What Are Radiation Injuries?
Radiation injuries refer to the damage inflicted on the body due to exposure to ionizing radiation. This type of radiation can come from various sources, including nuclear accidents, medical treatments, or even cosmic rays. The severity of radiation injuries can vary significantly, depending on the dose and duration of exposure. Understanding these injuries is crucial, especially in today’s world where nuclear technology and medical imaging are prevalent.
When we talk about radiation injuries, we often think of catastrophic events like the Hiroshima and Chernobyl disasters. These incidents highlighted the devastating effects of high-dose radiation exposure, leading to acute radiation syndrome (ARS) and long-term health complications. However, radiation injuries can also occur in less dramatic situations, such as during certain medical treatments or occupational exposures.
Types of Radiation Injuries
Radiation injuries can be categorized into two main types:
- Acute Radiation Injuries: These occur after a high dose of radiation over a short period. Symptoms can manifest within hours or days and may include nausea, vomiting, and skin burns.
- Chronic Radiation Injuries: These develop over time due to prolonged exposure to lower doses of radiation. They can lead to conditions such as cancer, cataracts, and other long-term health issues.
It’s essential to recognize that not all radiation exposure results in injuries. The human body can tolerate low levels of radiation without significant harm. However, when exposure exceeds safe limits, the risk of radiation injuries increases dramatically.
Symptoms of Radiation Injuries
The symptoms of radiation injuries can vary widely based on the type and severity of exposure. Understanding these symptoms is vital for early detection and treatment. Here are some common symptoms associated with radiation injuries:
Acute Symptoms
In cases of acute radiation exposure, symptoms can appear rapidly. Some of the most common acute symptoms include:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often one of the first signs, these symptoms can occur within minutes to hours after exposure.
- Skin Burns: Localized radiation exposure can lead to burns, which may appear red and blistered.
- Fatigue: A profound sense of tiredness can set in, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
- Hair Loss: High doses of radiation can lead to temporary or permanent hair loss, depending on the severity of exposure.
Long-Term Symptoms
Individuals who survive acute radiation exposure may experience long-term health effects. These can include:
- Cancer: Increased risk of various cancers, particularly leukemia and thyroid cancer, is a significant concern.
- Cataracts: Radiation exposure can lead to the development of cataracts, affecting vision.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Long-term exposure can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of radiation injuries can be similar to those of other medical conditions. Therefore, if you suspect radiation exposure, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Healthcare professionals can conduct tests to determine the extent of exposure and recommend appropriate treatment.
For more information on radiation injuries and their management, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers. Understanding the risks and symptoms associated with radiation exposure can empower individuals to take proactive steps in safeguarding their health.
In conclusion, radiation injuries are a serious health concern that can arise from various sources. By being aware of the symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with radiation exposure. Stay informed and prioritize your health! 🌟
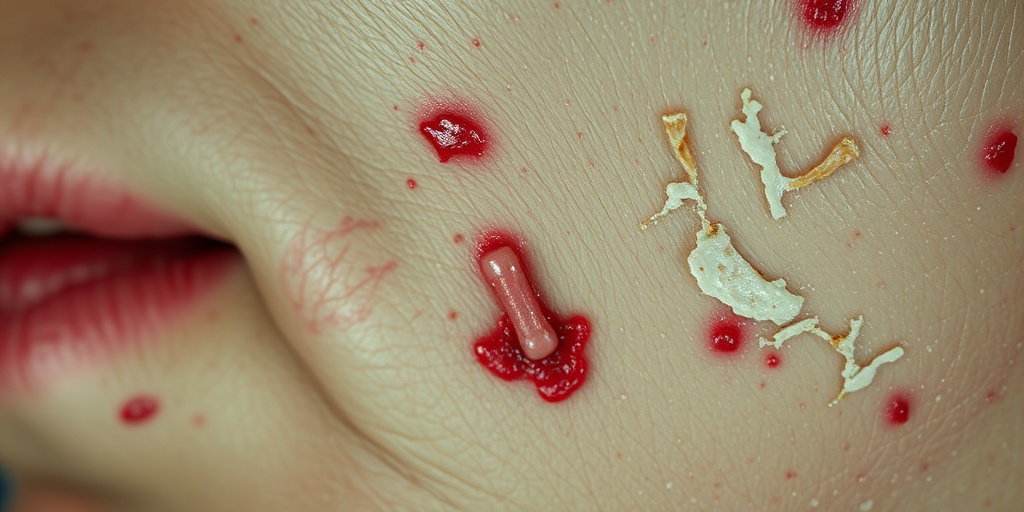
Causes of Radiation Injuries
Radiation injuries occur when the body is exposed to high doses of ionizing radiation, which can damage tissues and organs. Understanding the causes of radiation injuries is crucial for prevention and treatment. Here are some of the primary causes:
Nuclear Accidents
