What Is Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
Dowling-Meara Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the skin and hair. It is classified as a type of epidermolysis bullosa, which is a group of conditions that cause the skin to be fragile and blister easily. This syndrome is characterized by the presence of blisters and erosions on the skin, particularly in areas subjected to friction, such as the hands and feet. The condition is named after the researchers who first described it, and it is essential to understand its implications for those affected.
The genetic basis of Dowling-Meara Syndrome lies in mutations in the genes responsible for producing proteins that maintain the integrity of the skin. These mutations lead to a deficiency in the structural proteins, resulting in the characteristic symptoms of the syndrome. While the condition is rare, it is crucial for individuals and families affected by it to have access to accurate information and support.
Causes and Genetic Factors
Dowling-Meara Syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in their offspring. This genetic inheritance pattern can lead to varying degrees of severity in symptoms among family members. Understanding the genetic factors involved can help in managing the condition and providing appropriate care.
Symptoms of Dowling-Meara Syndrome
The symptoms of Dowling-Meara Syndrome can vary significantly from person to person, but they typically include:
- Blistering Skin: One of the most prominent features of this syndrome is the formation of blisters, which can occur spontaneously or as a result of minor trauma.
- Thickened Skin: Areas of the skin may become thickened, particularly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Hair Abnormalities: Individuals may experience hair loss or changes in hair texture, which can be distressing.
- Scarring: Blisters that heal can leave behind scars, leading to changes in skin appearance over time.
- Increased Sensitivity: The skin may be more sensitive to touch and temperature changes, making everyday activities challenging.
Impact on Daily Life
The symptoms of Dowling-Meara Syndrome can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The presence of blisters and skin fragility can lead to discomfort and pain, making it difficult to engage in physical activities. Additionally, the psychological effects of living with a visible skin condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and social withdrawal.
For families affected by Dowling-Meara Syndrome, understanding the condition is vital. Support groups and resources, such as Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com), can provide valuable information and community support for those navigating the challenges of this syndrome.
Management and Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for Dowling-Meara Syndrome, various management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Wound Care: Proper care of blisters and wounds is essential to prevent infections and promote healing.
- Moisturizers: Regular use of moisturizers can help maintain skin hydration and reduce friction.
- Protective Clothing: Wearing protective clothing can minimize the risk of skin injury and blister formation.
- Psychological Support: Counseling and support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
In conclusion, Dowling-Meara Syndrome is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the symptoms and seeking appropriate care, individuals and families can navigate the challenges associated with this syndrome more effectively. For more information and support, consider visiting Yesil Health AI for evidence-based health answers and resources. 🌟
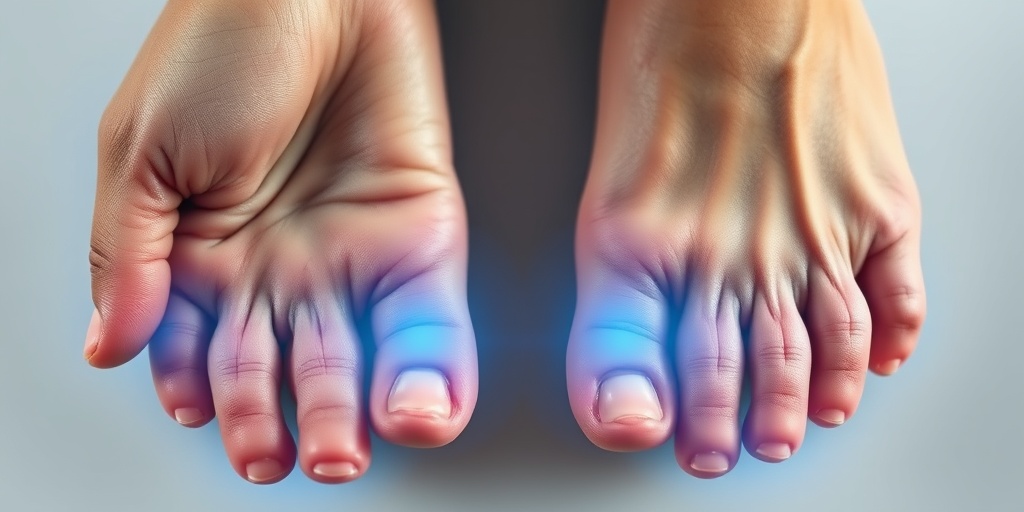
Causes and Genetics
Dowling-Meara Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the skin and hair. Understanding the causes and genetic underpinnings of this condition is crucial for those affected and their families. This syndrome is classified as a type of epidermolysis bullosa, which is characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily. Let’s delve into the genetic factors that contribute to this condition.
