What Is Hodgkin’s Disease?
Hodgkin’s Disease, also known as Hodgkin lymphoma, is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, which is a crucial part of the body’s immune system. This disease is characterized by the presence of an abnormal type of lymphocyte called Reed-Sternberg cells. These cells can be found in lymph nodes, spleen, and other lymphatic tissues, leading to the disruption of normal immune function.
The exact cause of Hodgkin’s Disease remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to its development. These include:
- Age: Hodgkin’s Disease is most commonly diagnosed in young adults aged 15 to 35 and in older adults over 55.
- Family History: A family history of Hodgkin’s Disease may increase the risk.
- Immune System Function: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are at a higher risk.
Understanding Hodgkin’s Disease is essential for early detection and treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Hodgkin’s Disease Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Hodgkin’s Disease is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can vary from person to person, but some common signs include:
Common Symptoms
- Painless Swelling of Lymph Nodes: The most noticeable symptom is the swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin.
- Fever: Unexplained fevers that come and go can be a sign of Hodgkin’s Disease.
- Night Sweats: Profuse sweating during the night, often soaking through clothing and sheets.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss without changes in diet or exercise.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Itching: Some patients experience severe itching without any apparent cause.
Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the common symptoms, some individuals may experience:
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest area due to swollen lymph nodes.
- Abdominal Pain: Swelling in the abdomen can lead to discomfort or pain.
- Respiratory Issues: Difficulty breathing or persistent cough if lymph nodes in the chest are affected.
If you notice any of these symptoms, especially if they persist for more than a few weeks, it’s important to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
For more detailed information about Hodgkin’s Disease, including treatment options and support resources, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to health!
In conclusion, Hodgkin’s Disease is a serious condition that requires attention and care. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking timely medical help, individuals can navigate this challenging journey with greater confidence and support. 🌟
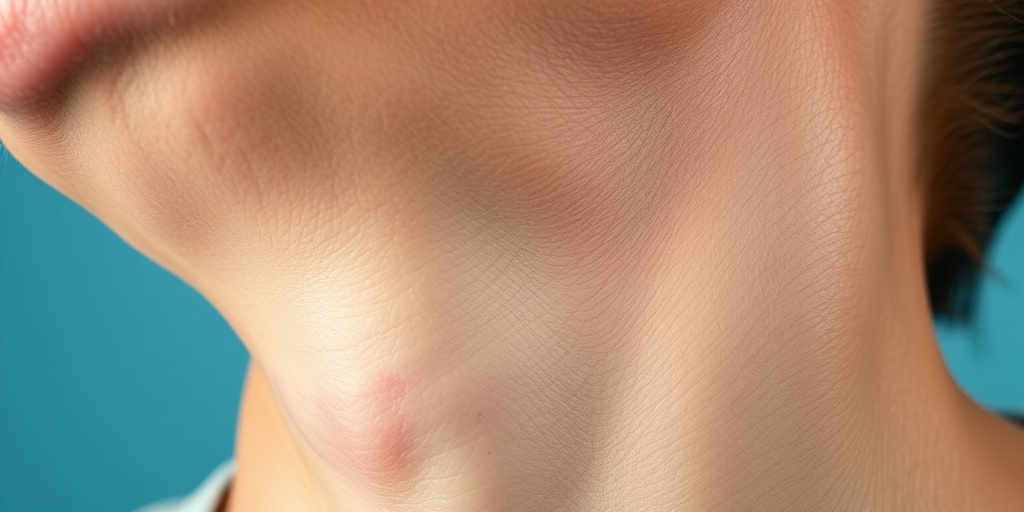
Hodgkin’s Disease Staging
Understanding the staging of Hodgkin’s disease is crucial for determining the most effective treatment plan. Staging helps doctors assess how far the disease has spread in the body and guides them in making informed decisions about therapy. Hodgkin’s disease is typically staged using the Ann Arbor system, which categorizes the disease into four main stages.
Stage I
In Stage I, the cancer is localized to a single lymph node region or a single organ. This means that the disease has not spread beyond this area. For example, if Hodgkin’s disease is found in one lymph node in the neck, it is classified as Stage I.
Stage II
Stage II indicates that the disease has spread to two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm. This stage may also involve a nearby organ. For instance, if the cancer has spread from the neck to the chest but remains on one side of the diaphragm, it is classified as Stage II.
Stage III
In Stage III, Hodgkin’s disease has spread to lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm. This stage may also involve the spleen or other nearby organs. The presence of cancer in multiple lymph node regions signifies a more advanced stage of the disease.
Stage IV
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of Hodgkin’s disease. At this point, the cancer has spread beyond the lymph nodes to other organs, such as the liver, bone marrow, or lungs. This stage indicates a more systemic involvement of the disease and often requires more aggressive treatment.
Additional Staging Information
Each stage can be further classified with the addition of letters:
- A: Indicates the absence of systemic symptoms.
