symptoms and enhance overall well-being. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
1. Dietary Adjustments
Nutrition plays a crucial role in managing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. A balanced diet can help regulate insulin levels and maintain a healthy weight. Here are some dietary tips:
- Focus on Whole Foods: Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of sugary snacks, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats.
- Consider Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods with a low glycemic index can help manage blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity is essential for managing symptoms of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Regular exercise can help with weight management, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. Here are some effective forms of exercise:
- Aerobic Activities: Walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming can boost cardiovascular health.
- Strength Training: Incorporating resistance exercises can help build muscle and improve metabolism.
- Yoga and Mindfulness: These practices can reduce stress and promote hormonal balance.
3. Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Finding effective ways to manage stress is vital. Consider the following techniques:
- Meditation: Regular meditation can help calm the mind and reduce anxiety.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practicing deep breathing can lower stress levels and improve overall well-being.
- Engaging in Hobbies: Spend time on activities you enjoy to help distract from stressors.
4. Monitoring Symptoms
Keeping track of your symptoms can provide valuable insights into your condition. Consider maintaining a journal to note:
- Menstrual Cycle: Track your cycle to identify any irregularities.
- Symptoms: Document any changes in symptoms, such as weight fluctuations or mood changes.
- Diet and Exercise: Record your food intake and physical activity to identify patterns.
Long-Term Outlook for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
The long-term outlook for individuals with Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome can vary widely based on several factors, including lifestyle choices, treatment adherence, and individual health conditions. Understanding the potential long-term effects is crucial for effective management.
1. Fertility Considerations
Many women with Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome may experience challenges with fertility due to irregular ovulation. However, with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, many can conceive. Options include:
- Medications: Fertility medications can help induce ovulation.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies: In some cases, procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
2. Risk of Other Health Conditions
Women with Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome are at a higher risk for certain health conditions, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance is common in PCOS, increasing the risk of diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Women with PCOS may have higher cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Endometrial Cancer: Irregular menstrual cycles can lead to a higher risk of uterine cancer.
3. Importance of Regular Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups are essential for monitoring health and managing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. These visits can help:
- Track Hormonal Levels: Regular blood tests can monitor hormone levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Adjust Treatment Plans: Healthcare providers can modify treatment plans based on individual progress.
- Screen for Associated Conditions: Early detection of related health issues can lead to better outcomes.
In conclusion, managing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome at home and understanding its long-term outlook can empower individuals to take control of their health. By making informed lifestyle choices and seeking regular medical advice, women can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this condition. 🌼

Frequently Asked Questions about Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
What is Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries, leading to various symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, and fertility issues.
What are the symptoms of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
- Irregular or absent menstrual periods
- Excessive hair growth (hirsutism)
- Acne and oily skin
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Infertility
How is Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome typically involves a combination of physical exams, medical history, blood tests to check hormone levels, and imaging tests like ultrasounds to identify cysts on the ovaries.
What are the treatment options for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Treatment for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome may include:
- Hormonal birth control to regulate menstrual cycles
- Medications to manage insulin levels
- Weight management through diet and exercise
- Fertility treatments if pregnancy is desired
Can Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome affect fertility?
Yes, Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome can lead to difficulties in conceiving due to irregular ovulation. However, many women with PCOS can still become pregnant with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes.
Is there a specific diet recommended for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats is often recommended for managing Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Reducing processed foods and sugars can also help in managing symptoms and maintaining a healthy weight.
What is the ICD-10 code for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
The ICD-10 code for Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is E28.2, which is used for medical billing and documentation purposes.
Where can I find more information about Bilateral Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
For more information, consider consulting healthcare professionals or reputable health websites that specialize in women’s health and hormonal disorders.