One of the most significant causes of radiation injuries is nuclear accidents. Events like the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 released large amounts of radioactive materials into the environment. Individuals living near these sites or emergency responders who were on the scene often suffered from acute radiation syndrome (ARS) and other long-term health effects.
Radiation Therapy
While radiation therapy is a common treatment for cancer, it can sometimes lead to radiation injuries if not administered correctly. Patients may experience side effects such as skin burns, fatigue, and damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Cutaneous radiation injuries are particularly concerning, as they can lead to severe skin damage and complications.
Occupational Exposure
Workers in certain industries, such as healthcare, nuclear power, and research facilities, may be at risk for radiation exposure. Prolonged exposure without adequate protective measures can lead to both acute and chronic radiation injuries. It’s essential for these workers to follow safety protocols to minimize their risk.
Radiological Weapons
In the unfortunate event of a nuclear attack or the use of radiological dispersal devices (often referred to as “dirty bombs”), individuals can suffer from radiation injuries due to the sudden release of radioactive materials. The effects can be devastating, leading to both immediate and long-term health issues.
Environmental Exposure
Natural sources of radiation, such as radon gas, can also contribute to radiation injuries over time. People living in areas with high levels of radon may be at risk for lung cancer and other health problems. Regular testing and mitigation strategies are essential for reducing exposure.
Risk Factors for Radiation Exposure
Understanding the risk factors for radiation exposure can help individuals take proactive measures to protect themselves. Here are some key factors to consider:
Geographic Location
Living in certain geographic areas can increase the risk of radiation exposure. For example, individuals residing near nuclear power plants or former nuclear testing sites may be at a higher risk. Additionally, areas with high natural background radiation, such as certain parts of Colorado, can also pose a risk.
Occupation
As mentioned earlier, certain professions expose individuals to higher levels of radiation. Healthcare workers, nuclear industry employees, and researchers handling radioactive materials must adhere to strict safety guidelines to minimize their risk. Regular monitoring and protective equipment are essential in these fields.
Medical History
Individuals with a history of cancer treatment involving radiation therapy may be at increased risk for developing radiation injuries later in life. It’s important for these patients to have regular follow-ups with their healthcare providers to monitor any potential long-term effects.
Age and Gender
Age and gender can also play a role in susceptibility to radiation injuries. Children are generally more sensitive to radiation than adults, making them more vulnerable to its harmful effects. Additionally, some studies suggest that women may be at a higher risk for certain radiation-induced cancers compared to men.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition can influence how individuals respond to radiation exposure. Some people may have genetic mutations that make them more susceptible to the damaging effects of radiation, leading to a higher risk of developing radiation-related health issues.
By understanding the causes and risk factors of radiation injuries, individuals can take informed steps to protect themselves and others from potential harm. Awareness and education are key in mitigating the risks associated with radiation exposure. 🌍💡

Diagnosis of Radiation Injuries
Radiation injuries can occur due to exposure to high doses of ionizing radiation, often resulting from nuclear accidents, medical treatments, or environmental disasters. Diagnosing these injuries is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis of radiation injuries.