Genetic Mutations
The primary cause of Dowling-Meara Syndrome is mutations in the KRT17 gene. This gene is responsible for producing keratin, a protein that plays a vital role in the structure and resilience of skin and hair. When mutations occur in this gene, it can lead to the symptoms associated with the syndrome, including:
- Fragile skin that blisters easily
- Thickened skin on the palms and soles
- Hair abnormalities, such as sparse or brittle hair
These mutations are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the syndrome in their offspring. This inheritance pattern highlights the importance of genetic counseling for families with a history of Dowling-Meara Syndrome.
Inheritance Patterns
As mentioned, Dowling-Meara Syndrome follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means:
- If one parent has the syndrome, there is a 50% chance that their child will inherit the condition.
- It can occur in individuals with no prior family history, due to new mutations in the gene.
Understanding these inheritance patterns can help families make informed decisions regarding family planning and genetic testing.
Risk Factors for Dowling-Meara Syndrome
While Dowling-Meara Syndrome is primarily caused by genetic mutations, certain risk factors can influence the likelihood of developing the condition. Here are some key factors to consider:
Family History
A family history of Dowling-Meara Syndrome or other forms of epidermolysis bullosa significantly increases the risk of inheriting the condition. If a parent is affected, their children are at a higher risk due to the autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
Genetic Predisposition
Individuals with a known genetic predisposition to skin disorders may also be at risk. Genetic testing can help identify mutations in the KRT17 gene, providing valuable information for those with a family history of skin conditions.
Environmental Factors
While Dowling-Meara Syndrome is primarily genetic, certain environmental factors can exacerbate symptoms. For instance:
- Trauma to the skin: Minor injuries or friction can lead to blistering in affected individuals.
- Infections: Skin infections can complicate the condition and require prompt medical attention.
Being aware of these environmental triggers can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively.
Age and Gender
Dowling-Meara Syndrome can affect individuals of any age, but symptoms often present at birth or during early childhood. There is no significant gender bias, as both males and females are equally affected. However, early diagnosis and intervention can lead to better management of the condition.
In summary, understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Dowling-Meara Syndrome is essential for affected individuals and their families. Genetic counseling and awareness of environmental triggers can play a crucial role in managing this rare condition effectively. 🌟

Diagnosis of Dowling-Meara Syndrome
Diagnosing Dowling-Meara Syndrome can be a complex process, primarily because it is a rare genetic disorder. This condition is characterized by a variety of symptoms, including distinctive skin features and skeletal abnormalities. Here’s a closer look at how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing Dowling-Meara Syndrome often involves a thorough clinical evaluation. Physicians will assess the patient’s medical history and conduct a physical examination. Key indicators that may prompt further investigation include:
- Skin manifestations: Patients may exhibit thickened skin, particularly on the palms and soles.
- Skeletal abnormalities: These can include short stature and limb deformities.
- Family history: Since this syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, a family history of similar symptoms can be a significant clue.
Genetic Testing
Once a clinical evaluation suggests the possibility of Dowling-Meara Syndrome, genetic testing is often recommended. This testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the KRT17 gene, which is known to be associated with this condition. Genetic counseling may also be beneficial for families, providing them with information about inheritance patterns and implications for other family members.
Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging studies such as X-rays may be utilized to assess skeletal abnormalities. These images can help in understanding the extent of any bone deformities and guide treatment options.
Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for Dowling-Meara Syndrome, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. The treatment plan is often tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and needs.
Dermatological Care
For patients experiencing skin issues, dermatological care is crucial. Treatments may include:
- Moisturizers: Regular use of emollients can help manage dryness and improve skin texture.
- Topical steroids: These may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and irritation.
- Regular skin checks: Monitoring for any changes in skin lesions is essential to prevent complications.
Orthopedic Interventions
Given the skeletal abnormalities associated with Dowling-Meara Syndrome, orthopedic interventions may be necessary. Options include:
- Physical therapy: This can help improve mobility and strengthen muscles.
- Surgical procedures: In some cases, surgery may be required to correct significant deformities or improve function.
Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing Dowling-Meara Syndrome. This can include:
- Psychological support: Counseling or support groups can help patients and families cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
- Educational support: For children, special educational resources may be necessary to accommodate any learning difficulties.
In conclusion, while the diagnosis and treatment of Dowling-Meara Syndrome can be challenging, a multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists, orthopedic specialists, and mental health professionals can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected. 🌟

Living with Dowling-Meara Syndrome
Dowling-Meara Syndrome is a rare genetic condition that primarily affects the skin and hair. Individuals with this syndrome often experience a range of symptoms that can impact their daily lives. Understanding how to manage these symptoms is crucial for improving quality of life.