- B: Indicates the presence of systemic symptoms, such as fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss.
Understanding the stage of Hodgkin’s disease is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. It not only influences treatment options but also helps in predicting the prognosis and potential outcomes. Regular follow-ups and imaging studies are often necessary to monitor the disease’s progression and response to treatment. 📈
Hodgkin’s Disease Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of Hodgkin’s disease remain largely unknown, but several factors may increase the risk of developing this type of lymphoma. Understanding these risk factors can help in early detection and prevention strategies.
Genetic Factors
Individuals with a family history of Hodgkin’s disease or other lymphomas may have a higher risk. Genetic predispositions can play a significant role in the development of this disease, suggesting that inherited factors may contribute to its onset.
Age and Gender
Hodgkin’s disease is most commonly diagnosed in young adults aged 15 to 35 and in older adults over 55. Additionally, it is slightly more prevalent in males than in females, indicating that gender may also influence risk.
Immune System Function
A weakened immune system can increase the risk of Hodgkin’s disease. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, organ transplants, or autoimmune diseases can compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to various cancers, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Infections
Certain viral infections have been linked to Hodgkin’s disease. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which causes mononucleosis, has been associated with an increased risk of developing this type of lymphoma. Other infections, such as those caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), can also elevate the risk.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain chemicals and environmental toxins may contribute to the development of Hodgkin’s disease. For example, individuals who have been exposed to herbicides, pesticides, or other carcinogenic substances may have a higher risk of developing this condition.
Conclusion
While the exact causes of Hodgkin’s disease are still being researched, understanding the risk factors can empower individuals to take proactive steps in monitoring their health. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. If you have concerns about your risk factors, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. 🩺

Hodgkin’s Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosing Hodgkin’s Disease, a type of lymphoma, involves a series of steps that help healthcare professionals determine the presence of the disease and its stage. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and better outcomes. Here’s a closer look at the diagnostic process.
Initial Consultation and Symptoms
The journey to diagnosis often begins with a visit to a healthcare provider. During this initial consultation, the doctor will ask about your medical history and any symptoms you may be experiencing. Common symptoms of Hodgkin’s Disease include:
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Itchy skin
If you present with these symptoms, your doctor may recommend further testing to confirm a diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests
Several tests may be conducted to diagnose Hodgkin’s Disease:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will perform a thorough physical exam, checking for swollen lymph nodes and other signs of the disease.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help assess your overall health and detect any abnormalities that may indicate lymphoma.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans are used to visualize the lymphatic system and identify any enlarged lymph nodes or tumors.
- Lymph Node Biopsy: The definitive diagnosis of Hodgkin’s Disease is made through a biopsy, where a sample of lymph node tissue is examined under a microscope for the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which are characteristic of the disease.
Staging of Hodgkin’s Disease
Once diagnosed, the next step is staging, which determines how far the disease has spread. Staging is crucial for planning treatment and may involve additional imaging tests. The stages range from I (localized) to IV (advanced), with various sub-stages in between.
Understanding the stage of Hodgkin’s Disease helps healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to the individual needs of the patient, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Hodgkin’s Disease Treatment Options
Treating Hodgkin’s Disease involves a multidisciplinary approach, often combining various therapies to achieve the best results. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences.
Common Treatment Modalities
The primary treatment options for Hodgkin’s Disease include:
- Chemotherapy: This is often the first line of treatment and involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered in cycles and may be combined with other treatments.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is often used after chemotherapy, especially in early-stage cases.
- Stem Cell Transplant: For advanced cases or relapsed Hodgkin’s Disease, a stem cell transplant may be recommended. This procedure involves replacing damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Newer treatments focus on specific characteristics of cancer cells. These therapies can be less harmful to normal cells and may be used in combination with traditional treatments.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Treatments
Patients may also consider participating in clinical trials, which test new treatments and therapies. These trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments that are not yet widely available. Discussing this option with your healthcare provider can help you stay informed about the latest advancements in Hodgkin’s Disease treatment.
Supportive Care
In addition to medical treatments, supportive care plays a vital role in the overall management of Hodgkin’s Disease. This includes:
- Pain Management: Addressing pain and discomfort through medications and therapies.
- Nutritional Support: Ensuring proper nutrition to help maintain strength and energy during treatment.
- Emotional Support: Counseling and support groups can help patients cope with the emotional challenges of a cancer diagnosis.
Understanding the various treatment options available for Hodgkin’s Disease empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action tailored to individual needs. 🌟

Hodgkin’s Disease Prognosis
When diagnosed with Hodgkin’s Disease, understanding the prognosis can be a crucial part of the journey. Prognosis refers to the likely course and outcome of the disease, which can vary significantly from person to person. Several factors influence the prognosis of Hodgkin’s Disease, including the stage at diagnosis, the patient’s age, and overall health.