Understanding Symptoms
The symptoms of radiation injuries can vary significantly depending on the dose and duration of exposure. Common symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting: Often one of the first signs, occurring within hours of exposure.
- Skin changes: This can range from mild redness to severe burns, known as cutaneous radiation injuries.
- Fatigue and weakness: A general feeling of tiredness that can persist for days or weeks.
- Hair loss: This may occur in patches or uniformly, depending on the exposure level.
- Infections: Due to a weakened immune system, patients may be more susceptible to infections.
Medical Evaluation
When a patient presents with symptoms suggestive of radiation exposure, a thorough medical evaluation is essential. This typically includes:
- Patient history: Understanding the circumstances of exposure, including the source and duration.
- Physical examination: Assessing visible symptoms, particularly skin changes and overall health.
- Laboratory tests: Blood tests can help determine the extent of damage to blood cells, which is a critical indicator of radiation exposure.
Imaging Techniques
In some cases, imaging techniques may be employed to assess internal damage. These can include:
- X-rays: Useful for identifying bone injuries or other internal damage.
- CT scans: Provide detailed images of internal organs and can help assess the extent of radiation damage.
Early diagnosis is vital for managing radiation injuries effectively. The sooner treatment begins, the better the chances of recovery. 🩺
Treatment Options for Radiation Injuries
Treating radiation injuries requires a multifaceted approach, tailored to the severity of the injury and the specific symptoms presented. Here are the primary treatment options available for those affected by radiation exposure.
Immediate Care
For individuals exposed to high levels of radiation, immediate care is crucial. This may involve:
- Decontamination: Removing contaminated clothing and washing the skin to reduce further exposure.
- Supportive care: Managing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and pain through medications.
Medications
Several medications can be used to treat radiation injuries, including:
- Potassium iodide: This can help protect the thyroid gland from radioactive iodine.
- Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): This medication can stimulate the production of white blood cells, helping to combat infections.
- Antibiotics: Used to prevent or treat infections that may arise due to a weakened immune system.
Long-term Management
For those with severe radiation injuries, long-term management may be necessary. This can include:
- Regular monitoring: Ongoing assessments to track recovery and manage any long-term effects.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy may be needed to regain strength and mobility.
- Psychological support: Counseling and support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of radiation injuries.
Research and Future Treatments
Ongoing research is focused on developing new treatments for radiation injuries. This includes exploring advanced therapies and potential protective agents that could mitigate the effects of radiation exposure. As our understanding of radiation injuries evolves, so too will the treatment options available to those affected. 🌟
Long-Term Effects of Radiation Injuries
Radiation injuries can have profound and lasting effects on the human body. Understanding these long-term consequences is crucial for both survivors and healthcare providers. The severity and type of radiation exposure can vary widely, leading to different health outcomes.
Types of Radiation Injuries
Radiation injuries can be categorized based on the type of radiation exposure:
- Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS): This occurs after a high dose of radiation over a short period, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
- Cutaneous Radiation Injuries: These injuries affect the skin and can result in burns, blisters, and long-term skin damage.
- Local Radiation Injuries: These are injuries that occur in specific areas of the body, often due to targeted radiation therapy or accidents.
- Nuclear Radiation Injuries: These injuries can result from nuclear accidents or attacks, leading to widespread health issues.
Common Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of radiation injuries can manifest in various ways, often depending on the dose and duration of exposure:
- Cancer: One of the most significant risks associated with radiation exposure is an increased likelihood of developing cancer, particularly leukemia and thyroid cancer.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Survivors of radiation exposure may experience an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
- Respiratory Problems: Lung damage can occur, leading to chronic respiratory issues, especially in cases of high-dose exposure.
- Neurological Effects: Cognitive impairments and neurological disorders can arise, particularly in cases of severe exposure.