Understanding the Symptoms
People with Dowling-Meara Syndrome typically present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Thickened skin: This is one of the hallmark features of the syndrome, often leading to a rough texture.
- Hair abnormalities: Individuals may have sparse hair or hair that is brittle and prone to breakage.
- Blistering: Skin may be prone to blisters, particularly in areas of friction.
- Hyperkeratosis: This condition leads to an excessive buildup of keratin on the skin’s surface.
These symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, making it essential for individuals and their families to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a tailored management plan.
Daily Management Strategies
Living with Dowling-Meara Syndrome requires a proactive approach to skin and hair care. Here are some effective strategies:
- Moisturizing: Regularly applying emollients can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce the risk of cracking and blistering.
- Gentle cleansing: Using mild, fragrance-free soaps can prevent irritation and maintain skin integrity.
- Protective clothing: Wearing loose-fitting, breathable fabrics can minimize friction and protect sensitive skin areas.
- Regular dermatological check-ups: Routine visits to a dermatologist can help monitor skin health and address any emerging issues promptly.
In addition to these strategies, emotional support is vital. Connecting with support groups or online communities can provide individuals and families with valuable resources and a sense of belonging. 🤝
Psychosocial Considerations
Living with a rare condition like Dowling-Meara Syndrome can sometimes lead to feelings of isolation or frustration. It’s important to address these psychosocial aspects:
- Open communication: Encourage discussions about feelings and experiences within the family to foster understanding and support.
- Seek professional help: Counseling or therapy can be beneficial for individuals struggling with the emotional impact of their condition.
- Engage in activities: Finding hobbies or interests that bring joy can help improve overall well-being and self-esteem.
Future Research and Outlook
The future of research into Dowling-Meara Syndrome holds promise as scientists and medical professionals continue to explore the genetic underpinnings and potential treatments for this condition. Here are some key areas of focus:
Genetic Research
Understanding the genetic mutations that cause Dowling-Meara Syndrome is crucial for developing targeted therapies. Ongoing research aims to:
- Identify specific genes: Researchers are working to pinpoint the exact genetic changes responsible for the syndrome.
- Explore gene therapy: Advances in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, may offer potential avenues for treatment in the future.
Clinical Trials
As research progresses, clinical trials may become available for individuals with Dowling-Meara Syndrome. These trials could focus on:
- New medications: Investigating the efficacy of new topical treatments or systemic therapies to manage symptoms.
- Supportive therapies: Exploring the benefits of physical therapy or occupational therapy to improve daily functioning.
Community Awareness and Support
Increasing awareness about Dowling-Meara Syndrome is essential for fostering understanding and support within the community. Efforts may include:
- Educational campaigns: Raising awareness among healthcare providers and the public to improve diagnosis and support.
- Support networks: Establishing connections between individuals with the syndrome and researchers can facilitate information sharing and collaboration.
As research continues to evolve, the outlook for individuals living with Dowling-Meara Syndrome is becoming increasingly optimistic. With advancements in genetics and a growing understanding of the condition, there is hope for improved management strategies and potential treatments in the future. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Dowling-Meara Syndrome
What is Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
Dowling-Meara Syndrome is a rare genetic condition characterized by specific skin and hair abnormalities. It is a form of epidermolysis bullosa, which leads to fragile skin that blisters easily. This syndrome is often associated with other symptoms that can affect the quality of life of those who have it.
What are the symptoms of Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
- Blistering of the skin, particularly in response to minor trauma
- Thickened skin on the palms and soles
- Hair abnormalities, such as sparse or brittle hair
- Potential for scarring and pigmentation changes
How is Dowling-Meara Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Dowling-Meara Syndrome typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and genetic testing. A healthcare provider may examine the skin and hair characteristics and may recommend a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis at the molecular level.
What causes Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
This syndrome is caused by mutations in the genes responsible for skin integrity. These genetic changes affect the structure and function of proteins that help maintain skin strength and resilience.
Is there a treatment for Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
Currently, there is no cure for Dowling-Meara Syndrome. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
- Wound care to manage blisters and prevent infections
- Use of moisturizers to maintain skin hydration
- Regular follow-ups with dermatologists and other specialists
Can Dowling-Meara Syndrome be inherited?
Yes, Dowling-Meara Syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the condition in their offspring.
What is the prognosis for individuals with Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
The prognosis varies among individuals. While the condition can lead to significant skin issues, many people with Dowling-Meara Syndrome can lead relatively normal lives with appropriate care and management of symptoms.
Where can I find support for Dowling-Meara Syndrome?
Support groups and organizations dedicated to rare diseases can provide valuable resources and community support for individuals and families affected by Dowling-Meara Syndrome. Online forums and local support groups can also be beneficial for sharing experiences and advice.