Understanding Staging
The stage of Hodgkin’s Disease is one of the most significant factors in determining prognosis. The stages range from I to IV, with:
- Stage I: The cancer is localized to one lymph node region.
- Stage II: The cancer is in two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm.
- Stage III: The cancer is found in lymph node regions on both sides of the diaphragm.
- Stage IV: The cancer has spread to other organs, such as the liver or bone marrow.
Generally, the earlier the stage at diagnosis, the better the prognosis. For instance, patients diagnosed at Stage I or II often have a high cure rate, with many achieving long-term remission. In contrast, those diagnosed at Stage III or IV may face a more challenging prognosis, although advancements in treatment have improved outcomes significantly.
Age and Overall Health
Age plays a critical role in the prognosis of Hodgkin’s Disease. Younger patients typically have a better prognosis compared to older adults. Additionally, a patient’s overall health and any pre-existing conditions can impact treatment options and outcomes. For example, individuals with a strong immune system may respond better to treatment.
Treatment Response
The response to treatment is another vital indicator of prognosis. Hodgkin’s Disease is highly responsive to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Patients who achieve a complete response to initial treatment often have a favorable prognosis. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are essential to detect any recurrence early.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for Hodgkin’s Disease have improved dramatically over the years. According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for individuals diagnosed with Hodgkin’s Disease is approximately 87%. This statistic varies based on the stage at diagnosis, with earlier stages showing even higher survival rates. It’s important to remember that these statistics are averages and individual outcomes can vary.
Hodgkin’s Disease Support and Resources
Facing a diagnosis of Hodgkin’s Disease can be overwhelming, but numerous support resources are available to help patients and their families navigate this journey. From emotional support to practical assistance, these resources can make a significant difference.
Support Groups
Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges can provide invaluable emotional support. Many organizations offer support groups specifically for Hodgkin’s Disease patients. These groups allow individuals to share their experiences, discuss treatment options, and provide encouragement to one another. Some well-known organizations include:
- The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society: Offers resources, support groups, and educational materials.
- Cancer Support Community: Provides online and in-person support groups for patients and caregivers.
- American Cancer Society: Offers a variety of resources, including support groups and educational materials.
Educational Resources
Understanding Hodgkin’s Disease is crucial for patients and their families. Numerous educational resources are available, including:
- Websites: Reliable websites like the National Cancer Institute and the American Cancer Society provide comprehensive information about Hodgkin’s Disease, including symptoms, treatment options, and coping strategies.
- Books: There are many books available that cover Hodgkin’s Disease from various perspectives, including medical, emotional, and practical aspects.
Professional Counseling
Sometimes, the emotional toll of a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Seeking professional counseling can be beneficial for patients and their families. Therapists who specialize in oncology can provide coping strategies and emotional support tailored to the unique challenges of living with Hodgkin’s Disease.
Financial Assistance
Medical treatment for Hodgkin’s Disease can be costly. Various organizations offer financial assistance to help cover treatment costs, medications, and other related expenses. Patients should inquire about financial aid programs through their healthcare providers or local cancer organizations.
In conclusion, while a diagnosis of Hodgkin’s Disease can be daunting, understanding the prognosis and accessing available support resources can empower patients and their families to navigate this journey with greater confidence. Remember, you are not alone, and help is available! 💪❤️

Frequently Asked Questions about Hodgkin’s Disease
What is Hodgkin’s Disease?
Hodgkin’s Disease, also known as Hodgkin lymphoma, is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system. It is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and can affect lymph nodes and other organs.
What are the common symptoms of Hodgkin’s Disease?
Common symptoms include:
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Itching
What causes Hodgkin’s Disease?
The exact cause of Hodgkin’s Disease is not known, but several factors may increase the risk, including:
- A family history of lymphoma
- Infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus
- Weakened immune system
How is Hodgkin’s Disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical examination to check for swollen lymph nodes
- Blood tests to assess overall health
- Imaging tests like CT scans or PET scans
- Biopsy to confirm the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells
What are the treatment options for Hodgkin’s Disease?
Treatment options may include:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Stem cell transplant
- Targeted therapy
Can Hodgkin’s Disease be cured?
Yes, many people with Hodgkin’s Disease can be cured, especially if diagnosed early. The prognosis varies based on the stage of the disease and the individual’s overall health.
Is Hodgkin’s Disease hereditary?
While there is no direct inheritance pattern, having a family member with Hodgkin’s Disease may increase your risk. Genetic factors and environmental influences may play a role.
How can I support someone with Hodgkin’s Disease?
Supporting someone with Hodgkin’s Disease can involve:
- Being there to listen and provide emotional support
- Helping with daily tasks and appointments
- Encouraging them to follow their treatment plan
- Joining them in healthy activities to boost their mood
Where can I find more information about Hodgkin’s Disease?
For more information, consider visiting reputable health websites, cancer organizations, or consulting with healthcare professionals who specialize in oncology.