Psychological Impact
The psychological effects of radiation injuries can be just as debilitating as the physical ones. Survivors may experience:
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Many individuals may struggle with PTSD following a traumatic radiation event.
- Anxiety and Depression: The fear of developing long-term health issues can lead to chronic anxiety and depression.
Understanding these long-term effects is essential for developing effective treatment plans and support systems for those affected by radiation injuries. 🌟
Preventing Radiation Injuries
Preventing radiation injuries is a critical aspect of public health, especially in environments where exposure is a risk. Here are some effective strategies to minimize the risk of radiation injuries:
Education and Awareness
One of the most effective ways to prevent radiation injuries is through education. Awareness programs can help individuals understand:
- Sources of Radiation: Knowing where radiation exposure can come from, such as medical treatments, industrial applications, or nuclear power plants, is vital.
- Safety Protocols: Learning about safety measures, such as wearing protective gear and following guidelines, can significantly reduce exposure.
Regulatory Measures
Governments and organizations play a crucial role in preventing radiation injuries through:
- Strict Regulations: Implementing and enforcing regulations on radiation use in medical and industrial settings helps ensure safety.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of radiation levels in environments where exposure is possible can help identify risks early.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
In environments where radiation exposure is a risk, using appropriate PPE is essential. This includes:
- Lead Aprons: Commonly used in medical settings to protect against X-ray exposure.
- Radiation Shields: Barriers that can be placed around sources of radiation to limit exposure.
Emergency Preparedness
In the event of a radiation accident, having an emergency preparedness plan can save lives. This includes:
- Evacuation Plans: Clear guidelines on how to evacuate affected areas quickly and safely.
- Medical Response Teams: Training healthcare professionals to respond effectively to radiation injuries can improve outcomes.
By implementing these preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the risk of radiation injuries and protect public health. 🌍

Frequently Asked Questions about Radiation Injuries
What are Radiation Injuries?
Radiation injuries refer to the damage caused to the body by exposure to ionizing radiation. This can occur from various sources, including nuclear accidents, medical treatments, or environmental exposure. The severity of these injuries can vary based on the dose and duration of exposure.
What are the symptoms of Radiation Injuries?
Symptoms of radiation injuries can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and weakness
- Skin burns or lesions (cutaneous radiation injuries)
- Hair loss
- Increased susceptibility to infections
How do Radiation Injuries occur?
Radiation injuries can occur through various means, such as:
- Accidental exposure during nuclear accidents (e.g., radiation injuries Hiroshima or radiation injuries Chernobyl)
- Medical treatments involving radiation (e.g., cancer therapies)
- Occupational exposure in certain industries
What are the types of Radiation Injuries?
There are several types of radiation injuries, including:
- Local radiation injuries: Damage to specific areas of the body, often resulting in skin burns.
- Nuclear radiation injuries: Injuries resulting from exposure to nuclear materials.
- Radiation poisoning injuries: Severe cases that can lead to systemic effects on the body.
How are Radiation Injuries treated?
Treatment for radiation injuries depends on the severity and type of injury. Common treatments include:
- Supportive care to manage symptoms
- Medications to treat infections
- Skin care for burns and lesions
- In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for intensive care
What are the long-term effects of Radiation Injuries?
Long-term effects of radiation injuries can include:
- Increased risk of cancer
- Chronic fatigue
- Long-lasting skin damage
- Potential psychological effects, such as anxiety or PTSD
Can Radiation Injuries be prevented?
While not all radiation injuries can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Adhering to safety protocols in environments with radiation exposure
- Using protective equipment during medical treatments
- Staying informed about potential radiation hazards in the environment
Where can I find more information on Radiation Injuries?
For more detailed information on radiation injuries, consider visiting reputable health organizations or government health websites. They often provide resources and guidelines on prevention, treatment, and research related to radiation exposure.




